
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Find the center of mass of a sphere of mass M and radius R and a cylinder of mass m, radius r, and height h arranged as shown below. Express your answers in a coordinate system that has the origin at the center of the cylinder. (Assume that the +x-axis is to the right, the +y-axis is up along the page, and the +z-axis is out of the page. Use any variable or symbol stated above as necessary.)
a) xCM=___, yCM=___, zCM=___
b) xCM=___, yCM=___, zCM=___

Transcribed Image Text:Find the center of mass of a sphere of mass M and radius R and a cylinder of mass m, radius r, and height h arranged as shown below. Express your answers in a coordinate system
that has the origin at the center of the cylinder. (Assume that the +x-axis is to the right, the +y-axis is up along the page, and the +z-axis is out of the page. Use any variable or
symbol stated above as necessary.)
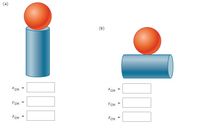
Transcribed Image Text:(а)
(ь)
X CM
X CM
Усм
Усм
ZCM
ZCM
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Part e and f full solution plsarrow_forwardUSE GRESA METHOD FOR THE SOLUTION 7. Three balls A, B, and C with masses 0.0500 kg, 0.0700 kg, and 0.0900 kg, respectively, are moving along the xy-plane and approaching the origin as shown in the figure below. Ignore friction. The initial velocities of balls A and B are shown in the figure. Suppose all three balls arrive at the origin at the same time and stick together after the collision. What must be the x- and y-components of the initial velocity of ball C in order for the three balls to move along the +x-axis at 1.00 m/s after the collision?arrow_forwardParts a-carrow_forward
- help please. If a 1467 kg car, moving at 9 m/s north, hits and sticks to a 2237 kg truck, moving at 10 m/s south, and they travel off together at the same speed, find that speed. Hint: here the masses are moving in opposite directions, so the velocities should have opposite signs. Call North positive and South negative. Use the "hit and stick" or inelastic formula Also, a positive answer would indicate motion to the north and a negative answer would show southward motion - leave positive/negative in your answer.arrow_forwardA B Carrow_forwardA cube of side a is cut out of another cube of side b as shown in the figure below. b a Find the location of the center of mass of the structure. (Use any variable or symbol stated above as necessary. Hint: Think of the missing part as a negative mass overlapping a positive mass. Assume the origin is in the bottom left corner shared by both cubes, and assume all values are positive with the x-axis to the right, the y-axis extending back into the page parallel to the sides of the cube, and the z-axis pointing up along the page.) XCM Усм = = ZCMarrow_forward
- Do as instructed:a. Simulate m1 = m2 with their respective velocities v1 = v2. Take a screenshot of the simulation. Explain the collision, reaction, and motion of the two masses.Here is the direct link to the simulator - https://ophysics.com/e2.htmlarrow_forwardFind the center of mass of a sphere of mass M and radius R and a cylinder of mass m, radius r, and height h arranged as shown below. Express your answers in a coordinate system that has the origin at the center of the cylinder. (Assume that the +x-axis is to the right, the +y-axis is up along the page, and the +z-axis is out of the page. Use any variable or symbol stated above as necessary.) (a) XCM = YCM = ZCM = (b)arrow_forwardSuppose that for the couple in the figure below, you were told that the girl's mass was one-half that of the boy's mass. The boy has a velocity of v = 0.38 m/s to the left. What would be the girl's velocity in this case? (Consider the ice to be frictionless. Enter the magnitude only.) Two ice skaters, a boy on the left and a girl on the right, face each other in figures a and b, which depict, respectively, before and after pushing off from each other. Before: The two ice skaters face each other with the palms of their hands facing towards each other and touching the other person's palms. After: The two ice skaters have pushed off and now have their arms outstretched facing each other. A left-pointing arrow above the left skater is labeled "v". A right-pointing arrow above the right skater is labeled "?".arrow_forward
- Please answer fastarrow_forwardPlease explain your answer.arrow_forwardIn order to answer this question, follow the steps provided and remember that the total initial momentum of the system must equal the total final momentum. Also, remember that momentum and velocity are vector quantities so you must specify a negative sign if the motion is to the left. A green truck of mass 2500 kg travels to the right with a velocity vig = 3.7 m/s. The green truck approaches a red truck with mass 1460 kg that is traveling to the left with a velocity of vir = -3 m/s. The trucks collide and stick together after the collision. What is the final velocity, vf of the green-red truck system after the collision. (look at the figure/picture)(a) What was the initial momentum of the green truck before the collision?pgi = 9250 kg m/s(b) What was the initial momentum of the red truck before the collision?pri = -4380 kg m/s(c) What was the total initial momentum of the system of trucks?pTf = 4870 kg m/s (d) What must be the total final momentum of the system after the collision if…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON