
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:PRINTER VERSION
4 ВАСК
NEXT
Chapter 11, Problem 026
Your answer is partially correct. Try again.
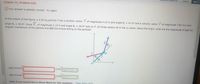
At the instant of the figure, a 3.00 kg particle P has a position vector r of magnitude 4.10 m and angle 0, = 41.0° and a velocity vector v of magnitude 7.60 m/s and
angle e, = 30.0°. Force F, of magnitude 2.10 N and angle 03 = 30.0° acts on P. All three vectors lie in the xy plane. About the origin, what are the magnitude of (a) the
angular momentum of the particle and (b) the torque acting on the particle?
(a) Number
Units
kg-m^2/sv
(b) Number
UnitsTN-m
Click if you would like to Show Work for this question:
Open Show Work
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Three electrons are located at the vertices of an equilateral triangle with side lengths of d. The electrons at the base of the triangle are stuck in place but the electron at the top is free to move. The mass of an electron is 9.109 *10-31 kg. a) Find the distance d such that the electron located at the top or apex of the triangle is balanced by the repulsive forces of the electrons below it and the gravitational force pulling it down.arrow_forwardA glider of mass 0.275kg is placed at rest on an air track that has an angle of inclination of 10°. The height of the glider above the table is 30cm. The glider is released traveling 1.15m down along the track. When the glider is at 10cm above the height of the table, the velocity is 1.5m/s. What is the frictional force acting on the glider?arrow_forwardA simple pendulum consists of a 2.0 kg bob attached to a light string 3.0 m in length. While hanging at rest with the string vertical, the bob is struck sharply giving it a horizontal speed of 4.5 m/s. When the string makes an angle of 30 with the vertical find a) its speed and the tension in the string. b) What is the angle of the string with the vertical when it reaches its highest point?arrow_forward
- The diagram shows the all of the forces acting on a body of mass 3.13 kg. The three forces have magnitudes F1 = 59.2 N, F2 = 27.7 N, and F3 = 74.4 N, with directions as indicted in the diagram, where θ = 55.8 degrees and φ = 21.4 degrees. The dashed lines are parallel to the x and y axes. At t = 0, the body is moving at a speed of 5.29 m/s in the positive x direction. 1.)What are the x and y components of the acceleration in m/s2?arrow_forwardA cart of mass m, = 6.7 kg is on an inclined ramp (ø = 34.1 degrees). It is attached to a string of negligible mass that goes over an ideal pulley. The other end of the string is attached to another block of mass m, = 11.9 kg, as shown below. The wheels on the cart are good enough that friction between the cart and the ramp is negligible. If the blocks are given an initial speed of v, = 9.1 m/s (with m, moving down the plane), what is the common magnitude of the acceleration of the blocks? (in m/s^2)arrow_forwardA biker is riding his Yamaha Raptor 700r (atv) on an upward hill in the middle of a desert in dubai. The hill has a slope of theta = 120 degrees. The mass of the atv and biker combined is 260 kg and the static friction coefficient between is .43. Determine the minimum speed of the atv to be able to drive over the hill.arrow_forward
- A object of mass 3.00 kg is subject to a force Fx that varies with position as in the figure below. A coordinate plane has a horizontal axis labeled x (m) and a vertical axis labeled Fx (N). There are three line segments. The first segment runs from the origin to (6,2). The second segment runs from (6,2) to (11,2). The third segment runs from (11,2) to (17,0). (a) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 0 to x = 6.00 m. J(b) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 6.00 m to x = 11.0 m. J(c) Find the work done by the force on the object as it moves from x = 11.0 m to x = 17.0 m. J(d) If the object has a speed of 0.450 m/s at x = 0, find its speed at x = 6.00 m and its speed at x = 17.0 m. speed at x = 6.00 m m/s speed at x = 17.0 m m/sarrow_forwardProblem 5: Consider the vectors, D = (6.00î - 8.00j) m, B = (-8.00î + 3.00j) m, and A = (26.0î + 19.0j) m.arrow_forwardThe ball launcher in a pinball machine has a spring that has a force constant of 50.0 N/m. The surface on which the ball moves is inclined 10.0° with respect to the horizontal. The spring is initially compressed 5.00 cm. Find the distance along the incline that the ball will go to (from the mean position of the spring), if the friction force = 0.1N. Mass of the ball = 20 gram.arrow_forward
- A big olive (m = 0.12 kg) lies at the origin of an xy coordinate system, and a big Brazil nut (M = 0.62 kg) lies at the point ( 1.1, 2.1) m. At t = 0, a force F 0 = :(3.8î + 2.13) N begins to act on the olive, and a force É N = (- 3.9î – 2.0j) N begins to act on the nut. What is the (a) x and (b) y displacement of the center of mass of the olive-nut system at t =3.5 s, with respect to its position at t = 0? (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Unitsarrow_forwardA man is attempting to lift a crate with a double-pulley system, as shown. A single rope is routed from the ceiling, through the two pulleys, and to where the man pulls on it. The crate has mass m2 = 68 kg, and the man has m1 = 75 kg. He pulls downward on the rope with a force of magnitude F = 599 N. The pulleys are both massless and frictionless, and the rope is ideal. What is the magnitude, in newtons, of the tension force, T?What is the acceleration, in meters per squared second, of the crate?arrow_forwardThe figure shows a block of mass m resting on a 20o slope. The block has coefficients of friction us=0.64 and uk=0.54 with the surface of the slope. It is connected using a very light string over an ideal pulley to a hanging block of mass 2.0 kg. The string above the slope pulls parallel to the surface. What is the minimum mass m so the system will remain at rest when it is released from rest?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON