
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
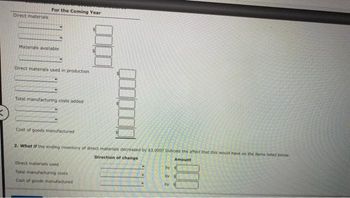
Transcribed Image Text:Direct materials
For the Coming Year
Materials available
Direct materials used in production
Total manufacturing costs added
Cost of goods manufactured
2. What if the ending inventory of direct materials decreased by $3,0007 Indicate the affect that this would have on the items listed below:
Direction of change
Direct materials used
Total manufacturing costs
Cost of goods manufactured
by
by
by
1000
Amount
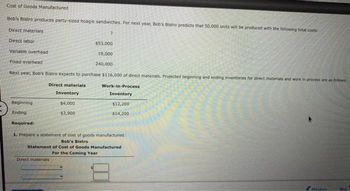
Transcribed Image Text:Cost of Goods Manufactured
Bob's Bistro produces party-sized hoagie sandwiches. For next year, Bob's Bistro predicts that 50,000 units will be produced with the following total costs:
Direct materials
Direct labor
Variable overhead
Fixed overhead
Next year, Bob's Bistro expects to purchase $116,000 of direct materials. Projected beginning and ending inventories for direct materials and work in process are as follows:
Direct materials
Beginning.
Ending
Required:
$53,000
19,000
240,000
Inventory
$4,000
$3,900
Direct materials
Work-in-Process
Inventory
$12,200
$14,200
1. Prepare a statement of cost of goods manufactured.
Bob's Bistro
Statement of Cost of Goods Manufactured
For the Coming Year
Previne
Next
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Required information Miami Solar manufactures solar panels for industrial use. The company budgets production of 4,200 units (solar panels) in July and 4,600 units in August. Each unit requires 4 pounds of direct materials, which cost $6 per pound. The company’s policy is to maintain direct materials inventory equal to 40% of the next month’s direct materials requirement. As of June 30, the company has 6,720 pounds of direct materials in inventory, which complies with the policy. Prepare a direct materials budget for July. MIAMI SOLAR Direct Materials Budget For Month Ended July 31 Budget production (units) 4,200 Materials needed for production (lbs.) Total materials requirements (lbs.) Materials to be purchased (lbs.) Budgeted cost of direct materials purchasesarrow_forwardPreparing an Ending Finished Goods Inventory Budget Andrews Company manufactures a line of office chairs. Each chair takes $14 of direct materials and uses 1.9 direct labor hours at $18 per direct labor hour. The variable overhead rate is $1.00 per direct labor hour, and the fixed overhead rate is $1.70 per direct labor hour. Andrews expects to have 670 chairs in ending inventory. There is no beginning inventory of office chairs. Required: 1. Calculate the unit product cost. Round your answer to the nearest cent.$fill in the blank 1 2. Calculate the cost of budgeted ending inventory. Round your answer to the nearest dollar.$fill in the blank 2arrow_forwardAllison Manufacturing produces a subassembly used in the production of jet aircraft engines. The assembly is sold to engine manufacturers and aircraft maintenance facilities. Projected sales in units for the coming 5 months follow: January 40,000 February 50,000 March 60,000 April 60,000 May 62,000 The following data pertain to production policies and manufacturing specifications followed by Allison Manufacturing: Finished goods inventory on January 1 is 32,000 units, each costing $166.06. The desired ending inventory for each month is 80% of the next month's sales. The data on materials used are as follows: Direct Material Per-Unit Usage DM Unit Cost ($) Metal 10 lbs. 8 Components 6 5 Inventory policy dictates that sufficient materials be on hand at the end of the month to produce 50% of the next month's production needs. This is exactly the amount of material on hand on December 31 of the prior year. The direct labor used per unit of…arrow_forward
- Activity Cost Driver Chosen asAllocation Base Conversion Cost Per Unit ofAllocation Base Materials handling Number of parts $1.00 Machining Machine hours 60.00 Packaging Number of finished units 2.00 Each windsock requires three parts and spends five minutes in the machining department. The total cost of direct materials and direct labor is $3.50 per windsock. Gale produces 20,000 windsocks each year and sells them at 140% of cost. The selling price per windsock is: Question 8 options: $13.50. $18.90. $16.10. $88.20.arrow_forwardPreparing an Ending Finished Goods Inventory Budget Andrews Company manufactures a line of office chairs. Each chair takes $18 of direct materials and uses 1.9 direct labor hours at $16 per direct labor hour. The variable overhead rate is $1.10 per direct labor hour, and the fixed overhead rate is $1.50 per direct labor hour. Andrews expects to have 770 chairs in ending inventory. There is no beginning inventory of office chairs. Required: 1. Calculate the unit product cost. Round your answer to the nearest cent.$fill in the blank 1 2. Calculate the cost of budgeted ending inventory. Round your answer to the nearest dollar.$fill in the blank 2arrow_forwardAccepting Business at a Special Price Forever Ready Company expects to operate at 90% of productive capacity during July. The total manufacturing costs for July for the production of 37,800 batteries are budgeted as follows: Direct materials $413,800 152,100 Direct labor Variable factory overhead 42,680 Fixed factory overhead 85,000 Total manufacturing costs $693,580 The company has an opportunity to submit a bid for 2,000 batteries to be delivered by July 31 to a government agency. If the contract is obtained, it is anticipated that the additional activity will not interfere with normal production during July or increase the selling or administrative expenses. What is the unit cost below which Forever Ready Company should not go in bidding on the government contract? Round your answer to two decimal places. per unitarrow_forward
- Oak Industrial has estimated that production for the next five quarters will be:. Production Information 1st quarter, 2020 44,100 units 2nd quarter, 2020 40,000 units 3rd quarter, 2020 48,200 units 4th quarter, 2020 37,600 units 1st quarter, 2021 45,700 units Finished units of production require 6 pounds of raw material per unit. The raw material cost is $7 per pound. There is $277,830 of raw material on hand at the beginning of the first quarter, 2020. Oak desires to have 15 percent of next quarter's material requirements on hand at the end of each quarter.Prepare quarterly direct materials purchases budgets for Oak Industrial for 2020.arrow_forwardThe following information is located in the production department of Mindy Ca Second First Quarter 14,300 Quarter Third Quarter Fourth Quarter 21,000 22,500 21,300 Units produced Other information found in the production department includes: Prior Year Ending RM Inventory Prior Year Ending A/P Pounds of RM per unit The ending raw material inventory per month should be 25% of the following month's production needs. The desired ending inventory for the fourth quarter is 3,700 pounds. Management plans to pay for 70% of the raw material purchases in the month bought and 30% in the following month. Direct Materials Budget Question: Given the data, the second quarter direct materials budget should be: Costs of Raw Materials per pound 5. $ Cost of DM Purchased: 10,725 11,775 First Second Quarter Quarter Third Quarter Fourth Quarter $ 4.50 $ 4.50 $ 4.50 $ 4.50arrow_forwardBreak-Even Units: Units for Target Profit Jay-Zee Company makes an in-car navigation system. Next year, Jay-Zee plans to sell 20,000 units at a price of $380 each. Product costs include: Direct materials $80.00 Direct labor $46.00 Variable overhead $11.00 Total fixed factory overhead $705,800 Variable selling expense is a commission of 6 percent of price; fixed selling and administrative expenses total $86,200. Required:arrow_forward
- Please do not give image formatarrow_forwardOrdering and Carrying Costs Ottis, Inc., uses 683,910 plastic housing units each year in its production of paper shredders. The cost of placing an order is $29. The cost of holding one unit of inventory for one year is $20. Currently, Ottis places 149 orders of 4,590 plastic housing units per year. Required: 1. Compute the annual ordering cost. $fill in the blank 1 2. Compute the annual carrying cost. $fill in the blank 2 3. Compute the cost of Ottis’s current inventory policy. $fill in the blank 3 Is this the minimum cost?arrow_forwardgodoarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education