
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
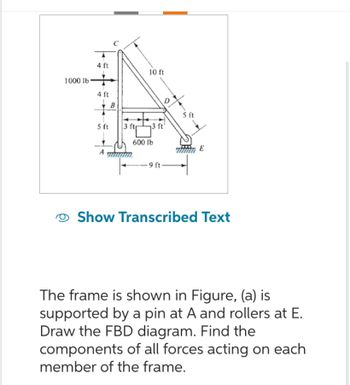
Transcribed Image Text:1000 lb
4 ft
4 ft
B
5 ft
A
3 ftr
10 ft
13 ft
600 lb
-9 ft-
5 ft
E
Show Transcribed Text
The frame is shown in Figure, (a) is
supported by a pin at A and rollers at E.
Draw the FBD diagram. Find the
components of all forces acting on each
member of the frame.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two weights, A and C, are fixed to a bar, B. Their masses are: A = 60 kg, B = 230 kg,C = 45 kg. B is, in turn, connected to a fixed vertical post by a hinge and a support cableD. The geometry of the system is shown at right. Treat weights A and C as point masses a)What is the tension in support cable D? Be sure to include a detailed freebody diagram to accompany your analysis.b) What is the magnitude of the force provided by the hinge?c) What is the moment of inertia of the A + B + C as a rigid system, for rotationabout the hinge? For analysis, break the beam into a short piece to the left of thehinge, and a separate longer piece to the right of the hinge. If the support cable D on should break,d) what is the angular acceleration of the beam and weights at the moment the cable breaks?e) what is the magnitude of the linear acceleration experienced by each of the weights, A and C, at moment the cable breaks?arrow_forwardQ3: For the structure shown in Figure, Compute the forces in all pines. 50 lb 5ft 80 Ib 8ft 6 ft 2 ft+ (20 Degree)arrow_forwardIn the figure, a nonuniform bar is suspended at rest in a horizontal position by two massless cords as shown in the figure here. One cord makes the angle 0 = 31.1° with the vertical; the other makes the angle p = 58.9° with the vertical. If the length L of the bar is 5.9 m, compute the distance x from the left end of the bar to its center of mass. L comarrow_forward
- A stoplight of mass m is hung from a massless wire that has segments to a horizontal pole and a vertical pole as shown in the figure. The stoplight is not moving. 162 T₂ 60° T₁ 60° The wire segments create angles 60° with respect to the horizontal pole and 60° with respect to the vertical pole as shown and the mass creates tensions in the segments of the wire of magnitude T₁, and T2, as labeled in the diagram. (A) Draw a free-body diagram for the hanging mass system showing (and labeling) all forces acting on the hanging stoplight mass. Then draw x and y axes for your free-body diagram. (B) Use Newton's-second law to write equations for forces acting on the stoplight in component forms (x and y, separately) in terms of: tension magnitudes T₁ and T2, the angles shown, the mass of the object m and the gravitational constant g. You do not need to solve the equations but simplify as possible. (C) The weight of the stoplight is determined to be 343 Newtons. Solve for magnitudes of T₁, T2.arrow_forwardNeed help please Include all units and stepsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY