
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
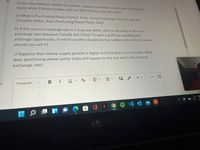
Transcribed Image Text:In the international market for lumber, suppose Canadian lumber sells for $100 per
tonne while Chinese lumber sells for 500 Chinese yuan per tonne.
a) What is Purchasing Power Parity? If the current exchange rate is 4 yuan per
Canadian dollar, does Purchasing Power Parity hold?
b) If the current exchange rate is 4 yuan per dollar, what is the value of the real
exchange rate between Canada and China? To earn a profit by exploiting the
arbitrage opportunity, in which country should you buy lumber and in which country
should you sell it?
c) Suppose that money-supply growth is higher in China than it is in Canada. What
does purchasing-power parity imply will happen to the real and to the nominal
exchange rate?
+ v
...
Paragraph
BIU A
EN
III
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please list and explain in your own words the benefits and costs when a country adopts a flexible exchange rate regime; Also the benefits and costs when a country adopts a fixed exchange rate regime.arrow_forwardSuppose the price of wheat increases in the world market. Explain and use diagrams to illustrate the effect of this change on the current account and the exchange rate of a wheat exporting country. a wheat importing country.arrow_forward1 Suppose that two countries, Indonesia and Vietnam, produce coffee. The currency unit used in Indonesia is the Rupiah (IDR). The currency unit used in Vietnam is the Dong (VND). In Vietnam, coffee sells for 4,500 dong (VND) per pound. The exchange rate is 1.57 VND per 1 IDR, EVND/IDR = 1.57. 2 If the law of one price holds, what is the price of coffee in Indonesia, measured in Rupiah (assume we are talking about the same type of coffee)? Please round your answer to the nearest whole number. Assume the price of coffee in Indonesia is actually 3000 IDR per pound. Compute the relative price of coffee in Indonesia versus Vietnam (round your answer to 2 decimal places). Where will coffee traders buy coffee? Where will they sell coffee in this case? How will these transactions affect the price of coffee in Vietnam? In Indonesia?arrow_forward
- Suppose that the US price level is $15,000/consumption bundle and that the UK price level is (Pounds) 10,000/consumption bundle. Let the exchange rate be 0.75 (Pound per Dollar). Assuming no transaction costs, if we buy goods in the United Kingdom with our $1 million and sell them in the United States, we will receive Please do fast ASAP fastarrow_forwardIf a Japanese car costs P*=1,000,000 yen, a similar American car costs P= 20,000, and a dollar can buy 100 yen, e= 100 yen/$. Car is assumed to be identical and japan is next door to New Hampshire for simplicity: a. What is the real exchange rate? In which country is car more expensive? b. From which country would you buy and which country would you sell?arrow_forwardview picturearrow_forward
- The Big Mac index is used as a rough measure of purchasing power parity across countries. The Economist magazine recently included the Vietnamese dong in its calculation of the Big Mac index. A Big Mac costs $5.06 in the United States but only 60,368 dong or $2.66 in Vietnam (at the current exchange rate). What does this information suggest about the value of the real exchange rate of the U.S. dollar relative to the Vietnamese dong (treating the United States as the domestic economy, so the nominal exchange rate is expressed as dong per dollar)? Is the real exchange rate likely to be greater than or less than 1?arrow_forwardPresently, the dollar is worth 140 Japanese yen in the spot market. The interest rate in Japan on 90-day government securities is 4 percent; it is 8 percent in the United States. a. If the interest-rate parity theorem holds, what is the implied 90-day forward exchange rate in yen per dollar? b. What would be implied if the U.S. interest rate were 6 percent?arrow_forwardIf the dollar/pound exchange rate is $2/pound, a Big Mac costs $5 in New York City and costs 2 pounds in London, the pound is and U.S. tourists will be overvalued; better off in New York undervalued; better off in New York undervalued; better off in London overvalued; better off in Londonarrow_forward
- The euro/dollar exchange rate is 1 euro = $1.20. According to the law of one price, a camera that sells for $240 in New York should sell for how many euros in Germany?arrow_forwardExplain why an increase in national saving (S) relative to investment (I) may lead to a current account surplus under flexible exchange rates.arrow_forwardWe look at the trade of gas between Russia and the EU and assumes that both areas' supply curves slope upwards and their demand curves slope downwards in the diagram with quantity on the horizontal axis and price on the vertical axis. To make the situation simple, we also initially assume that the exchange rate is constant, and it is 1 (so that we do not need to differentiate between the prices i Russia and the EU). In the autarky equilibria, prices are higher in the EU than in Russia. Unless otherwise specified, there are no trading costs, and the capacity of the pipelines is not binding (ie with free trade the prices are basically the same in the EU and Russia). (a) Draw and show the supply of export goods and the demand for import goods in relation to the two areas' supply and demand curves (three islands next to each other). (b) What happens (to welfare in the two countries and consumer surplus/producer surplus) if the EU stops importing Russian gas? (c) Without Nord Stream 1/2 in…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education