
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
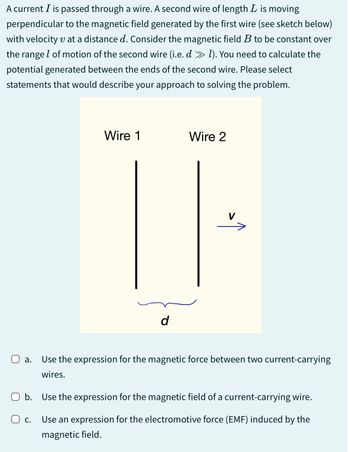
Transcribed Image Text:A current I is passed through a wire. A second wire of length L is moving
perpendicular to the magnetic field generated by the first wire (see sketch below)
with velocity v at a distance d. Consider the magnetic field B to be constant over
the range of motion of the second wire (i.e. d » 1). You need to calculate the
potential generated between the ends of the second wire. Please select
statements that would describe your approach to solving the problem.
Wire 1
Wire 2
d
V
☐ a. Use the expression for the magnetic force between two current-carrying
wires.
☐ b. Use the expression for the magnetic field of a current-carrying wire.
О с.
Use an expression for the electromotive force (EMF) induced by the
magnetic field.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A metal bar is sliding on conducting rails at a speed of 40 m/s as shown below. There is a magnetic field pointing out of the page. The resistance of the bar is 1.6 0. There is a, induced current of 4.1 A in the bar. What is the direction of the current in the bar? What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B? What is the magnitude of the applied force needed to keep the bar traveling at this speed? Put the value of B in the answer box. B 36 cm v = 40 m/s Answer:arrow_forwardA proton is moving on the circular arc in the region of the magnetic field B as shown in the figure. What is the direc the field that keeps the proton on that path? O Out of the plane O towards left O Into the plane towards right V Barrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current. The direction of the magnetic field due to this wire, directly above it is out of the page. In what direction is the currentarrow_forward
- Solve with no calculus.arrow_forwardThe figure shows a cross section of three very long parallel wires, eachcarrying a current of 2.0 A. The currents in the top and bottom rightwires are coming out of the page; the current of the bottom left wire isgoing into the page. The length of each leg of the triangle is R = 18.0mm.a) Draw a clear physics diagram of the problem with forces, fields, andimportant angles labeled.b) Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on a 4.0-mlength of the top wire due to the bottom right wire.c) Find the total magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on a 4.0-mlength of the top wire due to the other two wires.d) Find the total magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on a 4.0-mlength of the bottom left wire due to the other two wires.arrow_forwardA circuit is made with a resistor of resistance 25 ohms and a movable bar with length 15 cm moving to the left with speed 8 m/s. The whole circuit is in a magnetic field B = 1.5 T (into page). Use this set up to answer the following questions. What is the magnetic force on the bar in Newtons? Answer to 4 decimal places.arrow_forward
- A current I is passed through a wire. A second wire of length L is moving perpendicular to the magnetic field generated by the first wire (see sketch below) with velocity v at a distance d. Consider the magnetic field B to be constant over the range / of motion of the second wire (i.e. d > 1). You need to calculate the potential generated between the ends of the second wire. Please select statements that would describe your approach to solving the problem. Wire 1 Wire 2 d a. Use an expression for the electromotive force (EMF) induced by the magnetic field. b. Use the expression for the magnetic force between two current-carrying wires. C. Use the expression for the magnetic field of a current-carrying wire.arrow_forwardThe three conducting rings in the figure are all in the same plane as a long wire. The wire has a current / that is steadily decreasing with time at a constant rate. What can you say about the induced electromotive force in each of the rings A, B, and C? A O No electromotive force is induced in any of the rings. O A counter-clockwise electromotive force is induced in ring A, but a clockwise electromotive force is induced in rings B and C. O A clockwise electromotive force is induced in ring A. Ring B has no induced electromotive force, and ring C has a counterclockwise electromotive force. O All rings have a counterclockwise induced electromotive force. O A counter-clockwise electromotive force is induced in ring A. Ring B has no induced electromotive force, and ring C has a clockwise electromotive force.arrow_forwardThe figure shows a cross section of several conductors carrying currents through the plane. The currents have the magnitudes l₁ = 4 A, 1₂ = 6 A and 13 = 2A. The directions of the currents is shown at the picture. Four paths labeled a through d are shown. What is the line integral of the magnetic field across each path? Each integral involves going around the path in the counter clockwise direction. 1. What is the line integral of the magnetic field across path a? Enter the missing part in the expression Ho 2. What is the line integral of the magnetic field across path b? Enter the missing part in the expression Ho'l 3. What is the line integral of the magnetic field across path c? Enter the missing part in the expression Hol 4. What is the line integral of the magnetic field across path d? Enter the missing part in the expression Ho 110 b 120 d ) ) ) )arrow_forward
- Consider the following arrangement in the Figure: a) Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field at point P of the figure in terms of R, I₁, I₂. Express your answer in terms of the variables I1, I2, R, and magnetic constant po. b) What does your expression give when I1=I₂? 2arrow_forwardMagnetic and electric field lines are in many ways similar, with few crucial differences. Which of the properties listed below does NOT apply to both fields? O All of these properties apply to both E and B field lines. The density of lines is proportional to the field strength in that area. Field lines never intersect. Tangent to the line at a point gives you the direction of the field as that point. O Field lines form closed loops.arrow_forwardA loop of wire is perpendicular to a magnetic field. The magnetic field strength as a function of timeis given by the top graph. Draw a graph of the current in the loop as a function of time. Let apositive current represent a current that comes out of the top of the loop and enters the bottom of theloop. There are no numbers for the vertical axis, but your graph should have the correct shape andproportions.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON