
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
For a satellite to orbit Earth at a constant distance, its centrifugal acceleration
must be equal and opposite Earth's gravitational acceleration. If a satellite is
to orbit at a constant distance from Earth at a circular radius of 8,000,000 m,
what is the required velocity of the satellite? (Assume the acceleration due to
Earth's gravity is 6.2 m/s2 at this altitude.)
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
FBD of Satellite
# FBD of satellite
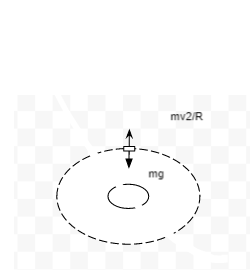
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A comet is in an elliptical orbit around the Sun. Its closest approach to the Sun is a distance of 4.9 x 1010 m (inside the orbit of Mercury), at which point its speed is 9.3 x 104 m/s. Its farthest distance from the Sun is far beyond the orbit of Pluto. What is its speed when it is 6 x 1012 m from the Sun? (This is the approximate distance of Pluto from the Sun.) speed = m/sarrow_forwardAt what height (in km) above the surface of Earth would the- gravitational acceleration be 2.2 m/s2?arrow_forwardA satellite is in a circular orbit around the Earth at an altitude of 3.82 x 106 m. (a) Find the period of the orbit. (Hint: Modify Kepler's third law so it is suitable for objects orbiting the Earth rather than the Sun. The radius of the Earth is 6.38 x 106 m, and the mass of the Earth is 5.98 x 1024 kg.) h (b) Find the speed of the satellite. km/s (c) Find the acceleration of the satellite. m/s2 toward the center of the eartharrow_forward
- A satellite is in a circular orbit around the Earth at an altitude of 2.62 × 106 m. (a) Find the period of the orbit. (Hint: Modify Kepler's third law so it is suitable for objects orbiting the Earth rather than the Sun. The radius of the Earth is 6.38 x 106 m, and the mass of the Earth is 5.98 x 1024 kg.) h (b) Find the speed of the satellite. km/s (c) Find the acceleration of the satellite. m/s² toward the center of the eartharrow_forwardA satellite is in a circular orbit around the Earth at an altitude of 3.94 x 106 m. (a) Find the period of the orbit. (Hint: Modify Kepler's third law so it is suitable for objects orbiting the Earth rather than the Sun. The radius of the Earth is 6.38 x 106 m, and the mass of the Earth is 5.98 x 1024 kg.) (b) Find the speed of the satellite. km/s (c) Find the acceleration of the satellite. m/s² toward the center of the eartharrow_forwardA satellite is in a circular orbit around the Earth at an altitude of 3.52 x 10^6 m. (a) Find the period of the orbit. (Hint: Modify Kepler's third law so it is suitable for objects orbiting the Earth rather than the Sun. The radius of the Earth is 6.38 x 10^6 m, and the mass of the Earth is 5.98 x 10^24 kg.) (b) Find the speed of the satellitearrow_forward
- (a) What linear speed must an Earth satellite have to be in a circular orbit at an altitude of 160 km above Earth's surface? (b) What is the period of revolution? Take the mass of earth as 5.98×1024 kg and the radius as 6.37×106 marrow_forwardTwo planets P1 and P2 orbit around a star S in circular orbits with speeds v₁ = 43.0 km/s, and v₂ = 59.2 km/s respectively. (a) If the period of the first planet P₁ is 700 years what is the mass, in kg, of the star it orbits around? × The gravitational force of the star on the planet supplies the centripetal force needed to keep the planet in its circular orbit. kg (b) Determine the orbital period, in years, of P2 2 × Consider the relationship between the orbital speed and the orbital period in terms of the known variables. yrarrow_forwardA satellite is in a circular orbit around the Earth at an altitude of 3.42 x 106 m. (a) Find the period of the orbit. (Hint: Modify Kepler's third law so it is suitable for objects orbiting the Earth rather than the Sun. The radius of the Earth is 6.38 x 10° m, and the mass of the Earth is 5.98 x 1024 kg. (b) Find the speed of the satellite. km/s (c) Find the acceleration of the satellite. m/s? toward the center of the eartharrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON