
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Can you please set up the ice table
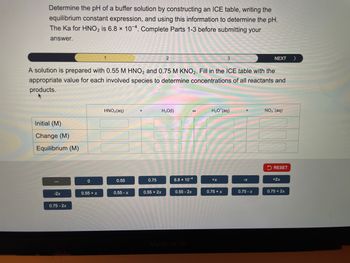
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the pH of a buffer solution by constructing an ICE table, writing the
equilibrium constant expression, and using this information to determine the pH.
The Ka for HNO2 is 6.8 x 104. Complete Parts 1-3 before submitting your
answer.
1
2
3
NEXT
>
A solution is prepared with 0.55 M HNO2 and 0.75 M KNO2. Fill in the ICE table with the
appropriate value for each involved species to determine concentrations of all reactants and
products.
Initial (M)
Change (M)
Equilibrium (M)
HNO2(aq)
H₂O(1)
H3O+(aq)
NO₂ (aq)
RESET
0
0.55
0.75
6.8 × 10-4
+x
-x
+2x
-2x
0.55 + x
0.55-x
0.55 + 2x
0.55 -2x
0.75 + x
0.75-x
0.75 + 2x
0.75 -2x
MacBook Air
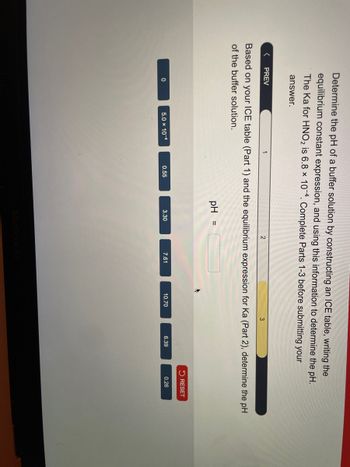
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the pH of a buffer solution by constructing an ICE table, writing the
equilibrium constant expression, and using this information to determine the pH.
The Ka for HNO2 is 6.8 x 104. Complete Parts 1-3 before submitting your
answer.
< PREV
1
2
3
Based on your ICE table (Part 1) and the equilibrium expression for Ka (Part 2), determine the pH
of the buffer solution.
pH =
RESET
0
5.0 × 10-4
0.55
3.30
7.61
10.70
6.39
0.26
MacBook Air
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- In our previous discussions, we discussed how phase changes (gas to liquid to solid, for example) can occur by manipulating the parameter of temperature. We defined temperature as the average kinetic energy of the particles, so when we raise or lower the temperature, we are adding or removing energy to the system, respectively. Gas Cool or compress Heat or reduce pressure Liquid Cool Heat Crystalline solid Based on your observations over the past two weeks, please explain why lowering the temperature can condense the helium gas into a liquid, a process by which the He atoms stick together?arrow_forwardBalance each chemical equation. H2(g)+N2(g)→NH3(g) Express your answer as a chemical equation. Identify all of the phases in your answer.arrow_forward23arrow_forward
- Please don't provide handwritten solution...arrow_forwardFour liquids are described in the table below. Use the second column of the table to explain the order of their freezing points, and the third column to explain the order of their boiling points. For example, select '1' in the second column next to the liquid with the lowest freezing point. Select '2' in the second column next to the liquid with the next higher freezing point, and so on. In the third column, select '1' next to the liquid with the lowest boiling point, '2' next to the liquid with the next higher boiling point, and so on. Note: the density of water is 1.00 g/mL. solution freezing point boiling point 2.7 g of potassium sulfate (K2SO4) dissolved in 100. mL of water (choose one) (choose one) 2.7 g of nitric acid (HNO3) dissolved in 100. mL of water (choose one) |(choose one) - 2.7 g of glycerin (C3H8O3) dissolved in 100. mL of water (choose one) (choose one) v 100. mL of pure water (choose one) |(choose one) v ?arrow_forwardFour liquids are described in the table below. Use the second column of the table to explain the order of their freezing points, and the third column to explain the order of their boiling points. For example, select '1' in the second column next to the liquid with the lowest freezing point. Select '2' in the second column next to the liquid with the next higher freezing point, and so on. In the third column, select '1' next to the liquid with the lowest boiling point, '2' next to the liquid with the next higher boiling point, and so on. Note: the density of water is 1.00 g/mL. solution freezing point boiling point (choose one) ↑ 6.7 g of potassium iodide (KI) dissolved in 350. mL of water (choose one) O (choose one) (choose one) ↑ 6.7 g of hydroiodic acid (HI) dissolved in 350. mL of water 6.7 g of sucrose (C₁2H22011) dissolved in 350. mL of water (choose one) (choose one) î 350. mL of pure water (choose one) ✪ (choose one) × Ś ?arrow_forward
- Four liquids are described in the table below. Use the second column of the table to explain the order of their freezing points, and the third column to explain the order of their boiling points. For example, select '1' in the second column next to the liquid with the lowest freezing point. Select '2' in the second column next to the liquid with the next higher freezing point, and so on. In the third column, select '1' next to the liquid with the lowest boiling point, '2' next to the liquid with the next higher boiling point, and so on. Note: the density of water is 1.00 g/mL. solution freezing point boiling point 7.7 g of hydroiodic acid (HI) dissolved in 500. mL of water (choose one) O (choose one) 7.7 g of potassium hydroxide (KOH) dissolved in 500. mL of water (choose one) C (choose one) O 7.7 g of calcium chloride (CaCl2) dissolved in 500. mL of water (choose one) C (choose one) O 500. mL of pure water (choose one) (choose one)arrow_forwardFour liquids are described in the table below. Use the second column of the table to explain the order of their freezing points, and the third column to explain the order of their boiling points. For example, select '1' in the second column next to the liquid with the lowest freezing point. Select '2' in the second column next to the liquid with the next higher freezing point, and so on. In the third column, select '1' next to the liquid with the lowest boiling point, '2' next to the liquid with the next higher boiling point, and so on. Note: the density of water is 1.00 g/mL. solution 10. g of glycerin (C3H8O3) dissolved in 100. mL of water 10. g of hydrochloric acid (HCI) dissolved in 100. mL of water 10. g of potassium hydroxide (KOH) dissolved in 100. mL of water 100. mL of pure water freezing point (choose one) (choose one) (choose one) (choose one) X boiling point (choose one) O (choose one) (choose one) 0 (choose one) O 5arrow_forwardSteam at a temperature of 113.0°C with a mass of 24.00 grams is cooled until it reaches a final temperature of 34.0°C. Use the provided data and the heating curve to calculate the amount of energy (in kJ) is required to complete this process. If the process is exothermic be sure to include the appropriate sign. Hint: Condensation is exothermic. How does that affect AH? 130 A Gas 100 IGas - Liquid ! Liquid Liquid- ! Solid Solid erature H20 (°C)arrow_forward
- Capillary action is the process of water moving up plants, against gravity. Two different properties of liquids work together to allow this process. Please list and define one of these properties. B IUarrow_forwardSearch on google ptable.com… and do question 6a tell me the property and compound 1 and 2 please do it for me don’t return the question ?arrow_forwardFour liquids are described in the table below. Use the second column of the table to explain the order of their freezing points, and the third column to explain the order of their boiling points. For example, select '1' in the second column next to the liquid with the lowest freezing point. Select '2' in the second column next to the liquid with the next higher freezing point, and so on. In the third column, select '1' next to the liquid with the lowest boiling point, '2' next to the liquid with the next higher boiling point, and so on. Note: the density of water is 1.00 g/mL. solution freezing point boiling point 7.3 g of glycerin (C3H8O3) dissolved in 100. mL of water (choose one) (choose one) 7.3 g of glucose (C6H1206) dissolved in 100. mL of water (choose one) (choose one) 7.3 g of potassium iodide (KI) dissolved in 100. mL of water (choose one) (choose one) 100. mL of pure water (choose one) (choose one)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY