
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
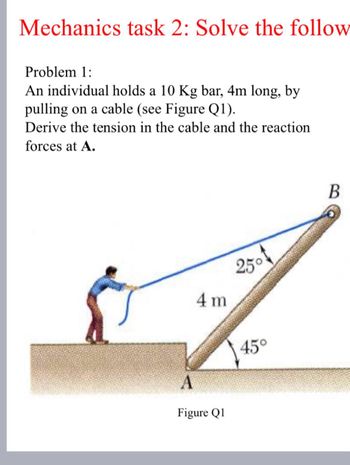
Transcribed Image Text:Mechanics task 2: Solve the follow
Problem 1:
An individual holds a 10 Kg bar, 4m long, by
pulling on a cable (see Figure Q1).
Derive the tension in the cable and the reaction
forces at A.
A
4 m
Figure Q1
25°
45°
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Chapter 12, Problem 010 GO The system in the figure below is in equilibrium, with the string in the center exactly horizontal. Block A weighs 35.0 N, block B weighs 57.0 N, and angle p is 39.0°. What are Find (a) tension T1, (b) tension T2, (c) tension T3, and (d) angle 0. (a) Number Units (b) Number Units (c) Number Units (d) Number Units Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Work GO TUTORIAL LINK TΟ ΤΕXΤ LINK TO SAMPLE PROBLEM LINK TO SAMPLE PROBLEM VIDEO MINI-LECTUREarrow_forwardigure 2. Assume that the rod is massless, perfectly rigid, and pivoted at point P. When the rod is perfectly horizontal, the angle 0 = 0, the displacement y 0, and the springs are in neither tension nor compression. Gravity acts on the system (e.g. on mass M). We assume that y is a small displacement. A mass M is attached at the end of the rod. DE only 225 Your tasks: X k 0 3k a F a M y A Derive an equation of motion for the system in terms of the angular displacement 0, and its derivatives (you should not have y or its derivatives in this equation.) B Derive an equation of motion for the system in terms of the displacement y, and its derivatives (you should not have or its derivatives in this equation. C Assuming there is no external actuator force F acting on the system, write down the total energy H of the system in terms of 0,0 and element constants. Derive an expression for the time derivative H of the total energy. D Transform the equation from part B, which is in y, to another…arrow_forwardmb: L d- ms A horizontal L=1.2 m long mb=12 kg uniform bar is hinged on the left end and pulled at the right end by a cable. The cable makes 31° angle with horizontal. A 18 kg store sign is suspended below the bar at d=0.18 m from the right end. Find the magnitude of vertical hinge force.arrow_forward
- c) The pulley system shown in Figure Q1c lifts a mass, m, of 550 kg. Calculate the force FAnecessary to maintain the suspended mass in static equilibrium; and determine the forces at the ceiling anchor points A and B. Assume frictionless and weightless pulleys and use g 9.81 m/s.arrow_forwardA sandwich board advertising sign is constructed as shown in the figure below. Hinge- Chain G2001 Brooks/Cole Thomson Learning CG CG 0.50 m Uniform board (CG at center) 1.10 m 1.30m The sign's mass is 5.30 kg. (a) Calculate the tension in newtons in the chain assuming no friction between the legs and the sidewalk. XN (b) What force is exerted in newtons by each side on the hinge? X Narrow_forwardor 5, 2. You have a massless spring of force constant 64 N/m, but it is wound tightly enough that you must apply 16 N of force to it before it begins to stretch. You attach a 12 kg mass to one end of the spring. The other end is fixed in place above the mass (e.g. it is clamped to the room's ceiling). A second mass of 1.0 kg is connected to the bottom of this first mass via a thin string of negligible mass. The system is initially in equilibrium, but then the string connecting the smaller mass suddenly snaps. 2.1 What is the initial acceleration of the spring-mass system? 2.2. What is the amplitude of oscillation for this system? 2.3 What would be the period of oscillation for this system? 2.4 Determine the maximum value of the kinetic energy of the mass still connected to the spring. Assume negligible damping.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY