
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
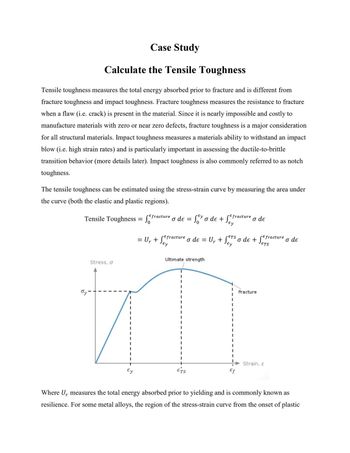
Transcribed Image Text:Case Study
Calculate the Tensile Toughness
Tensile toughness measures the total energy absorbed prior to fracture and is different from
fracture toughness and impact toughness. Fracture toughness measures the resistance to fracture
when a flaw (i.e. crack) is present in the material. Since it is nearly impossible and costly to
manufacture materials with zero or near zero defects, fracture toughness is a major consideration
for all structural materials. Impact toughness measures a materials ability to withstand an impact
blow (i.e. high strain rates) and is particularly important in assessing the ductile-to-brittle
transition behavior (more details later). Impact toughness is also commonly referred to as notch
toughness.
The tensile toughness can be estimated using the stress-strain curve by measuring the area under
the curve (both the elastic and plastic regions).
Tensile Toughness = f
Stress, σ
Ty-
Ey
Efracture
ETS
Ur
Ey
Efracture o de = U₁ + SETS o de + Sefracture o de
Ey
Ey
o de = Ser o de + Ser
= U₁ + Sey
Ur
Ey
Ultimate strength
ETS
Efracture
I
I
Ef
o de
Fracture
Strain, &
r
Where U measures the total energy absorbed prior to yielding and is commonly known as
resilience. For some metal alloys, the region of the stress-strain curve from the onset of plastic

Transcribed Image Text:deformation (₂) to the point at which necking begins (Ers) may be approximated by o = Ke”.
The constant values K and n vary by alloy and also depend on the condition of the material (e.g.
%CW, heat-treatment, etc. - more details later). The parameter n is often termed the strain-
hardening exponent and has a value less than one.
Find the tensile toughness for a metal alloy with modulus of elasticity of 103 GPa. Assume the
plastic deformation begins at a strain value of 0.007 and fracture occurs at a strain value of 0.60.
Assume also that fracture occurs at the point where necking begins and that the K and n values
are 1520 MPa and 0.15 respectively.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Kajarrow_forwardPlease show the complete solution. Thank youarrow_forwardO) In Figure show the fatigue curve for a metal. a) If a sample was taken from this material with diameter 5mm and tested on fatigue device under constant load 29,4 N far 125.2 mm from the specimen. Find the critical number of cycle in revolution ? b) Find the endurance limit for this material. 500 (ee 200 leo 4. 6 7 2. No.of cycles (logM) stress N/mmarrow_forward
- I need a step by step answer please how to solve this :)arrow_forwardFRACTURE TOUGHNESSarrow_forward(ii) The turbine blade root is found to contain a surface fatigue crack of 3.3 mm during a routine maintenance inspection. The major stop-start load cycle is experienced twice per day with a minimum stress of 34 MPa and a maximum stress of 195 MPa. The turbine blade has a KIC of 75 MPa√m. Fatigue crack growth rate data for this alloy is given by: the Paris law constant, A = 4.5 x 10-11 and the Paris law exponent, m = 3.8. How many more stop-starts would you recommend be used? Explain your reasoning. You can assume the shape factor Q = 1.2, K is in MPaNm and a (crack length) is in marrow_forward
- For a large plate, the geometry factor, f, is 1.03. Suppose a steel casting alloy has a critical fracture toughness of 78,886 psi*in1/2. The steel will be exposed to a stress of 40,295 psi during service. Calculate the minimum size of an edge crack that will grow. Repeat the calculation for Al2O3 with a fracture toughness of 1,600 psi*in1/2. How many times larger is the minimum size edge crack in the steel versus the alumina?arrow_forwardDetermine the tensile yield strength (0.2% offset) and the maximum strength of a metal alloy having the following tensile stress-strain diagram. Select one: The tensile yield strength Sy = 100 Mpa and the maximum strength Smax = 250 Mpa. The tensile yield strength Sy = 170 Mpa and the maximum strength Smax = 250 Mpa. The tensile yield strength Sy = 150 Mpa and the maximum strength Smax = 200 Mpa. The tensile yield strength Sy = 240 Mpa and the maximum strength Smax = 250 Mpa. The tensile yield strength Sy = 80 Mpa and the maximum strength Smax = 250 Mpa.arrow_forward1. A part made of Aluminum 6061-T6 has a yield strength = 400 MPa. For each stress state below, draw all 3 Mohr's circles, find the principal stresses, and calculate the safety factor against yield using both the distortion-energy (von Mises) and maximum shear stress (Tresca) criterions. (If relevant) A clearly labeled diagram (or diagrams) clearly pertaining to your analysis with a coordinate system and relevant labels. Final answer with appropriate units and significant figures. You can use the fprintf() command in MATLAB to format numerical results A 2-3 sentence reflection on your answer. Does it make sense? Why or why not? What are some implications?arrow_forward
- Estimate the linear relationship between the Ultimate Tensile Strength and HBN for the range of brass alloy shown in Figure 4b (ii).arrow_forwardWhat would be the compressive stress in MPa developed in the silica glass furnace tube constrained in the way illustrated in the figure if it were heated to 1000C?arrow_forwardNeed help on this Qarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY