
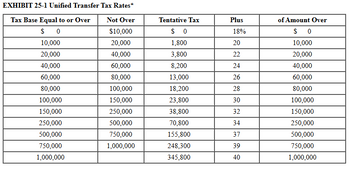
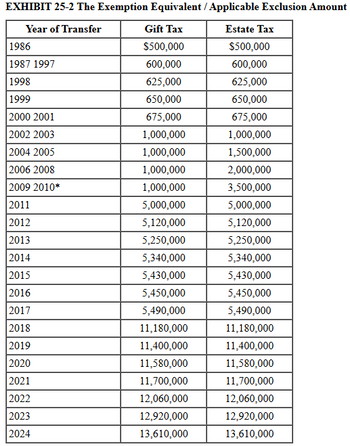
In 2010 Casey made a taxable gift of $6.9 million to both Stephanie and Linda (a total of $13.8 million in taxable gifts).
Calculate the amount of gift tax due this year and Casey's unused exemption equivalent under the following alternatives. (Refer to Exhibit 25-1 and Exhibit 25-2.)
Note: Enter your answers in dollars, not millions of dollars. Leave no answer blank. Enter zero if applicable.
a. This year Casey made a taxable gift of $1 million to Stephanie. Casey is not married, and the 2010 gift was the only other taxable gift he has ever made.
Gift tax due - $0
Unused applicable credit - ?
b. This year Casey made a taxable gift of $16.9 million to Stephanie. Casey is not married, and the 2010 gift was the only other taxable gift he has ever made.
Gift tax due - ?
Unused applicable credit - $0
c. This year Casey made a gift worth $16.9 million to Stephanie. Casey married Helen last year, and they live in a common-law state. The 2010 gift was the only other taxable gift Casey or Helen has ever made. Casey and Helen elect to gift-split this year.
Casey's gift tax due - $0
Casey's unused applicable credit - ?
Helen's gift tax due - $0
Helen's unused applicable credit - ?
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- EXHIBIT 25-1 Unified Transfer Tax Rates* Tax Base Equal to or Over Not Over Tentative Tax Plus of Amount Over $ 0 $10,000 $ 0 18% $ 0 10,000 20,000 1,800 20 10,000 20,000 40,000 3,800 22 20,000 40,000 60,000 8,200 24 40,000 60,000 80,000 13,000 26 60,000 80,000 100,000 18,200 28 80,000 100,000 150,000 23,800 30 100,000 150,000 250,000 38,800 32 150,000 250,000 500,000 70,800 34 250,000 500,000 750,000 155,800 37 500,000 750,000 1,000,000 248,300 39 750,000 1,000,000 345,800 40 1,000, EXHIBIT 25-2 The Exemption Equivalent Year of Transfer Gift Tax Estate Tax 1986 $500,000 $500,000 1987–1997 600,000 600,000 1998 625,000 625,000 1999 650,000 650,000 2000–2001 675,000 675,000 2002–2003 1,000,000 1,000,000 2004–2005 1,000,000 1,500,000 2006–2008 1,000,000 2,000,000 2009–2010* 1,000,000 3,500,000 2011 5,000,000 5,000,000 2012 5,120,000 5,120,000 2013 5,250,000 5,250,000 2014 5,340,000 5,340,000 2015…arrow_forwardPlease don't give image formatarrow_forwardd cion The table given below shows the absolute tax amounts under five different tax policies for respective income levels. Table 19.2 Annual Pretax Income Tax Policy Alpha O Gamma. Alpha. SO $0 $0 $0 $0 $10,000 $1,000 $1,000 $1,000 $1,000 $1,000 $50,000 $5,000 $6,000 $4,000 $1,000 $900 $100,000 $10,000 $15,000 $6,000 $1,000 $800 Beta. O Eta. Refer to Table 19.2. The tax structure which leads to maximum income inequality is: Delta. Tax Policy Beta Question 18 Tax Policy Gamma 27 Tax Policy Delta Tax Policy Eta $0 tv 9 N 4.nts. Narrow_forward
