
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
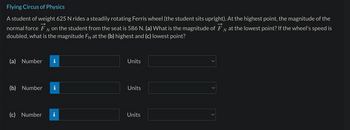
Transcribed Image Text:Flying Circus of Physics
A student of weight 625 N rides a steadily rotating Ferris wheel (the student sits upright). At the highest point, the magnitude of the
normal force FN on the student from the seat is 586 N. (a) What is the magnitude of FN at the lowest point? If the wheel's speed is
doubled, what is the magnitude FN at the (b) highest and (c) lowest point?
(a) Number
(b) Number
(c) Number
I
M.
Units
Units
Units
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An object with a mass of 14 kg is at rest on a frictionless surface. The following forces are applied simultaneously to the object: 97.4 N at 123° 53.4 N at –136° • 80.8 N at 178° •50.9 N at 157° 117.1 N at –99° (a) What is the magnitude of the acceleration? (b) What is the direction that the object will be moving?arrow_forwardA student of weight 651 N rides a steadily rotating Ferris wheel (the student sits upright). At the highest point, the magnitude of the normal force FN on the student from the seat is 589 N. (a) What is the magnitude of FN at the lowest point? If the wheel's speed is doubled, what is the magnitude FN at the (b) highest and (c) lowest point? (a) Number Units (b) Number Units (c) Number Unitsarrow_forwardq3arrow_forward
- A particle with mass m = 10 mg travels from the origin with initial velocity = 50 through a S uniform force field ♬ = (1002 + 3007) m.N. The particle impacts a vertical screen located at a = = 10 cm. Determine the y-coordinate of the impact location, and the speed of the particle at impact. Yimpact Vimpact = cm m m Sarrow_forwardParticles q1 = -53.0 µC, q2 = +105 µC, and q3 = -88.0 µC are in a line. Particles q1 and q2 are separated by 0.50 m and particles q2 and q3 are separated by 0.95 m. What is the net force on particle q3? Remember: Negative forces (-F) will point Left Positive forces (+F) will point Right -53.0 μ C +105 uC -88.0 µC 91 + 42 q3 E 0.50 m 0.95 m Enterarrow_forwardA 230-kg object and a 530-kg object are separated by 3.90 m. (a) Find the magnitude of the net gravitational force exerted by these objects on a 65.0-kg object placed midway between them. N (b) At what position (other than an infinitely remote one) can the 65.0-kg object be placed so as to experience a net force of zero from the other two objects? m from the 530 kg mass toward the 230 kg massarrow_forward
- pls helparrow_forwardNEXT Chapter 04, Problem 032 Chalkboard Video A spacecraft is on a journey to the moon. At what point, as measured from the center of the earth, does the gravitational force exerted on the spacecraft by the earth balance that exerted by the moon? This point lies on a line between the centers of the earth and the moon. The distance between the earth and the moon is 3.85 × 108 m, and the mass of the earth is 81.4 times as great as that of the moon. moon m earth emarrow_forwardYou and your family take a road trip on a long holiday weekend. In a certain section of the trip where the road is particularly uneven, the car goes over a bump that is curved downward with a radius of 16.0 m. See diagram below. The mass of the car and its passengers is 1200 kg. (a) When the car is at the highest point of the bump its speed is 7.05 m/s. Determine the magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the road on the car at this highest point. magnitude direction N |---Select-- v (b) If the speed at the highest point is above a certain maximum value the car will lose contact with the road. Calculate this maximum speed. m/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON