Question

Transcribed Image Text:Question #3 (Flow Cytometry):
| Because the droplets are conductors, a dropletť's positive and negative charges will
separate while the droplet is in the region between the deflection plates. Suppose a neutral
droplet passes between the plates. The droplet's dipole moment will point
A. Up.
B. Down.
C. Left.
D. Right.
Question #4:
|| BIO A protein molecule in an electrophoresis gel has a negative charge. The exact
charge depends on the pH of the solution, but 30 excess electrons is typical. What is the
magnitude of the electric force on a protein with this charge in a 1500 N/C electric field?
Question #5:
II| A small metal bead, labeled A, has a charge of 25 nC. It is touched to metal bead B,
initially neutral, so that the two beads share the 25 nC charge, but not necessarily equally.
When the two beads are then placed 5.0 cm apart, the force between them is 5.4 x 10-4 N.
What are the charges qa and qB on the beads?
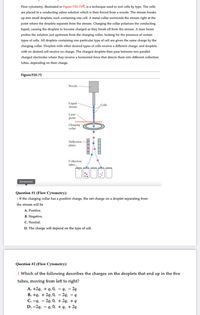
Transcribed Image Text:Flow cytometry, illustrated in Figure P20.750, is a technique used to sort cells by type. The cells
are placed in a conducting saline solution which is then forced from a nozzle. The stream breaks
up into small droplets, each containing one cell. A metal collar surrounds the stream right at the
point where the droplets separate from the stream. Charging the collar polarizes the conducting
liquid, causing the droplets to become charged as they break off from the stream. A laser beam
probes the solution just upstream from the charging collar, looking for the presence of certain
types of cells. All droplets containing one particular type of cell are given the same charge by the
charging collar. Droplets with other desired types of cells receive a different charge, and droplets
with no desired cell receive no charge. The charged droplets then pass between two parallel
charged electrodes where they receive a horizontal force that directs them into different collection
tubes, depending on their charge.
Figure P20.75
Nozzle
Liquid
stream
Cells
Laser
probe
Charging
collar
Deflection
plates
Collection
tubes
Screenshot
Question #1 (Flow Cytometry):
| If the charging collar has a positive charge, the net charge on a droplet separating from
the stream will be
A. Positive.
B. Negative.
C. Neutral.
D. The charge will depend on the type of cell.
Question #2 (Flow Cytometry):
| Which of the following describes the charges on the droplets that end up in the five
tubes, moving from left to right?
А. +2q, + q, 0, — 9. — 2q
В. +9, + 2q, 0, — 2q, — 9
С. -q, — 2q, 0, + 2q, + q
D. -24, – q, 0, + q, + 2q
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- To see why, compute the force of Earth’s gravity on an electron and compare it with the force exerted on the electron by an electric field of magnitude 14000 V/m (a relatively small field). Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardA futuristic gun uses a strong electric field to accelerate small charged bullets to very fast speeds. The specially made bullets have a mass of 0.01kg and a hold charge of 0.1C. If the gun accelerates the bullets over a distance of 0.6m to a speed of vf = 10*m/s, what must be the strength of the electric field inside the gun? Give your answer in scientific notation with 2 or 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardTwo large parallel plates are separated by a 0.015-m gap. The plates are connected to the terminals of a 12-V battery, which remains connected. a) What is the strength of the electric field in the region between the plates? b) What happens to the strength of the electric field if the gap between the plates is reduced to 0.010 m? Justify your answer. c) Does charge flow through the battery as the separation between the plates is being reduced? Explain your answer.arrow_forward
- A capacitor is composed of two metal plates. The two plates have the dimensions L = 0.11 m and W = 0.56 m. The plates have a distance between them of d = 0.1 m, and are parallel to each other. Part (a) The plates are connected to a battery and charged such that the first plate has a charge of q. Write an expression for the magnitude of the electric field, |E|, halfway between the plates. Part (b) Input an expression for the magnitude of the electric field, |E2|, just in front of plate two. Part (c) If plate two has a total charge of q = -1 mC, what is its charge density, σ, in C/m2?arrow_forwardA charged conducting sphere with capacitance, C = 26.7 pF, produces an electric field that points radially outward. At a distance, d = 61.2 cm, from the center of the sphere, the strength of the electric field is E = 71.3 kV/m. (a) What is the radius of the charged sphere? R = m (b) Find the sphere's surface charge density. μC/m² J =arrow_forwardFirst questionarrow_forward
- Two large (treat as infinite) parallel conducting plates are charged to t Q as shown by the battery. A proton is released from rest at point A and is measured to be moving with a speed v, = 2 x 105 m/s when at point B. The right plate is then moved closer to the left as shown in the %3D X X rightmost figure. The experiment is repeated. What will be the speed of the proton at point B? A) Greater B) Smaller C) Equal D) Impossible to determinearrow_forwardThe next 5 questions all have to do with the diagram shown, on which I have placed an electron at the origin. The grid spacing is 1 Angstrom per small square. Now place an atomic nucleus with 6 protons on positive x-axis, at x = 4.7 Angstroms. How much work did it take you to bring this nucleus in from 1 m away? 15.7 eV 18.4 eV 12.9 eV 23.9 eVarrow_forwardYou are working in a laboratory, using very sensitive measurement equipment. Your supervisor has explained that the equipment is also very sensitive to electrical discharge from human operators. Specification tables for the equipment indicate that an electrical discharge providing even a very small amount of energy of 250 μJ is enough to damage the equipment. Your supervisor wants to install an apparatus that will be used to remove the electrical charge from individuals’ bodies before they touch the equipment. To do this, she asks you to estimate (a) the capacitance of the human body and determine (b) the charge on the body and (c) the electric potential of the body, relative to a point infinitely far away, corresponding to the energy transfer that will damage the equipment.arrow_forward
- You and your colleagues have been tasked with launching a weather balloon into the Earth's stratosphere via rocket ship. In order to reduce fuel usage to meet with newly imposed fuel-consumption regulations, you are hoping to use the electric interaction between charges to your advantage. You have decided on the design below. You are able to place two Q = 1.98 C charges in the rocket ship and into the launching platform so that they are separated by a distance of yo = 2.93 m. You are allowed enough fuel to boost the rocket to an initial speed of vo = 309 m/s without accounting for the extra boost from the charges. The rocket on its own has a mass of 2.095x104 kg. The more equipment you can attach to your weather balloon (which is inside the rocket), the better. What limit do you put on the mass of the weather balloon and attached equipment? You may want to know the formula for gravitational potential energy for an object of mass m and height h: Egray = mgh, where g=9.81 m/s?. Edge of…arrow_forwardNear the surface of the Earth there is an electric. field of about 150 V/m which points downward. Two identical balls with mass m = 0.620 kg are dropped from a height of 2.30 m, but one of the balls is positively charged with q₁ = 950 μC, and the second is negatively charged with 92 = -950 μC. Part A Use conservation of energy to determine the difference in the speed of the two balls when they hit the ground. (Neglect air resistance.) Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. V1 V2 = Submit Provide Feedback Value Request Answer Units ?arrow_forwardE7P9arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios