
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
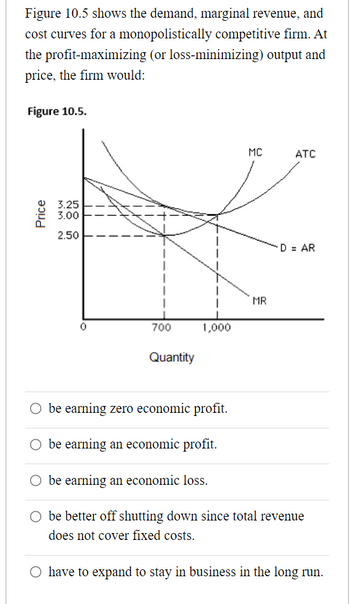
Transcribed Image Text:**Figure 10.5** illustrates the demand, marginal revenue, and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm. It poses a question about the firm's economic status at its profit-maximizing (or loss-minimizing) level of output and price.
**Diagram Description:**
- The horizontal axis represents Quantity, ranging from 0 to about 1,000 units.
- The vertical axis represents Price, ranging from $2.50 to $3.25.
- **Demand Curve (D = AR):** Slopes downward from left to right, indicating a typical demand scenario where higher quantities are demanded at lower prices.
- **Marginal Revenue (MR):** Also slopes downward but is steeper than the demand curve.
- **Marginal Cost (MC):** Upward sloping, crossing the MR curve from below.
- **Average Total Cost (ATC):** U-shaped curve, indicating economies and diseconomies of scale, and crosses the demand curve above the MR curve.
**Key Points in the Graph:**
- The intersection of the MR and MC curves determines the profit-maximizing quantity.
- The corresponding point on the demand curve (D = AR) at this quantity level gives the price the firm can charge.
- The ATC curve lies above the price at the profit-maximizing quantity, indicating that average total costs exceed price.
**Question Options:**
1. Be earning zero economic profit.
2. Be earning an economic profit.
3. Be earning an economic loss.
4. Be better off shutting down since total revenue does not cover fixed costs.
5. Have to expand to stay in business in the long run.
Based on the graph, the firm would be earning an economic loss (Option 3), as the price (from the demand curve) is less than the average total cost at the profit-maximizing output level.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- DE Quantity MC MR ATC Demand The graph above represents a firm in a monopolistically competitive market. Which of the following is true? The firm's profit-maximizing quantity is E. The firm is making a profit of (A - B) x D. The firm is making zero economic profits. The firm is making a loss of (A - B) x D.arrow_forwardPlease help me correct the incorrect answers. Thanks!arrow_forwardI need both answers typing no chatgptarrow_forward
- Part II | The graph below shows a monopolistically competitive firm in the short run. Price and Cost 8 9 8 20 0 100 MR 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 Output MC 9. What is the firm's profit-maximizing price and quantity? 10. How much profit does that firm make at that price and quantity? 900 ATC -d-parrow_forwardThe table below shows the total cost (TC) and marginal cost (MC) for Choco Lovers, a monopolistic firm producing different quantities of chocolate gift boxes. Fill in the blanks in the table. Quantity 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Price $22 20 16 14 12 10 Profit Profit-maximizing quantity Profit-maximizing price 18 Total Revenue 50 100 180 240 280 300 300 Total Cost $50 55 57.5 62.5 72.5 122.5 Marginal Cost Marginal Revenue $1 0.5 2 4 6 1 10 12 8 Instructions: Enter your answers as whole numbers. For profit, round your answer to 2 decimal places. 0 20arrow_forward33 $100 $90 MC АТС $80 E of $70 $60 $50 $40 $30 Demand = P $20 $10 MR $0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Output (Q) The firm shown in the diagram above is in long run equilibrium in a monopolistically competitive market. According to the graph, the Markup is Select one: а. $40 b. $60 с. $50 d. $30arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education