
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
9/12
Determine the critical values for these test of a population standard deviation.
a. A right tail test with 13° of freedom at the standard deviation = 0.01 level of significance.
b. A left tailed test for a
c. A two tailed test for a sample of size n=31 at the standard deviation = 0.1 level of significance.
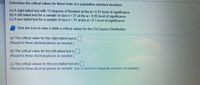
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the critical values for these tests of a population standard deviation.
(a) A right-tailed test with 13 degrees of freedom at the a= 0.01 level of significance
(b)A left-tailed test for a sample of size n= 27 at the a 0.05 level of significance
(c)A two-tailed test for a sample of size n= 31 at the a = 0.1 level of significance
E Click the icon to view a table a critical values for the Chi-Square Distribution.
(a) The critical value for this right-tailed test is |
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
(b) The critical value for this left-tailed test is
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
(c) The critical values for this two-tailed test are
(Round to three decimal places as needed Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)

Transcribed Image Text:Chi-Square (x) Distribution
Area to the Right of Critical Value
Degrees of
Freedom
0.995
0.99
0.975
0.95
0.90
0,10
0.05
0.025
0.01
0.005
7.879
10.597
3.841
5.991
7.815
9.488
11.070
5.024
7.378
9.348
11.143
12.833
6.635
9.210
1
2,
3.
4
0.010
0.072
0.207
0.412
0.020
0.115
0,297
0.554
0.001
0.051
0.216
0.484
0.831
0.004
0.103
0.352
0.711
1.145
0.016
0.211
0.584
1.064
1.610
2.706
4.605
6.251
7.779
9,236
11.345
13.277
15.086
12.838
14.860
16.750
14.449
16.013
17.535
19.023
20.483
18.548
20.278
21.955
23.589
25.188
16.812
9.
7.
8.
6.
10
0676
0.989
1.344
1.735
2.156
0.872
1.239
1.646
2.088
2.558
1.237
1.690
2.180
2.700
3.247
1635
2167
2.733
3,325
3.940
2.204
2.833
B.490
4.168
4.865
10.645
12.017
13.362
14.684
15.987
12.592
14.067
15.507
16.919
18.307
18.475
20.090
21.666
23.209
19.675
21.026
22.362
24.725
26.217
27.688
26.757
28.300
29.819
21.920
4.575
5.226
5.892
5.578
6.304
7042
17.275
18.549
19.812
3,816
11
12
13
2.603
3.074
3.565
3.053
3.571
4.107
4.404
5.009
23.337
24.736
Print
Done
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The mean pulse rate for adult males is approximately 61.4 beats per minute. In a sample of 27 overweight males, the mean pulse rate was 62.1 beats per minute with a standard deviation of 4.19 beats per minute. Test at a = 0.10 whether these findings suggest that the mean pulse rate for all such overweight males is significantly greater than 61.4. You obtain a sample of size 27 with a mean of 62.1 and a standard deviation of 4.19. You believe that the population is normally distributed. (a). The null and alternative hypotheses are O Ho: ữ = 62.1 Ha:ữ > 62.1 Ho:µ = 61.4 Ha: µ > 61.4 Ο H0: μ = 61.4 На:р 62.1 Part 2 of 4 (b). The test statistic is (use 4 decimal places)arrow_forwardData on the weights (lb) of the contents of cans of diet soda versus the contents of cans of the regular version of the soda is summarized to the right. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations, and do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. Use a 0.01 significance level for both parts. a. Test the claim that the contents of cans of diet soda have weights with a mean that is less than the mean for the regular soda. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? OA. Ho: H₁ H₂ H₁: Hy #4₂ OC, Hoi ky tuy H₁: Hy O L P H command n X S Time Remaining: 01:13:11 V : • Diet H₁ 30 0.79861 lb 0.00445 lb ; x { [ option ? I Regular H₂ 30 0.80936 lb 0.00742 lb Next deletearrow_forwardPart Variability is critical in the manufacturing of the ball bearings. Large variances in the size of the ball bearings cause bearing failure and rapid wear out. Production standards call for a maximum variance of .0001 when the bearing sizes are measured in inches. A sample of 15 bearings shows a sample standard deviation of .014. a. Compute the 90% confidence interval estimate of the variance of the ball bearings in the population. b. Use a= 0.10 to determine whether the sample indicates that the maximum acceptable variance is being exceeded. Use critical value approach. ( Note: You must state null and alternative hypotheses, compute the test statistic, Report the critical Value, and draw a conclusion.arrow_forward
- The average salary for American college graduates is $48,600. You suspect that the average is less for graduates from your college. The 49 randomly selected graduates from your college had an average salary of $46,486 and a standard deviation of $9,200. What can be concluded at the αα = 0.01 level of significance? For this study, we should use Select an answer t-test for a population mean z-test for a population proportion The null and alternative hypotheses would be: H0:H0: ? p μ Select an answer = ≠ > < H1:H1: ? μ p Select an answer > ≠ = < The test statistic ? z t = (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) The p-value = (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) The p-value is ? > ≤ αα Based on this, we should Select an answer reject accept fail to reject the null hypothesis. Thus, the final conclusion is that .arrow_forwardThe average salary for American college graduates is $45,100. You suspect that the average is less for graduates from your college. The 50 randomly selected graduates from your college had an average salary of $42,788 and a standard deviation of $5,940. What can be concluded at the αα = 0.05 level of significance? For this study, we should use Select an answer t-test for a population mean z-test for a population proportion The null and alternative hypotheses would be: H0:H0: ? μ p Select an answer > < = ≠ H1:H1: ? p μ Select an answer ≠ > = < The test statistic ? z t = (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) The p-value = (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) The p-value is ? > ≤ αα Based on this, we should Select an answer fail to reject reject accept the null hypothesis. Thus, the final conclusion is that ... The data suggest that the population mean is not significantly less than 45,100 at αα = 0.05, so there is…arrow_forwardA researcher wants to measure average cardiovascular health of university students and compare those scores to the average scores in the general population. Assuming that population variance is known, what statistical test is most appropriate for this study? independent-samples t-test single-sample t-test z-test for sample mean related-samples t-testarrow_forward
- A sample of 42 observations is selected from one population with a population standard deviation of 4.5. The sample mean is 100.5. A sample of 56 observations is selected from a second population with a population standard deviation of 3.8. The sample mean is 98.5. Conduct the following test of hypothesis using the 0.10 significance level. H₂ H₁ H₂ H₁ H₁ H₂ a. Is this a one-tailed or a two-tailed test? O One-tailed test O Two-tailed test b. State the decision rule. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) The decision rule is to reject H0 if z is the interval (arrow_forwardData on the weights (lb) of the contents of cans of diet soda versus the contents of cans of the regular version of the soda is summarized to the right. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations, and do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. Use a 0.05 significance level for both parts. a. Test the claim that the contents of cans of diet soda have weights with a mean that is less than the mean for the regular soda. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? OA. Ho: H₁ H₂ H₁: H₁ H₂ O C. Ho: H#2 H₁ H₁arrow_forwardSystolic blood pressure levels above 120 mm Hg are considered to be high. For the 100 systolic blood pressure levels listed in the accompanying data set, the mean is 128.86000 mm Hg and the standard deviation is 15.28254 mm Hg. Assume that a simple random sample has been selected. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the sample is from a population with a mean greater than 120 mm Hg.LOADING... Click the icon to view the data set of systolic blood pressure levels. the attachement is listed below. and the systolic blood pressure data is listed below Body and exam measurements are from 100 subjects. SYSTOLIC is systolic blood pressure (mm…arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman