Question
Transcribed Image Text:Question A6
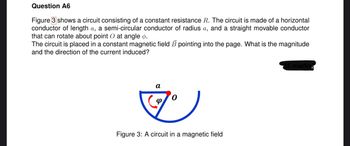
Figure 3 shows a circuit consisting of a constant resistance R. The circuit is made of a horizontal
conductor of length a, a semi-circular conductor of radius a, and a straight movable conductor
that can rotate about point O at angle ø.
The circuit is placed in a constant magnetic field B pointing into the page. What is the magnitude
and the direction of the current induced?
1)
Figure 3: A circuit in a magnetic field
a
marks
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Consider a straight conductor of length 6.3 cm. The conductor moves at right angles to a magnetic field of uniform strength B = 10-3 T generating e.m.f. of 2.5 × 10-5 v. Calculate the velocity of the straight conductor. Give your answer in SI units. Answer: Choose... + Next page Previous pagearrow_forwardWhich statement about magnetic fields is NOT true? O The spacing of the field lines indicates the strength of the field. O Field lines do not cross one another. O The field weakens as the distance from the magnet increases. There is no magnetic field inside a magnet. The field is three-dimensional.arrow_forwardConsider two magnetic fields B1 and B2, with components B1x = 0, B1y = 2ax, and B1z = 0 and B2x = -ay, B2y = ax, and B2z = 0, respectively, where a is a constant. a. Draw a picture of each field. (Hint: Show that the second field points circularly around the origin. How does its magnitude depend on the distance from the origin?) b. Show that these fields have the same curl everywhere. c. Consider the following statement: "If we know a magnetic field's curl at all points, we can determine the magnetic field at all points." In light of what you have discovered above, why is this statement false?arrow_forward
- A long, cylindrical conductor of radius ? has two cylindrical cavities each of diameter ? through its entire length. A current ? is directed out of the page and is uniform through a cross section of the conducting material. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field in terms of ??,?,? and ? at § point ?? § point ??arrow_forwardConsider two very long cylindrical wires (see image) of radius R, with current moving in the same direction. The centers of the wires are a distance 4R apart. Both wires have a uniform current density Jo. In the image, the line connecting the centers of the wires is an imaginary line to help visualize distances. a. What is the magnetic field at point (a), midway between the wires? b. What is the magnetic field at point (b) which is a point R/3 from the center of the left wire along the line connecting the two wire centers? c. What is the magnetic field at point (c), the center of the left wire? Side view current flows right Cross - Section View current into page -42arrow_forwardA rectangular semi- conductor of length 50 mm, width 30 mm and depth 20 mm in the same uniform magnetic field of 12500 Oersteds. It was observed that 12500 Oersteds produces Hall voltage of 0.5 milli Volts. Find the number density of charge carriers. a. 9.72 x 1024 /m³ b. 3.9 x 1024 /m³ 9.72 x 1028 / m³ d. 3.9 x 1028 /m³ C. e. None of the abovearrow_forward
- Two circular loops of wire lie in the x-y plane, centered at the origin. The radius of the loops is 5.00 and 7.00 cm. The current in the outer loop is 50.0 mA in the clockwise direction. a. If the current in the inner wire is also 50.0 mA in the clockwise direction, what is the magnetic field strength at the origin? b. What current magnitude and direction in the inner wire will cause the magnetic field to be zero at the origin?arrow_forwardA proton is moving on the circular arc in the region of the magnetic field B as shown in the figure. What is the direc the field that keeps the proton on that path? O Out of the plane O towards left O Into the plane towards right V Barrow_forwardA toroid has 490 turns of wire and carries a current of 30 A. Its inner and outer radii are 5.4 and 11.2 cm. Find the magnetic field at r= 7.8, 8.2, and 10 cm. Hint a. Choose the description that most correctly describes the direction of the magnetic field at these locations. O The magnetic field is perpendicular to the toroid plane. O The magnetic field points in radial direction. O The magnetic field points in tangential direction. O The magnetic field points in the z direction. mT. b. Magnetic field at r = 7.8 cm is mT. C. Magnetic field at r = 8.2 cm is mT. d. Magnetic field at r = 10 cm isarrow_forward
- A particle with mass 1,67x10-3 kg and charge of +1.32x10-8 C has, at a given instant, a velocity of 2.90x10 m/s along the +-axis, as shown in the figure. (Figure 1) Figure 1 of 1 45.0° C X Part A What is the magnitude of the particle's acceleration produced by a magnetic field of magnitude 1.19 T in the -y plane, directed at an angle of 45.0" counterclockwise from the +-axis? Express your answer with the appropriate units to three significant figures. 0.178 m Submit Previous Answers Request Answer Part B ? * Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining +-direction -a-direction What is the direction of the particle's acceleration?arrow_forwardChapter 30, Concept Question 04 The figure shows two circuits in which a conducting bar is slid at the same speed v through the same uniform magnetic field and along a U- shaped wire. The parallel lengths of the wire are separated by 24 in circuit 1 and by L in circuit 2. The current induced in circuit 1 is counterclockwise. e (2) Is the magnetic field into or out of the page? Into Out of Is the current induced in circuit 2 clockwise or counterclockwise? Counterclockwise Clockwise Is the emf induced in circuit 1 larger than, smaller than, or the same as that in circuit 2? Larger The same as Smallerarrow_forwardpag Question 1: Magi A point charge of value q = 3.10μC has a speed of = 1.75 x 107-0.81 x 107k when it is at the point (0 cm, 0 cm, 0 cm). What is the magnetic field vector in component form at position (1cm, 1cm, 0cm)? Answer Magnetic Field Vector Mo = 4π *10-7 T.m² c.m S Clectric Potential from Point Chargesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios