
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
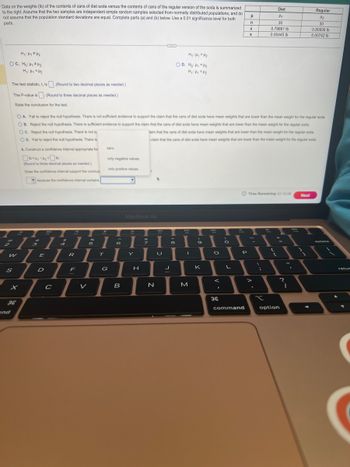
Transcribed Image Text:Data on the weights (lb) of the contents of cans of diet soda versus the contents of cans of the regular version of the soda is summarized
to the right. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations, and do
not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. Use a 0.01 significance level for both
parts.
My: Hy FH₂
OC. Ho: Hy #4₂
H₁: Hy <H₂
The test statistic, t, is (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
The P-value is. (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
State the conclusion for the test.
CD
S
and
x
H
I
7
3
1 1
R
E
OA. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that the cans of diet soda have mean weights that are lower than the mean weight for the regular soda.
OB. Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that the cans of diet soda have mean weights that are lower than the mean weight for the regular soda.
OC. Reject the null hypothesis. There is not su
laim that the cans of diet soda have mean weights that are lower than the mean weight for the regular soda.
claim that the cans of diet soda have mean weights that are lower than the mean weight for the regular soda.
OD. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is
b. Construct a confidence interval appropriate for
10<44-1₂-16
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Does the confidence interval support the conclusi
because the confidence interval contains
D
C
$5
F
96
5
zero.
only negative values.
G
only positive values.
I
T
6
B
MacBook Air
I
H
H₁ H₁ H₂
OD. Ho: ₁ = ₂
H₁: Hy <H₂
N
8
U
H
J
I
M
(
9
K
O
<
F
H
2
O
L
FV0
P
H
command
n
X
S
Diet
H₁
30
0.79861 lb
0.00445 lb
Time Remaining: 01:12:46
P
x
(
+
?
option
I
Regular
H₂
30
0.80936 lb
0.00742 lb
Next
retur
(
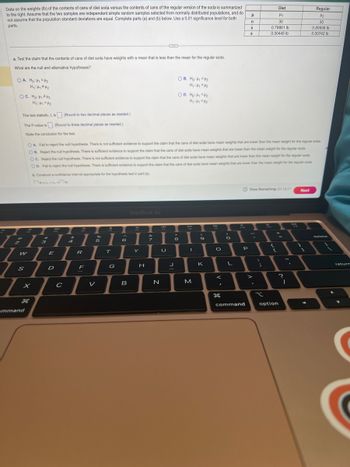
Transcribed Image Text:Data on the weights (lb) of the contents of cans of diet soda versus the contents of cans of the regular version of the soda is summarized
to the right. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations, and do
not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. Use a 0.01 significance level for both
parts.
a. Test the claim that the contents of cans of diet soda have weights with a mean that is less than the mean for the regular soda.
What are the null and alternative hypotheses?
OA. Ho: H₁ H₂
H₁: Hy #4₂
OC, Hoi ky tuy
H₁: Hy <H₂
The test statistic, t, is. (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
The P-value is
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
State the conclusion for the test.
W
Z I
7
T
S
x
H
emmand
3
E
290
D
OA. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that the cans of diet soda have mean weights that are lower than the mean weight for the regular soda.
OB. Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that the cans of diet soda have mean weights that are lower than the mean weight for the regular soda.
OC. Reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that the cans of diet soda have mean weights that are lower than the mean weight for the regular soda.
OD. Fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that the cans of diet soda have mean weights that are lower than the mean weight for the regular soda
b. Construct a confidence interval appropriate for the hypothesis test in part (a).
с
I
R
4
F
96
%
5
V
T
G
6
B
MacBook Air
Y
H
&
7
N
OB. Ho: ₁ ₂
H₂: Hy ₂
J
OD. Ho: H₁ H₂
H₁: H₁ H₂
o
8
DI
I
(
9
K
O
1
H
>
O
L
P
H
command
n
X
S
Time Remaining: 01:13:11
V
:
•
Diet
H₁
30
0.79861 lb
0.00445 lb
;
x
{
[
option
?
I
Regular
H₂
30
0.80936 lb
0.00742 lb
Next
delete
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Given in the table are the BMI statistics for random samples of men and women. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations, and do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. Use a 0.05 significance level for both parts. Male BMI Female BMI u u1 u2 n 46 46 x 28. 4773 26. 3875 s 7. 618885 5. 488392arrow_forwardUse the data below taken from a random sample of adults, and the a = 0.01 level of significance, to determine whether or not there is a significant, positive linear correlation between the length of a person's arm and the amount of money they contribute annually to charity. Which would be correct hypotheses for this test? Sample Data: Ho: p= 0; H₁: p=0 Ho p= 0; H₁: p > 0 Ho : μ = 0; H1 :μ > 0 Ho: p = 0; H₁: p<0 Arm length (cm) Charitable Giving ($) 199 368.6 202 348.74 209 358.41 200 356.72 199 350.71 202 213 193 198 207 208 195 .627 What is the Pearson Correlation Coefficient for the sample data (n)? (Round to three decimals) .029 349.7 374.59 345.04 343.88 358.67 349.41 343.95 Give the P-value: (Round to three decimals) Xarrow_forwardA physical therapist wanted to know whether the mean step pulse of men was less than the mean step pulse of women. She randomly selected 54 men and 70 women to participate in the study. Each subject was required to step up and down a 6-inch platform. The pulse of each subject was then recorded. The following results were obtained. Two sample T for Men vs Women N Mean StDev SE Mean Men Women 98% CI for mu Men - mu Women (- 12.20, - 1.00) T-Test mu Men = mu Women (vs H2 O C. Ho: H1 = H2; Ha: H1 #H2 (b) Identify the P-value and state the researcher's conclusion if the level of significance was a = 0.01. What is the P-value? P-value =arrow_forward
- I need help solving part a and b of the following question attached.arrow_forwardListed below are systolic blood pressure measurements (mm Hg) taken from the right and left arms of the same woman. Assume that the paired sample data is a simple random sample and that the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Use a 0.10 significance level to test for a difference between the measurements from the two arms. What can be concluded? Right arm 142 132 127 137 130 D Left arm 174 172 184 137 147 O A. Ho: Hd =0 B. Ho: Ha 0 H1: Hd =0 %3D OC. Ho: Hd = 0 H1: Hd 0 Identify the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) t= Identify the P-value. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What is the conclusion based on the hypothesis test?arrow_forwardOur environment is very sensitive to the amount of ozone in the upper atmosphere. The level of ozone normally found is 7.97.9 parts/million (ppm). A researcher believes that the current ozone level is at an excess level. The mean of 2424 samples is 8.18.1 ppm with a variance of 0.250.25. Does the data support the claim at the 0.10.1 level? Assume the population distribution is approximately normal. Step 3 of 5: Specify if the test is one-tailed or two-tailed.arrow_forward
- A researcher takes sample temperatures in Fahrenheit of 17 days from New York City and 18 days from Phoenix. Test the claim that the mean temperature in New York City is different from the mean temperature in Phoenix. Use a significance level of α=0.05. Assume the populations are approximately normally distributed with unequal variances. You obtain the following two samples of data. New York City Phoenix 99 94.2 95.5 72 93.2 86.8 102 122.1 85.4 114.4 80 94.7 86.4 89.7 75.4 104.7 79.5 77.6 83.4 106.8 64.3 98.6 65.5 91.5 87.7 82 104 97.7 74.3 64.9 59.5 82 82.8 72 116.2 The Hypotheses for this problem are: H0: μ1 = μ2 H1: μ1μ2 Find the p-value. Round answer to 4 decimal places. Make sure you put the 0 in front of the decimal. p-value =arrow_forwardGiven in the table are the BMI statistics for random samples of men and women. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations, and do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. Use a 0.05 significance level for both parts. Male BMI Female BMI μ μ1 μ2 n 41 41 x 28.3981 26.4624 s 7.246507 5.820596 a. Test the claim that males and females have the same mean body mass index (BMI). What are the null and alternative hypotheses? A. H0: μ1=μ2 H1: μ1≠μ2 B. H0: μ1≥μ2 H1: μ1<μ2 C. H0: μ1≠μ2 H1: μ1<μ2 D. H0: μ1=μ2 H1: μ1>μ2 The test statistic, t, is ______.(Round to two decimal places as needed.) The P-value is _____.(Round to three decimal places as needed.) State the conclusion for the test. A. Fail to reject the null…arrow_forwardI need the p value, please.arrow_forward
- Need sub part B answered onlyarrow_forwardChoose the appropriate statistical test. When computing, be sure to round each answer as indicated. A dentist wonders if depression affects ratings of tooth pain. In the general population, using a scale of 1-10 with higher values indicating more pain, the average pain rating for patients with toothaches is 6.8. A sample of 30 patients that show high levels of depression have an average pain rating of 7.1 (variance 0.8). What should the dentist determine? 1. Calculate the estimated standard error. (round to 3 decimals). [st.error] 2. What is thet-obtained? (round to 3 decimals). 3. What is the t-cv? (exact value) 4. What is your conclusion? Only type "Reject" or Retain"arrow_forwardCalculate the test statistic (t) and p-value.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman