
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%

Transcribed Image Text:Each graph illustrates three short-run cost curves for firms, where ATC is average total cost (also referred to as average
cost), MC is marginal cost, and AVC is average variable cost.
Please classify each of the graphs as valid or invalid based on what you know about the relationships between these curves.
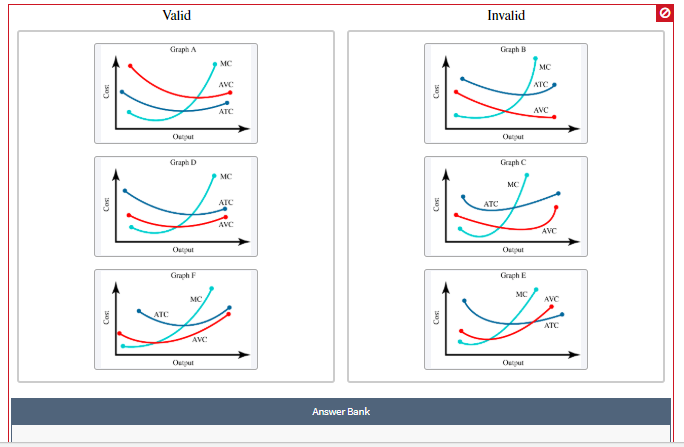
Transcribed Image Text:Valid
Invalid
Graph A
Скаph B
MC
мС
AVe
ATC
AVC
ATC
Ougut
Outut
Graph D
Graph C
мс
мC
AIC
ATC
AVC
AVC
Otut
Outut
Graph F
Graph E
мC
мC
AVC
ATC
ATC
AVC
Ouut
Outut
Answer Bank
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 9 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Let F be the fixed cost of production, let VC be the variable cost of production, C be the total cost, MC be the marginal cost, AFC, the average fixed cost, AVC, the average variable cost, and AC, the average cost. Complete the following cost table. (Enter numeric responses rounded to two decimal places.) Output (q) 12 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 F $100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 VC $32 56 72 80 96 C MC $132 $32 156 24 172 16 8 16 24 196 220 152 252 192 292 240 340 296 40 48 56 AFC AVC AC $100.00 $32.00 $132.00 50.00 28.00 78.00 33.33 24.00 25.00 20.00 45.00 20.00 39.20 16.67 36.67 14.29 36.00 36.50 37.78 20.00 21.71 24.00 11.11 26.67 10.00 29.60arrow_forward6arrow_forwardDouglas Fur is a small manufacturer of fake-fur boots in San Diego. The following table shows the company’s total cost of production at various production quantities. On the following graph, plot Douglas Fur’s average total cost (ATC) curve using the green points (triangle symbol). Next, plot its average variable cost (AVC) curve using the purple points (diamond symbol). Finally, plot its marginal cost (MC) curve using the orange points (square symbol). (Hint: For ATC and AVC, plot the points on the integer; for example, the ATC of producing one pair of boots is $210, so you should start your ATC curve by placing a green point at (1, 210). For MC, plot the points between the integers: For example, the MC of increasing production from zero to one pair of boots is $90, so you should start your MC curve by placing an orange square at (0.5, 90).) Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically.arrow_forward
- The table below represents incomplete information on the short-run production costs for a firm, where: FC is fixed cost; TVC is total variable cost; TC is total cost; MC is marginal cost; and AFC, AVC, and ATC are average fixed, average variable, and average total cost, respectively. Based on the information provided in the table, complete the rest of the table. Note that values for FC, TVC, TC, AFC, AVC, and ATC should be placed on the same line as the corresponding quantity; values for MC should be placed between quantities. For example, the marginal cost of increasing output from 2 units to 3 units is $110, thus $110 is entered between Q=2 and Q=3 in the table. Find the quantity at which diminishing marginal returns set in. TVC TC Q 1 FC MC AFC AVC ATC 400 300 2 920 110 3 4 180 5 272arrow_forwardGraphically, the marginal cost curve and the average total cost curve intersect wherearrow_forward4. Various measures of cost Douglas Fur is a small manufacturer of fake-fur boots in San Francisco. The following table shows the company's total cost of production at various production quantities. Fill in the remaining cells of the following table. Average Variable Cost (Dollars per pair) Average Total Cost (Dollars per pair) Quantity Total Cost Marginal Cost Fixed Cost Variable Cost (Pairs) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) 120 1 210 2 270 3 315 4 380 5 475 630arrow_forward
- The following table shows the capital and labor requirements for 10 different levels of production. Assuming that the price of labor (PL) is $8 per unit and the price of capital (PK) is $6 per unit, compute and graph total cost, marginal cost, and average cost for the firm. To do this, fill in the total cost for each output level in the table below. (Enter your responses as whole numbers.) 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 K 0 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 L 0 3 7 10 13 17 23 31 41 53 67 TC 0 Cost per unit ($) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Units of output Q ✔arrow_forwardThe Mini-Case "Economies of Scale at Google describes economies of scale for Google Cloud Storage. The cost function for this service is well-approximated by K C(q)-F+cq where C is total cost, F is fixed cost, c is a constant and q is output. What is marginal cost for this cost function? What are the average fixed cost, average variable cost, and average cost? Over what range of output does Google have economies of scale? The marginal cost function (MC) is The average fixed cost function (AFC) is AFC- The average variable cost function (AVC) is AVC- MC-C The average cost function (AC) is AC- (Property format your expressions using the tools in the palette. Hover over tools to see keyboard shortcuts. Eg, a fraction can be created with the character) Time Remaining: 02.09.09arrow_forwardGraph the Average Total Costs, Average Variable Costs, and Marginal Costs on the same graph.arrow_forward
- Provide a diagram that illustrates, for the short-run analysis, the average cost function, the marginal cost function, the average variable cost function and the variable cost function. Provide clear explanations for why these functions have common points of intersection.arrow_forwardA firm has a fixed production cost of $4000. For the first 100 units of production, the firm has a marginal cost of $50 per unit produced. Producing more than 100 units has a marginal cost of $70 per unit produced. The firm cannot produce more than 150 units. How much does it cost to produce at q=0? at q=50? at q=100? at q=125? at q=150? Graph the firm’s marginal cost functionarrow_forwardSuppose that the Acme Gumball Company has a fixed proportions production function that requires it to use two gumball presses and one worker to produce 1,000 gumballs per hour. a. Explain why the cost per hour of producing 1,000 gumballs is 2v + w (where v is the hourly rent for gumball presses and w is the hourly wage). b. Assume Acme can produce any number of gumballs they want using this technology. Explain why the cost function in this case would be TC = q(2v +w), where q is output of gumballs per hour, measured in thousands of gumballs. c. What is the average and marginal cost of gumball production (again, measure output in thousands of gumballs)? (show the complete formula) Draw the graph for the average and marginal cost curves for gumballs assuming v=3, w-5 (show working) Now draw the graph for these curves for v=6, w=5.( show working) Explain why these curves have shifted.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education