
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The satellite is moving in an elliptical orbit with an eccentricity e = 0.30. Determine its speed when it is at its maximum distance A and minimum distance B from the earth
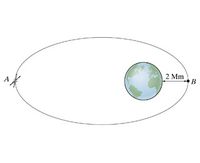
Transcribed Image Text:2 Mm
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A comet is in an elliptical orbit around the Sun. Its closest approach to the Sun is a distance of 4.9 x 1010 m (inside the orbit of Mercury), at which point its speed is 9.3 x 104 m/s. Its farthest distance from the Sun is far beyond the orbit of Pluto. What is its speed when it is 6 x 1012 m from the Sun? (This is the approximate distance of Pluto from the Sun.) speed = m/sarrow_forwardA satellite is in a circular orbit around the Earth at an altitude of 3.82 x 106 m. (a) Find the period of the orbit. (Hint: Modify Kepler's third law so it is suitable for objects orbiting the Earth rather than the Sun. The radius of the Earth is 6.38 x 106 m, and the mass of the Earth is 5.98 x 1024 kg.) h (b) Find the speed of the satellite. km/s (c) Find the acceleration of the satellite. m/s2 toward the center of the eartharrow_forwardA satellite is in a circular orbit around the Earth at an altitude of 2.62 × 106 m. (a) Find the period of the orbit. (Hint: Modify Kepler's third law so it is suitable for objects orbiting the Earth rather than the Sun. The radius of the Earth is 6.38 x 106 m, and the mass of the Earth is 5.98 x 1024 kg.) h (b) Find the speed of the satellite. km/s (c) Find the acceleration of the satellite. m/s² toward the center of the eartharrow_forward
- In 2000 , NASA placed a satellite in orbit around an asteroid. consider a spherical asteroid with a mass of 1.50 * 10^16 kg and a radius of 10.0 km what is the speed of a satellitie orbiting 5.90 km above the surface ? express with appropriate units what is the escape speed from the asteroid (express with appropriate units)arrow_forwardHow much energy is required to lift a 10 kg rock from the surface of the Earth and place it in a circular orbit just 10 km above sea level? Assume Earth's radius is about 6371 km.arrow_forwardAn asteroid is discovered to have a tiny moon that orbits it in a circular path at a distance of 147 km and with a period of 35.0 h. The asteroid is roughly spherical (unusual for such a small body) with a radius of 24.3 km. a) Find the acceleration of gravity at the surface of the asteroid. b) Find the escape velocity from the asteroid.arrow_forward
- A 150-kg satellite is in a 310-km altitude stable circular orbit around earth. What is its orbital kinetic energy? a) 4.46*107 J. b) 4.46*1011 J. c) 4.46*109 J. Data: mass of earth = 5.97*1024 kg, radius of earth = 6380 km, G = 6.67*10-11.arrow_forwardAn engineer wants a satellite to orbit the earth with a period of 20 hours. You may enter answers in scientific notation as shown: 1.23 x 105 = 1.23e5 At what orbital radius must the satellite orbit? m How far is this location above the earth's surface? m At what speed must the satellite travel to maintain the orbit? m/s earth data mass: 5.97 x 1024kg radius: 6.37 x 10 m Reference M 3 5 6arrow_forwardA satellite orbits a planet of unknown mass in a circle of radius 2 × 107 m. The magnitude of the gravitational force on the satellite from the planet is F = 80 N. a) What is the kinetic energy of the satellite in this orbit? b) What would F be if the orbit radius were increased to 3 x 107 m?arrow_forward
- Problem 3. A tracking station determines that an Earth-observation satellite has perigee and apogee altitudes of 350 and 1,206 km, respectively. Determine the orbital period (in minutes) and the parameter p.arrow_forwardMacmillan Learning A planet is in an elliptical orbit around a distant star. At periastron (the point of closest approach to the star), the planet is rp = 3.90 × 108 km from the star and is moving with a speed of Up = 21.5 km/s. When the planet is at apastron (the point of greatest distance from the star), it is ra = 9.00 × 108 km from the star. "P Va = HH How fast is the planet moving at apastron? V km/sarrow_forwardA satellite is given a boost of 495 MJ of energy to move it from its initial orbit at an altitude of 150 km to a higher altitude orbit. If the satellite has a mass of 1.19 ✕ 103 kg, what is the new altitude it reaches? Take the mass of the Earth to be 5.97 1024 kg and its radius to be 6.371 106marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON