
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Determine the mass of solid NaCH:CO0 that must be dissolved in an
existing 500.0 mL solution of 0.200 M CH:COOH to form a buffer with a
pH equal to 5.00. The value of Ka for CH;COOH is 1.8 x 10-5.
1
NEXT >
Let x represent the original concentration of CH3CO0 in the water. Based on the given
values, set up the ICE table in order to determine the unknown.
CH:COOH(аq) +
H2O(I)
H3O*(aq)
+ CH:COO (aq)
Initial (M)
Change (M)
Equilibrium
(M)
2 RESET
1L
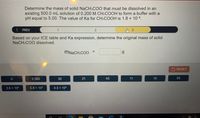
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the mass of solid NaCH:COO that must be dissolved in an
existing 500.0 mL solution of 0.200 M CH:COOH to form a buffer with a
pH equal to 5.00. The value of Ka for CH:COOH is 1.8 x 10-5.
< PREV
1
の3
Based on your ICE table and Ka expression, determine the original mass of solid
NaCH:COO dissolved.
%3D
MNACH.COO =
5 RESET
0.360
30
21
43
11
15
59
3.6 x 103
5.9 x 105
4.3 x 105
C
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the resulting pH when 0.003 mol of solid NaOH is added to a 100.0 mL buffer containing 0.13 M HClO and 0.37 M NaClO. The value of Ka for HClO is 2.9 × 10⁻⁸. Determine the moles of the ractant and product after the reaction of the acid and base. (Similar to ICE format but is instead Before (mol), Change (mol), and After (mol) Determine the ICE table for HClO (aq) + H2O - H3O+ + ClO- (aq) Fill in Ka= ? = 2.9 * 10-8 Calculate pHarrow_forward1) You have 10 mL of a buffer that is 0.1 M acetic acid and 0.1 M sodium acetate. How many mLs of 0.025 M HCl will need to be added in order to reach a pH of 4.65? (Kafor acetic acid is 1.82 x 10-5)arrow_forwardA student needs to prepare a buffer made from HNO2 and NaNO2 with pH 3.115. If K, for HNO2 is 4.50 x 10 what ratio of [HNO₂] [NO₂-] is required? [HNO₂] [NO₂-]arrow_forward
- In the titration of 25.00 mL of 0.150 M HCl with 0.250 M NaOH a) the initial pH; b) pH after 50.0% completion of neutralization; c) pH after 100.0% completion of neutralization; d) Calculate the pH when 1 mL more NaOH is added after the equivalence point.arrow_forwardDetermine the pH of a solution by constructing a BCA table, constructing an ICE table, writing the equilibrium constant expression, and using this information to determine the pH. The value of Ka for HA is 3.2 x 10⁹. Complete Parts 1-4 before submitting your answer. NEXT > 0.0015 mol of solid Ba(OH), is added to a 0.350 L buffer containing 0.110 M weak acid, HA, and 0.220 M of its conjugate base, A. Fill in the table with the appropriate value for each involved species to determine the moles of reactant and product after the reaction of the acid and base. You can ignore the amount of water in the reaction. H₂O(1) + A (aq) Before (mol) Change (mol) After (mol) HA(aq) + OH (aq) -arrow_forward7arrow_forward
- 24. How many moles of NH,Br must be added to 2 L of 0.1 M NH,OH to form a buffer whose pH is 9.00? (K, of NH,OH = 1.76 x 0*)arrow_forwardA buffer solution with a pH of...arrow_forwardDetermine the resulting pH when 0.040 mol of solid NaOH is added to a 200.0 mL buffer containing 0.100 mol C6H5NH3CI and 0.500 M C6H5NH2. The value of Kb for C6H5NH2 is 4.3 x 101°. 1 2 3 4 NEXT Use the table below to determine the moles of reactant and product after the reaction of the acid and base. You can ignore the amount of liquid water in the reaction. C6H;NH3*(aq) Он (aq) H20(1) C6H;NH2(aq) + + Before (mol) Change (mol) After (mol) 5 RESET 0.040 -0.040 0.500 -0.500 0.100 -0.100 +x 0.040 + x 0.040 - x 0.100 + x 0.100 - x 0.060 -0.060 -x 0.140 -0.140 0.020 -0.020arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY