
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
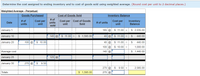
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using weighted average. (Round cost per unit to 2 decimal places.)
Weighted Average - Perpetual:
Goods Purchased
Cost of Goods Sold
Inventory Balance
# of
units
sold
# of
Cost per Cost of Goods
unit
Cost per
Cost per
Inventory
Balance
Date
# of units
units
unit
Sold
unit
January 1
185 @
$ 11.00 =
$ 2,035.00
January 10
145 @
$ 11.00 =
$ 1,595.00
40 @
$ 11.00 =
$
440.00
January 20
100 @
$ 10.00
40 @
$ 11.00 =
$
440.00
100 @
$ 10.00 =
1,000.00
Average cost
140 @
$ 1,440.00
January 25
125 @
January 30
270 @
$
9.50
270 @
$
9.50
2,565.00
Totals
$ 1,595.00
270 @
![Required information
Use the following information for the Exercises below.
[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]
Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product.
Activities
Units Acquired at Cost
185 units @ $11.00 = $2,035
Date
Units sold at Retail
Jan. 1 Beginning inventory
Jan. 10 Sales
145 units @ $20.00
Jan. 20 Purchase
100 units @ $10.00 =
1,000
Jan. 25 Sales
125 units @ $20.00
Jan. 30 Purchase
270 units @ $ 9.50 =
2,565
Totals
555 units
$5,600
270 units
The Company uses a perpetual inventory system. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 285 units, where
270 are from the January 30 purchase, 5 are from the January 20 purchase, and 10 are from beginning inventory.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/6a02b260-ff6c-4d5e-84bc-57397ca3f648/61781942-744f-4146-a229-4a19166badbb/dm9jppr_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:Required information
Use the following information for the Exercises below.
[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]
Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product.
Activities
Units Acquired at Cost
185 units @ $11.00 = $2,035
Date
Units sold at Retail
Jan. 1 Beginning inventory
Jan. 10 Sales
145 units @ $20.00
Jan. 20 Purchase
100 units @ $10.00 =
1,000
Jan. 25 Sales
125 units @ $20.00
Jan. 30 Purchase
270 units @ $ 9.50 =
2,565
Totals
555 units
$5,600
270 units
The Company uses a perpetual inventory system. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 285 units, where
270 are from the January 30 purchase, 5 are from the January 20 purchase, and 10 are from beginning inventory.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using FIFO. 2. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using Weighted Average. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using Weighted Average. (Round average cost per unit to 2 decimal places.) Average Cost Ending Inventory Date March 1 March 5 March 18 March 25 Total Cost of Goods Available for Sale Cost of Goods Available for Sale $5,000.00 100 400 $ 22,000.00 120 $ 7,200.00 200 $ 12,400.00 820 $59.80 $ 46,600.00 # of units Average Cost per unit # of units sold Cost of Goods Sold Average Cost per Unit 580 $ 59.80 240 Average Cost per unit $59.80 Ending Inventory $ 14,352arrow_forwardCont of pictures: Calculate gross profit rate under each of the following methods 1. LIFO 2. FIFO 3. Average-cost (Round answers to 1 decimal place, e.g. 51.2%)arrow_forwardDetermine the unit value that should be used for inventory costing following "lower-of-cost-or-market value". (Round answers to 2 decimal places, e.g. 52.75.) A B C D E F Cost $2.80 $2.44 $2.80 $2.62 $2.44 $2.44 Replacement cost 2.25 3.00 2.25 2.60 2.37 2.46 Net realizable value 2.95 2.95 2.95 2.41 2.50 2.50 Net realizable value less normal profit 2.70 2.75 2.85 2.25 2.30 2.30 Case A $ Case B $ Case C $ Case D Case E $ Case F $arrow_forward
- Given the following data, what is cost of goods sold as determined by the FIFO method? Sales Beginning inventory Purchases OA. $1,750 O B. $2,040 O C. $1,600 OD. $3,200 320 units 290 units at $5 per unit 88 units at $10 per unitarrow_forwardRiverbed Corp reports the following for the month of June. Date Explanation Units Unit Cost Total Cost June 1 Inventory 129 $ 5 $ 645 12 Purchases 344 6 2,064 23 Purchases 203 7 1,421 30 Inventory 234 Correct answer icon Your answer is correct. Calculate weighted-average unit cost. (Round answer to 3 decimal places, e.g. 5.125.) Weighted-average unit cost $ enter weighted-average unit cost in dollars rounded to 3 decimal places Compute the cost of the ending inventory and the cost of goods sold under FIFO, LIFO, and average-cost. (Round answers to 0 decimal places, e.g. 125.) FIFO LIFO Average-cost The cost of the ending inventory $ enter a dollar amount rounded to 0 decimal places $ enter a dollar amount rounded to 0 decimal places $ enter a dollar amount rounded to 0 decimal places The cost of goods sold $ enter a dollar amount rounded to 0…arrow_forwardUsing the specific identification method: Date Units purchased Cost per unit Ending inventory March 1 18 Xbox′s 360 $ 265 4 Xbox′s from March April 1 43 Xbox′s 360 240 15 Xbox′s from April May 1 68 Xbox′s 360 230 12 Xbox′s from May a. Calculate the ending inventory. b. Calculate the cost of goods sold.arrow_forward
- The following are the transactions for the month of July. Units Unit Cost Unit Selling Price July 1 Beginning Inventory 55 $ 10 July 13 Purchase 275 11 July 25 Sold (100 ) $ 14 July 31 Ending Inventory 230 Calculate cost of goods available for sale and ending inventory, then sales, cost of goods sold, and gross profit, under FIFO. Assume a periodic inventory system is used. How would i creat a FIFO periodic table?arrow_forwardSheffield Corp. markets CDs of numerous performing artists. At the beginning of March, Sheffield had in beginning inventory 2,500 CDs with a unit cost of $8. During March, Sheffield made the following purchases of CDs. March 5. March 13 1,900 @ 3,500 @ $9 $10 March 21 March 26 5,200 @ $11 $12 1,900 @ During March 11,500 units were sold. Sheffield uses a periodic inventory system.arrow_forwardConsider the following information: Units Cost per unit Total costs Goods in inventory at start of year 1,600 $1.92 $3,072 Purchases, quarter 1 800 $1.40 $1,120 Purchases, quarter 2 1,000 $1.60 $1,600 Purchases, quarter 3 1,200 $1.80 $2,160 Purchases, quarter 4 800 $2.00 $1,600 5,400 $9,552 Goods sold during the year: 3000 units Using the weighted-average-cost method, the value of ending inventory is:arrow_forward
- Subject: accountingarrow_forward[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Trey Monson starts a merchandising business on December 1 and enters into the following three inventory purchases. Monson uses a perpetual inventory system. Also, on December 15, Monson sells 15 units for $23 each. Purchases on December 7 Purchases on December 14 Purchases on December 21 10 units @ $9.00 cost 20 units @ $15.00 cost 15 units @ $17.00 cost Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory when costs are assigned based on the LIFO method. Perpetual LIFO: Goods purchased Cost of Goods Sold Cost of Goods # of Date Cost per Cost per Cost of ( unit # of units Available for units unit Sol Sale sold December 7 10 at $ 9.00 $ 90.00 20 at $ 15.00 $ 300.00 December 14 Total December 14 15 at $ 23.00 = December 15 Total December 15 15 at $ 17.00 $ 255.00 %3D December 21 Totalsarrow_forwardWildhorse Co. is a retailer operating in Calgary, Alberta. Wildhorse uses the perpetual inventory method. Assume that there are no credit transactions; all amounts are settled in cash. You are provided with the following information for Wildhorse for the month of January 2022. Date Description Quantity Unit Cost or Selling Price Dec. 31 Ending inventory 150 $ 20 Jan. 2 Purchase 100 21 Jan. 6 Sale 180 42 Jan. 9 Purchase 70 25 Jan. 10 Sale 60 42 Jan. 23 Purchase 112 26 Jan. 30 Sale 128 49arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education