
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Use the fatigue curves below to answer the following questions.:
Which curve(s) represent(s) a non-ferrous metal? (Select all that apply)
Group of answer choices
Curve B
Curve A
Curve C
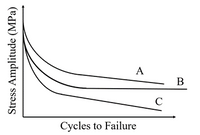
Transcribed Image Text:A
B
C
Cycles to Failure
Stress Amplitude (MPa)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider a dislocation condition as shown below. A) what is the strain state in the upper region and B) how would addition of small impurity atoms in the region indicated by "*"s change it? oooooo OOOOO DO Select one: a. Compressive, would reduce compressive strain O b. Tensile, would decrease tensile strain O C. Compressive, would increase compressive strain Od. Tensile, would increase tensile strain Oe. Shear, would increase compressive strainarrow_forwardPick the best soultion for the multiple choices. Modulus of resilience is: Slope of elastic portion of stress – strain curve Area under the elastic portion of the stress –strain curve Energy absorbed during fracture in a tension test Energy absorbed during fracture in an impact test Slope of the plastic portion of the stress- strain curve ( ) Fatigue failure occurs under the condition of: High elastic stress High corrosivity High stress fluctuations High temperature High rate of loading ( ) Creep failure of a material occurs most rapidly when the operating temperature is: Cryogenic temperature Equal to its melting point Grater than 0.4 times its melting point in K Greater than 200 oF Close to boiling point ( ) Young’s modulus of a material is indicative of its: Tensile strength Yield Strength Ductility Stiffness Corrosion Resistance…arrow_forwardAs an R&D engineer, your input is requested to design an enhanced device that will be permanently implanted to repair the load-bearing function of a joint. Details on the candidate metals are presented here: Material SS 316 type Pure Ti Density (p) Yield stress (g/cm³) (MPa) 8 4.5 Ti6A14V 4 (F136) 190 140 795 Maximum elongation (%) 40 15 10 Elastic modulus (GPa) 190 110 114 Lo Shess leve O What force can each of the materials carry without permanent deformation? Which one offers better properties as a load-bearing implant? Explain. Describe the primary consequences of choosing the wrong material; consider in your answer the effect of density, yield stress, elongation, and Young's modulus on the implant's performance.arrow_forward
- Based on these results, which material would be better to use for constructing an earthquake-resistant structure? Explain.arrow_forwardTag question Consider the graph below for 3 metals which have been cold-worked. From the graphs, which of the following statements are true? Stress Select one or more: a. C. Strain & A e. B C b. B and C have similar hardness; C has greater brittleness B is softer than C and has nearly similar ductility A is harder than C and is more ductile d. A and B have similar hardness; A has greater brittleness A is harder than C and is less ductile f. B is harder than C but has nearly similar ductility 5 up i A Carrow_forward(b) A cylindrical rod made from an unknown metal is 350mm long and has a diameter of 10mm. The rod is subjected to a tensile load. It experiences only elastic deformation and elongates by less than 1.0mm under an applied load of 19,800N. Could any of the four metals listed in the table below could be the unknown metal? If so which ones and why? Material Modulus of Yield Ultimate Elasticity / GPa Strength / MPa Tensile Strength / MPa Aluminium 70 255 420 alloy Brass 100 345 420 Copper alloy Steel 110 250 290 207 450 550arrow_forward
- Consider the graph below for 3 metals which have been cold-worked. From the graphs, which of the following statements are true? Stress o Select one or more: □ c. Strain & A e. B a. B and C have similar hardness; C has greater brittleness b. B is softer than C and has nearly similar ductility A is harder than C and is more ductile C d. B is harder than C but has nearly similar ductility A is harder than C and is less ductile f. A and B have similar hardness; A has greater brittlenessarrow_forwardfor four different metals: 2014-T6 aluminum, 6061-T6 aluminum, structural A-36 steel, and 304 stainless steel. highlight differences (for example, you can rank them on things like strength, stiffness, ductility, etc.).arrow_forwardFor each question, provide an explanation, identifying the correct choice ( it is marked in red) and explaining why it's the right answer, as well as why the other options are incorrect.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY