
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
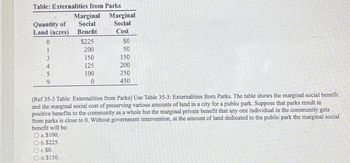
Transcribed Image Text:Table: Externalities from Parks
Marginal
Social
Benefit
Quantity of
Land (acres)
0
34593
$225
200
150
125
100
0
d. $150.
Marginal
Social
Cost
$0
50
150
200
250
450
(Ref 35-3 Table: Externalities from Parks) Use Table 35-3: Externalities from Parks. The table shows the marginal social benefit
and the marginal social cost of preserving various amounts of land in a city for a public park. Suppose that parks result in
positive benefits to the community as a whole but the marginal private benefit that any one individual in the community gets
from parks is close to 0. Without government intervention, at the amount of land dedicated to the public park the marginal social
benefit will be:
O a. $100.
O b. $225.
O c. $0.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1arrow_forward3. The effect of negative externalities on the optimal quantity of consumption Consider the market for paper. Suppose that a paper factory dumps toxic waste into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living downstream from the factory. Producing an additional ton of paper imposes a constant marginal external cost (MEC) of $175 per ton. The following graph shows the demand (marginal private benefits, or MPB) curve and the supply (marginal private costs, or MPC) curve for paper. Use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the marginal social costs (MSC) curve when the marginal external cost is $175 per ton. PRICE (Dollars per ton of paper) 500 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 0 O O 2 0 3 U 5 QUANTITY (Tons of paper) The market equilibrium quantity is O O 6 Supply (MPC) Demand (MPB) 7 MSC tons of paper, but the socially optimal quantity of paper production is To create an incentive for the firm to produce the socially optimal quantity of paper, the government…arrow_forwardRobert and Bruce have identical marginal private cost curves and demand curves and use the same amount of land to graze their mules. They both have access to a common grazing area, which must only be maintained on a volunteer basis. If they had to maintain the land, it would cost each person an additional $200. The maximum sustainable quantity of grazing animals on the land is 14. The graph depicts the marginal private cost curves and the farmers' individual demand curves, which are identical for 800 each farmer. Individual farmer's demand 700 600 Individual farmer's supply 500 400 300 200 100 10 12 14 16 18 20 Ouantity of Animals Cost ($) coarrow_forward
- 3. The effect of negative externalities on the optimal quantityof consumption Consider the market for paper. Suppose that a paper factory dumps toxic waste into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living downstream from the factory. Producing an additional ton of paper imposes a constant external cost of $450 per ton. The following graph shows the demand (private value) curve and the supply (private cost) curve for paper. Use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the social cost curve when the external cost is $450 per ton, 1500 PRICE (Dollars per ton of paper) 1350 1200 1050 900 750 600 450 300 150 0 D O QUANTITY (Tons of paper) Supply (Private Cost) The market equilibrium quantity is Demand (Private Value) Social Cost tons of paper, but the socially optimal quantity of paper production is To create an incentive for the firm to produce the socially optimal quantity of paper, the government could impose a of paper. tons. per tonarrow_forward1. Briefly discuss some ways the government could ensure a market with a positive externality could encourage production of the socially optimal output. 2. Do you believe higher education provides our economy with a positive externality? Why or why not? Do you believe the steps that the federal government takes to encourage the socially optimal amount of higher education be produced/consumed is appropriate? Too much? Too little? Why? (Use appropriate economic theory to support your position.)arrow_forward3. The effect of negative externalities on the optimal quantity of consumption Consider the market for steel. Suppose that a steel manufacturing plant dumps toxic waste into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living downstream from the plant. Producing an additional ton of steel imposes a constant marginal external cost (MEC) of $165 per ton. The following graph shows the demand (marginal private benefits, or MPB) curve and the supply (marginal private costs, or MPC) curve for steel. Use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the marginal social costs (MSC) curve when the marginal external cost is $165 per ton. PRICE (Dollars per ton of steel) 1100 990 880 770 660 550 440 330 220 110 0 0 + 1 O ☐ O 2 0 H 3 ▬ The market equilibrium quantity is O 4 5 QUANTITY (Tons of steel) ☐ ☐ 6 Supply (MPC) Demand (MPB) 7 MSC ? tons of steel, but the socially optimal quantity of steel production is To create an incentive for the firm to produce the socially optimal quantity…arrow_forward
- A. Figure 10-8 (above)- For the described positive externality, what is the market quantity without any efforts to correct the market? B. For a positive externality, briefly explain why and how the government may get involved in the market. In your response, provide an example (type of product or service).arrow_forward5arrow_forwardConsider the market for trees in a public forest, illustrated in the figure to the right, where S, is marginal private cost and 600- D, is marginal private benefit. 550- Trees are an example of a common resource. 500- 450- Suppose that the use of trees in a public forest generates a negative externality of $75 per unit. 400- If so, then according to the figure, the optimal quantity of trees in a public forest for society is units. (Enter your 2 350- response as an integer.) 300- E 250- 200- E 150- 100- 50- 0- 10 11 12 13 Quantity of trees in a public forest Help Me Solve This eText Pages Get More Help - Clear All % & 8 Price of trees in a public forest (per ton)arrow_forward
- 2. The effect of negative externalities on the optimal quantity of consumption Consider the market for paper. Suppose that a paper factory dumps toxic waste into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living downstream from the factory. Producing an additional tonne of paper imposes a constant external cost of $105 per tonne. The following graph shows the demand (private value) curve and the supply (private cost) curve for paper. Use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the social cost curve when the external cost is $105 per tonne. (?) paper) PRICE (Dollars per tonne 700 630 560 490 420 350 280 210 140 70 0 0 ◇ 1 0 2 O 3 e O O The market equilibrium quantity is 3.5 O QUANTITY (Tonnes of paper) D Supply (Private Cost) Demand (Private Value) 7 Social Cost tonnes of paper, but the socially optimal quantity of paper production is 3 To create an incentive for the firm to produce the socially optimal quantity of paper, the government could impose a tax tonne of…arrow_forward7.arrow_forwardConsider a market with the following supply and demand. (It may help to draw a graph for these questions.) P 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 QS 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 QD 800 750 700 650 600 550 500 450 400 35 For the questions assume that there is a $3 external COST. 1. Now imagine that they use tradable allowances. If they cap the quantity at 400 what would the value of these allowance be in the market? (Assume the market is perfectly competitive and that "one allowance" lets you produce one unit of the good.) 2. What will they be worth if the quantity is capped at 500? 3. What if it is capped at 700?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education