- Chapter 3 Activity – Taxes Individual Income Tax Brackets (2021) Marginal Tax Rate Single, taxable income over: Joint, taxable income over: Head of Household, taxable income over: 10% $0 $0 $0 12% $9,950 $19,900 $14,200 22% $40,525 $81,050 $54,200 24% $86,375 $172,750 $86,350 32% $164,925 $329,850 $164,900 35% $209,425 $418,850 $209,400 37% $523,600 $628,300 $523,600 Standard Deduction Amounts (2021) Filing Status Deduction Amount Single $12,550 Married Filing Jointly $25,100 Head of Household $18,800 Long-term Capital Gains & Qualified Dividends (2021) Tax Rate Single Joint Head of Household 0% Under $40,000 Under $80,800 Under $54,100 15% $40,400 $80,800 $54,100 20% $445,850 $501,600 $473,750 Additional 3.8% Net Investment Income Tax for MAGI over $200,000 / $250,000 / $200,000 Calculate the federal income…arrow_forward1. Use the following information to answer the following questions: Taxable income Tax rate $ 0 – $ 50,000 15% $ 50,001 – $ 75,000 25% $ 75,001 – $100,000 34% $ 100,001 – $335,000 39% $ 335,001 – $10.000 million 34% $10,000,001 – $15.000 million 35% $15,000,001 – $18.333 million 38% $18,333,334 and above 35% A. If a firm has taxable income of $16.2 million, its marginal tax rate is . B. If a firm has taxable income of $16.2 million, its average tax rate is _____.arrow_forwardTable 1.4 Use the following tax rates and income brackets to answer the following question(s). Tax Rate Individual Returns 10% $0 to $8,350 15% $8,351 to $33,950 $33,951 to $82,250 $82,251 to $171,550 $171,551 to $372,950 Over $372,951 25% 28% 33% 35% Joint Returns $0 to $16,700 $16,701 to $67,900 $67,901 to $137,050 $137,051 to $208,850 $208,851 to $372,950 $16,750 $18,836 $22,425 $25,116 Over $372,951 Josh earned $89,700 in taxable income and files an individual tax return. What is the amount of Josh's taxes for the year?arrow_forward
- Problem 16-145 Four independent situations are described below. Each involves future deductible amounts and/or future taxable amounts produced by temporary differences reported first on: Income Statement Tax Return Revenue Expense Revenue Expense $21,000 (1.) (2.) (3.) (4.) $21,000 $15, 200 $21,000 $15, 200 $21, 000 $10, 200 Required: For each situation, determine the taxable income assuming pretax accounting income is $100,000. (Amounts to be deducted should be indicated by a minus sign.) 1 2 3 4 Accounting income Temporary differences: Income statement first: Revenue Expense Tax return first: Revenue Expense Taxable incomearrow_forwardPlease Do not Give image formatarrow_forwardQUESTION 12 Range of taxable income $ 0 to $9,875 Marginal rate 10% 9,875 to 40,125 12 40,125 to 85,525 22 85,525 to 163,300 24 163,300 to 207,350 32 207,350 to 518,400 35 Calculate the total tax liability, after-tax earnings, and average tax rates if before-tax earnings are $25000, $82,000, and $120,000.arrow_forward
- Please do stepwise and correct please ill like..arrow_forward↑ (Corporate income tax) G. R. Edwin Inc had sales of $6.09 million during the past year. The cost of goods sold amounted to $2.5 million Operating expenses totaled $2.54 million, and interest expense was $25,000. Use the corporate tax rates shown in the popup window to determine the firm's tax liability What are the firm's average and marginal tax rates? The firm's tax liability for the year is $ (Round to the nearest dollar)arrow_forwardSubject: accountingarrow_forward
