
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
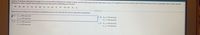
Transcribed Image Text:A group of students estimated the length of one minute without reference to a watch or clock, and the times (seconds) are listed below. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that these times are from a population with a mean equal to 60 seconds. Does it appear that students are reasonably good at estimating one minute?
Times (in seconds): 80, 88, 48, 75, 52, 36, 66, 74, 73, 54, 72, 78, 104, 95, 76
Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the null and alternative hypotheses?
Options:
- A: \( H_0: \mu = 60 \text{ seconds} \)
\( H_1: \mu \neq 60 \text{ seconds} \)
- B: \( H_0: \mu \leq 60 \text{ seconds} \)
\( H_1: \mu > 60 \text{ seconds} \)
- C: \( H_0: \mu \geq 60 \text{ seconds} \)
\( H_1: \mu < 60 \text{ seconds} \)
- D: \( H_0: \mu \neq 60 \text{ seconds} \)
\( H_1: \mu = 60 \text{ seconds} \)
A diagram or graph is not present in the image.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Determine the test statistic
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Determine the test statistic
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A group of students estimated the length of one minute without reference to a watch or clock, and the times (seconds) are listed below. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that these times are from a population with a mean equal to 60 seconds. Does it appear that students are reasonably good at estimating one minute? 66, 79, 39, 65, 41, 26, 58, 62, 68, 47, 63 73, 91, 87, 68. 1. Determine the test statistic 2. P-value 3. State the final conclusion that addresses the original claim.arrow_forward1) Is the test significant? A. Unable to determine B. No, p = .448 C. Yes, p = <. 001 D. Yes, p = .448 2) In order to determine where the main mean differences lie, the researcher would also need to conduct a ____? A. Correlation B. MANOVA C. post-hoc analysis D. t-testarrow_forwardA group of students estimated the length of one minute without reference to a watch or clock, and the times (seconds) are listed below. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that these times are from a population with a mean equal to 60 seconds. Does it appear that students are reasonably good at estimating one minute? 78 92 51 72 52 36 66 70 72 56 70 79 104 95 77 O A. Ho: H= 60 seconds O B. Ho: u= 60 seconds H1: µ> 60 seconds H1: µ< 60 seconds O C. Ho: H+ 60 seconds O D. Ho: µ = 60 seconds H1: µ= 60 seconds H1: µ+60 seconds Determine the test statistic (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) State the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. V Họ. There is evidence to conclude that the original claim that the mean of the population of estimates is 60 seconds correct. It that, as a group, the students are reasonably good at estimating one minute. does not appear Click to select your answer(s).…arrow_forward
- A magazine reported that at the top 50 business schools in a region, students studied an average of 13.3 hours. Set up a hypothesis test to try to prove that the mean number of hours studied at your school is different from the reported 13.3 hour benchmark. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. O E. H X#13.3 H: X= 13.3 P. Ho p=13.3 H, p#13.3 O G. H, p= 13.3 H, X+13.3 OH. H, p#13.3 H, p=13.3 OL H a 13.3 H: a = 13.3 O J. Ho a= 13.3 H a# 13.3 O K. H, p# 13.3 H1: X= 13.3 OL Ho B#13.3 H B= 13.3 b. What is a Type I error for your test? A. Concluding that the mean number of hours studied at your school is different from the reported 13.3 hour benchmark when in fact it is not different O B. Concluding that the mean number of hours studied at your school is different from the reported 13.3 hour benchmark when in fact it is different C. Concluding that the mean number of hours studied at your school is not different from the reported 13.3 hour benchmark when in fact it is different c. What is a…arrow_forwardwhich of the following sample data: sample size= 100 sample mean= 340z/hr sample variance= 90z/ hr construct a 98% confidence interval for μ. the population mean is what?arrow_forwardA group of students estimated the length of one minute without reference to a watch or clock, and the times (seconds) are listed below. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that these times are from a population with a mean equal to 60 seconds. Does it appear that students are reasonably good at estimating one minute? 75 88 50 77 49 34 66 75 72 58 71 81 105 95 73 What are the null and alternative hypotheses? O A. Ho: µ= 60 seconds B. Ho: µ = 60 seconds %3D %3D H1: µ 60 seconds C. Ho: µ + 60 seconds D. Ho: µ = 60 seconds H1: µ= 60 seconds H1: µ# 60 seconds Determine the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) State the final conclusion that addresses the original claim. Ho. There is estimating one minute. evidence to conclude that the original claim that the mean of the population of estimates is 60 seconds correct. It that, as a group, the students are reasonably good atarrow_forward
- A group of students estimated the length of one minute without reference to a watch or clock, and the times (seconds) are listed below. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that these times are from a population with a mean equal to 60 seconds. Does it appear that students are reasonably good at estimating one minute? 75 88 48 77 50 33 69 72 78 59 73 82 100 101 75 D S Assuming all conditions for conducting a hypothesis test are met, what are the null and alternative hypotheses? O A. Ho: μ= 60 seconds OB. Ho: 60 seconds H₁ μ 60 seconds H₁: #60 seconds Determine the test statistic. lete (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Determine the P-value. (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardStudents estimated the length of one minute without reference to a watch or clock, and the times (seconds) are listed below. Assume that a simple random sample has been selected, Use a 0.10 significance level to test the claim that these times are from a population with a mean equal to 60 seconds. Does it appear that students are reasonably good at estimating one minute? 69 82 38 66 41 21 58 64 64 46 63 72 97 90 67 Perform the test assuming that the requirements are met. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.)arrow_forwardA hospital has a main campus and three satellite locations. Management wants to reduce waiting time for ER cases. A random sample of 11 ER cases at each location was selected, and the waiting time was measured. Excel.) Complete parts (a) through (d) to determine if there is statistical evidence of a difference in the mean waiting times betweeen the four locations. a. State the two hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. O B. Ho: H1 = H2 = ••• = H4 H;: 41 H2# • • • # µ4 O A. Ho: H1 =H2 = ••• = H4 H;: Not all H are equal (where j= 1,2,.4) OC. Họ: H1 = H2 = • •• = H1 H;: 41 # H2# • •• #H11 D. Ho: H1 = H2= • •• - H11 H;: Not all H; are equal (where j= 1,2,.,11) b. At the 0.05 level of significance, state the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places to the right of the decimal point as needed.) O A. FSTAT = 0.005 , from the first row of the ANOVA table O B. FSTAT = 4.91 , from the first row of the ANOVA table O C. FSTAT = 2.05 , from the first row of the ANOVA table O D. FSTAT =…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman