
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
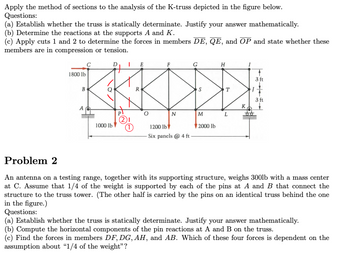
Transcribed Image Text:### K-Truss Analysis Using the Method of Sections
**Questions:**
1. **(a)** Establish whether the truss is statically determinate. Justify your answer mathematically.
2. **(b)** Determine the reactions at the supports A and K.
3. **(c)** Apply cuts 1 and 2 to determine the forces in members DE, QE, and OP. State whether these members are in compression or tension.
**Diagram:**
The diagram is of a K-truss structure. Key features include:
- Multiple panels labeled C through I.
- Support reactions are located at points A and K.
- External loads applied: 1800 lb at C, 1000 lb at P, 1200 lb at O, and 2000 lb at M.
- The truss consists of six panels, each 4 feet wide.
- Points P and O are highlighted with red cuts labeled ① and ②.
---
### Problem 2: Antenna Support Truss Analysis
**Description:**
An antenna and its supporting structure weigh 300 lb with the mass center at point C. It's assumed that 1/4 of the weight is supported by pins at A and B, with the rest carried by an identical truss behind the one shown.
**Questions:**
1. **(a)** Establish whether the truss is statically determinate. Justify your answer mathematically.
2. **(b)** Compute the horizontal components of the pin reactions at A and B.
3. **(c)** Find the forces in members DF, DG, AH, and AB. Identify which force depends on the assumption about "1/4 of the weight".
**Diagram:**
Similar to the K-truss, featuring multiple triangles typically used for stability. Forces are distributed across its nodes.
---
**Note:** Detailed mathematical calculations are necessary to resolve the queries in both problems.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The two vertical steel [E = 200 GPa] rods that support rigid bar ABCD are initially free of stress. Rod (1) has an area of A₁ = 350 mm² and a length of L₁ = 2.1 m. Rod (2) has an area of A₂ = 375 mm² and a length of L₂ = 1.5 m. Assume dimensions of a = 3.2 m, b = 1.1 m, and c = 1.4 m. After a load of P = 130 kN is applied to the rigid bar at D, determine: (a) the normal stresses in rods (1) and (2) (b) the magnitude of the downward deflection of the rigid bar at D. y,v (2) a L2 Rigid bar L₁ Answer: (a) σ₁ = i 02= i (b) VD= i (1) B MPa MPa mm -X,U b C ↓ С D Parrow_forwardCalculate the forces in members AC, AD, and DE for the loaded truss. Restraining link BC is horizontal. Forces are positive if in tension, negative if in compression. B Answer: AC = 3' AD = i i DE = i C 3' 600 lb D 3' E lb lb lbarrow_forward1arrow_forward
- The truss structure shown below is subjected to the following loads F1= 437 lb F2= 726 lb and has the following geometry: w = 10 ft F2 F1 F1 W W -B D G. F -AC E Determine the support reactions at A and E. Determine the forces in members BC, CG, and FG and state whether they are in tension or compression. Determine the forces in members ED and EF and state whether they are in tension or compression.arrow_forwardPlease help on the 3 questions in the photoarrow_forwardI tried to solve the first problem by cutting a section at s and then taking the sum of moments with respect to point H (HJ, HI, DJ are now not relevant) which looks like it yields compression which seems right but I keep on getting the wrong answerarrow_forward
- Problem 2: Determine the force in ALL the members of the truss. State if the members are in tension or compression. Show all your work to receive full credit. (Hint: It is not needed to find the reaction forces at C and E if you use the Method of Joints). Note: P1= 1000 lb and P: = 500 lb B C30 45 999 4 ft E 550 D. -4 ft- - 4 ft- 999 299arrow_forwardPlease show complete solution. Thank you!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning