
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
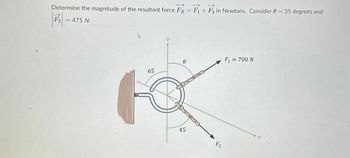
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR = F1+F2 in Newtons. Consider 0 = 35 degrees and
F2
475 N.
65
0
45
F2
F₁ = 700 N
u
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5. The body on the 30° incline is acted upon by force P inclined at 20° with the horizontal. If P is resolved into components parallel and perpendicular to incline and the value of parallel component is 1800N, compute the value of the perpendicular component of P. P 20 30 Figure P-009arrow_forward1. Consider the forces acting on these three changes and list in order of the magnitude of the force starting with the smallest. A --- r B -4 +q +q Find FA Find Fa Find Fe List in order of the magnitudearrow_forwardA student of weight 670 N rides a steadily rotating Ferris wheel (the student sits upright). At the highest point, the magnitude of the normal force ?→?�→� on the student from the seat is 597 N. (a) What is the magnitude of ?→?�→� at the lowest point? If the wheel's speed is doubled, what is the magnitude FN at the (b) highest and (c) lowest point?arrow_forward
- If we know the direction of the normal force, then we know the direction of the frictional force. True or false? And why?arrow_forwardQ4: Two identical metal spheres are placed 0.2m apart, q1= 9µC and 92= -3uC as shown in the figure. (a) What is the force on each of ue spheres? (b) If the two spheres are brought together and touched and then returned to their original positions, what will be the force on each sphere? F1 Fn Fu +92arrow_forwardL A B A m m q 9 Two point charges (each of mass m and charge q),A and B, are suspended by very thin threads as shown above. a. Which of the diagrams below represents the free body diagram for object A (Here is FBA is the electrostatic force exerted by object B on object A, WA is the weight of object A, TA is the string tension, and N is the normal force)? O O O W FBA YA ap FBA WA TA TA O None of the above. y I 1. FBA Xarrow_forward
- 25) In a movie stunt, a car leaves an inclined ramp with a speed of 32.0 m/s. The car's mass is 1050 kg and its velocity is 29.0 m/s at the peak of its flight. How high in the air (relative to the location where it left the ramp) is the car at the peak of its flight? Assume that there is no air problem can be done using Kinematics too. g although the v = 32 m/s h = ? m = 1050 kg 0.01 lo ribar a and boa pugi oq anoiudover '01arrow_forwardPRINTER VERSION 4 ВАСК NEXT Chapter 11, Problem 026 Your answer is partially correct. Try again. At the instant of the figure, a 3.00 kg particle P has a position vector r of magnitude 4.10 m and angle 0, = 41.0° and a velocity vector v of magnitude 7.60 m/s and angle e, = 30.0°. Force F, of magnitude 2.10 N and angle 03 = 30.0° acts on P. All three vectors lie in the xy plane. About the origin, what are the magnitude of (a) the angular momentum of the particle and (b) the torque acting on the particle? (a) Number Units kg-m^2/sv (b) Number UnitsTN-m Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Workarrow_forwardDe 600 N 4 m 900 N 4 m A -6m 22- forces in member [ED] : F(ED) forces in member [DC]: F(DC) forces in member [BC] : F(BC) Which following one is TRUE? O A) F(EC)=1500 N O B) F(DC).cos37 = F(BC) O F(DC).sin37 = F(ED) O D) F(ED).sin53- F(DC) O E) F(ED).cos53 = F(DC)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON