
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
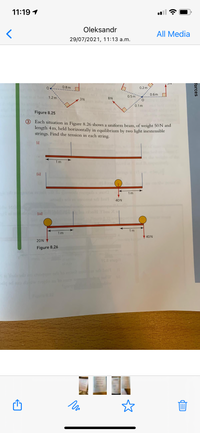
Each situation in Figure 8.26 shows a uniform beam, of weight 50N and length 4 m, held horizontally in equilibrium by two light inextensible strings. Find the tension in each string.
hi can you please explain it fully?
please see the image attached for the diagram
if you use * can you explain what it means.
thank you
Transcribed Image Text:11:19 1
Oleksandr
All Media
29/07/2021, 11:13 a.m.
O 0.8m
0.2 m
0.6m
1.2 m
0.5m
3N
8N
0.1 m
Figure 8.25
3 Each situation in Figure 8.26 shows a uniform beam, of weight 50N and
length 4 m, held horizontally in equilibrium by two light inextensible
strings. Find the tension in each string.
(i)
1m
(ii)
1m
40N
(iii)
1m
1m
Y 40N
20N
Figure 8.26
dla o h b
led n
wdo m lo
forces
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A horizontal L=1.2 m long mb=14 kg uniform bar is hinged on the left end and pulled at the right end by a cable. The cable makes 23° angle with horizontal. A 24 kg store sign is suspended below the bar at d=0.18 m from the right end. Find the magnitude of horizontal hinge force.arrow_forwardFor the truss structure in Figure Q5a, determine the forces in members AD and AB; and state whether each of these members are in tension or in compression. *Assume that the truss is in static equilibrium.arrow_forwardIf F = 810 N , determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC, and ADarrow_forward
- GOAL Apply the two conditions of equilibrium. (a) A uniform beam attached to a wall and supported by a cable. (b) A force diagram for the beam. (c) The component form of the force diagram. Three figures (labeled a, b, and c) are shown for the person-beam system. In Figure (a), an illustration of the scenario is shown. The left end of a horizontal beam of length 5.00 m is connected to a pin on a vertical wall. A cable connects the right end of the beam to the top of the wall, creating an acute angle 53.0° with the horizontal. A person stands on the beam between the left end and the center. In Figure (b), a horizontal beam is under the influence of four forces. A force vector R acts up and right on the left end of the beam. A force of magnitude 600 N acts downwards on the beam between the left end and the center. A force of magnitude 300 N acts downwards on the center of the beam. A force vector T acts up and left on the right end of the beam at an acute angle 53.0° from the…arrow_forwardQuestion 3 When the structure shown in figure (3) below is supported at point P, it is in equilibrium. If the weight of the structure is negligible. Find the magnitude of force F and the force applied at P. Figure 3 2.0 m 4.0 m 2.0 m + 2.0 m - 3.0 m 2000 N 1000 Narrow_forwardPlease help me with this qs with workings thank you so much :)arrow_forward
- Mechanics task 2: Solve the follow Problem 1: An individual holds a 10 Kg bar, 4m long, by pulling on a cable (see Figure Q1). Derive the tension in the cable and the reaction forces at A. A 4 m Figure Q1 25° 45° Barrow_forwardA journal 25 mm in diameter supported in sliding bearings has a maximum end reaction of 2500 N. Assuming an allowable bearing pressure of 5 N/mm², find the length of the sliding bearingarrow_forwardWeight=255 Can you also explain in detail thank youarrow_forward
- Show complete and detailed solution. View Image.arrow_forwardFigure Q5a shows a truss structure in static equilibrium that is simply supported at A and C. Calculate the reaction forces RA and RC when subjected to vertical loads of 50 kN, 25 kN and 15 kN at nodes D, E & C, respectively.arrow_forwardAn electric light fixture weighing 15 N hangs from a point C, by two strings AC and BC. AC is inclined at 60° to the horizontal and BC at 45° to the vertical as shown in Fig. Using Lame's theorem determine the forces in the strings ACand BC 45 15 N MLA Muem angage Aioc and Sany aal Mechanics n:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY