
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
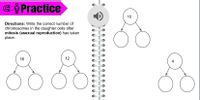
Transcribed Image Text:G: Practice
10
Directions: Write the correct number of
chromosomes in the daughter cells after
mitosis (asexual reproduction) has taken
place.
16
12
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Answer: Determine the diploid number of chromosome in the nucleus.arrow_forwardMatch the phases of the cell cycle.arrow_forwardv Part A Match the description with the stage of the cell cycle. Reset Help Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell DNA condenses to form chromosomes Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell Chromosomes Split and Move to opposite ends of the cell Cell begins to split into two DNA replicates Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase UnitConversionSE.pdf Type here to search 99+ RB (1arrow_forward
- The failure of chromosomes to separate normally during cell division is calledarrow_forwardThe nuclear envelope is broken into smaller components. Kinetochore microtubules are assembled and are connected to kinetochores. Name: The chromosomes become aligned in a plane at the cellular equator. Name:arrow_forwardSpecify the correct number of chromosomes and chromatids in each of the following human cell types. A spermatagonial precursor about to enter meiosis has 46 chromosomes and chromatids. An egg cell has chromosomes and chromatids. A cell entering meiosis II has chromosomes and chromatids.arrow_forward
- Explain how interference with mitotic structures or disruption of mitotic processes affects cell reproduction and ultimately the organism.arrow_forward* Summary of mitosisarrow_forwardAnswer each question with a paragraph; 3-5 sentences each. Explain the difference between a proto-oncogene and a tumor-suppressor gene. Explain the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Explain the difference between positive regulation of the cell cycle and negative regulation of the cell cycle. Explain the difference between normal p53 and mutated p53. Find two differences and two similarities between binary fission and mitosis.arrow_forward
- The cell cycle is typically thought of as having four stages. Describe the stages of the cell cycle and identify the mechanism(s) involved in progressing or not progressing through the stages with reference to proteins and signalling processes involved. Please keep brief - 10 sentences/dot points max.arrow_forwardLabel each stage of the cell cycle and describe the events that occurarrow_forwardName: Class Period: 2.3 Cell Division - use pages 56-63 Fill in the blanks in the table below. Then answer the questions. Stages of Cell Cycle Stage Event Interphase 1. cell 2. DNA is Prophase - chromosomes 4. 3. 5. - chromosomes line up in the middle Anaphase-chromosomes 6. 7. chromosomes - 2 new nuclei form around the Cytokinesis 8. 9. Which stage of the cell cycle usually lasts the longest? 10. During which stage of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur? 11. During which stage of the cell cycle does the cell membrane pinch the cell into two? 12. What is the final result of the cell cycle? 13. What are the three functions of cell division? a. b. C. Building Vocabulary Match each term with its definition by writing the letter of the correct definition in the right column on the line beside the term in the left column. 14. C interphase 15. mitosis 16. cell cycle 17. cytokinesis 18. ✓ replication 19. 20. b f DNA chromosome a regular sequence of growth and division that cells undergo…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education