
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Continued monetary tightening
05 October 2022
The Monetary Policy Committee today increased the Official Cash Rate (OCR) to 3.5% from 3.0%. The Committee agreed it remains appropriate to continue to tighten monetary conditions at pace to maintain price stability and contribute to maximum sustainable employment. Core consumer price inflation is too high and labour resources are scarce. Global consumer price pressures remain heightened. The global demand for goods and services is exceeding supply capacity, putting upward pressure on prices. Food and energy prices are being particularly exacerbated by the war in Ukraine. A recent decline in oil prices and an easing in some supply-chain constraints have seen headline inflation measures fall in some countries. However, core measures of inflation have risen and persist. Central banks are tightening monetary conditions, implying a weaker growth outlook for New Zealand's trading partners. In New Zealand, the level of domestic spending has remained resilient to date, in the face of slowing global growth and higher domestic interest rates. Employment levels are high, and household balance sheets remain resilient despite the fall in house prices. New Zealand's productive capacity is still being constrained by labour shortages and wage pressures are heightened. Overall, spending continues to outstrip the capacity to supply goods and services, with a range of indicators continuing to highlight broad-based pricing pressures. Committee members agreed that monetary conditions needed to continue to tighten until they are confident there is sufficient restraint on spending to bring inflation back within its 1 to 3% per annum target range. The Committee remains resolute in achieving the Monetary Policy Remit.
How is tightening monetary conditions by other central banks likely to impact on New Zealand’s inflation and growth?
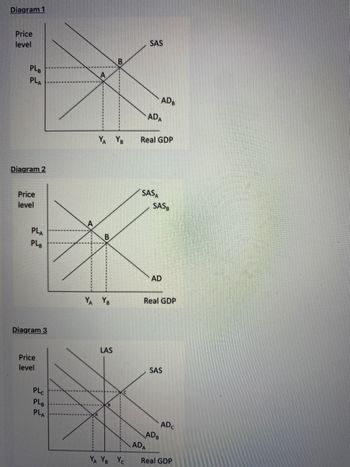
Transcribed Image Text:Diagram 1
Price
level
PLB
PLA
Diagram 2
Price
level
PLA
PLB
Diagram 3
Price
level
PLC
PLB
PLA
B
YA YB
YA YB
B
LAS
--------
YA YB YC
SAS
ADB
ADA
Real GDP
SASA
SASB
ADA
AD
Real GDP
ADB
SAS
ADC
Real GDP
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate? A temporary increase in a country's money supply causes a proportional long- run depreciation of its currency against foreign currencies. A permanent increase in a country's money supply causes a proportional long- run appreciation of its currency against foreign currencies. A permanent increase in a country's money supply causes a proportional short- run appreciation of its currency against foreign currencies. A permanent increase in a country's money supply causes a proportional long- run depreciation of its currency against foreign currencies. A permanent increase in a country's money supply causes a proportional short- run depreciation of its currency against foreign currencies.arrow_forwardContinued monetary tightening 05 October 2022 The Monetary Policy Committee today increased the Official Cash Rate (OCR) to 3.5% from 3.0%. The Committee agreed it remains appropriate to continue to tighten monetary conditions at pace to maintain price stability and contribute to maximum sustainable employment. Core consumer price inflation is too high and labour resources are scarce. Global consumer price pressures remain heightened. The global demand for goods and services is exceeding supply capacity, putting upward pressure on prices. Food and energy prices are being particularly exacerbated by the war in Ukraine. A recent decline in oil prices and an easing in some supply-chain constraints have seen headline inflation measures fall in some countries. However, core measures of inflation have risen and persist. Central banks are tightening monetary conditions, implying a weaker growth outlook for New Zealand's trading partners. In New Zealand, the level of domestic spending has…arrow_forward8) Using the aggregate demand-aggregate supply diagram, graphically illustrate and explain the impact of an expansionary monetary policy on the price level and real income in the long run.arrow_forward
- Suppose the economy is experiencing inflation. If the Federal Reserve enacts contractionary monetary policy, interest rates will likely Multiple Choice rise causing prices to decrease. fall causing prices to increase. fall causing prices to decrease. rise causing prices to increasearrow_forwardC = 100 + 0.5 - (Y –T) I = 500 – 1000 - r where Y is real output and r is the real interest rate. Government purchases and taxes are Ĝ = 500, Ť= 100. The LM (money market equilibrium) curve is M Y where P is the price level and i is the nominal interest rate. The Central Bank (CB) is initially supplying M = 8000 units of money, and expected inflation is xª = 0. Assume that the long-run equilibrium level of output is Y = 2000. Short-run equilibrium output is initially at the same level (Y = 2000). Suddenly, news of a new world-beating super-vaccine raises expected inflation to “ = 0.05. 3. Continue to suppose the government doesn't do anything, and the CB wants to stabilise the shock in the short-run but instead of output, the CB wants to bring the nominal interest rate i back to its long-run equilibrium level. Explain whether it should decrease or increase money supply M, and what happens to short-run output Y and the real interest rate r if this policy is followed. 4. Suppose the CB…arrow_forwardAssuming that the Bank of Canada determines that inflation is the most significant problem in the economy and that it wishes to employ all of its policy instruments, what should the Bank of Canada do with its policy tools? The Bank of Canada should make open market make loans to chartered banks, conduct and the policy interest ratearrow_forward
- The Wakandan Central Bank has set an inflation target of 4%. For the past 6 months, the target overnight rate has been 2.5% and the core rate of inflation has been 6%. This suggests that the Central Bank should engage in monetary policy and the target overnight rate. expansionary; increase expansionary; decrease contractionary; increase contractionary; decreasearrow_forwardHigher potential output levels without any monetary policy intervention will lead to Multiple Choice higher real interest rates. lower real interest rates and higher inflation rates. lower real interest rates and lower inflation rates. higher real interest rates and lower inflation rates.arrow_forwardThe aggregate economy of India has a rate of money growth equal to 7. Initially the velocity of money is not changing. The long-run aggregate supply curve equals 2 But then there is a banking panic, causing the growth rate of the velocity of money to fall to -6 percent per year. In the absence of government intervention, the resulting recession would last for 3 years (meaning it would grow at the recession growth rate for 3 years, then return to long-run equilibrium after that). Assume that just before the recession started, India's level of GDP was equal to $100 billion. Your boss has proposed that the government should step in and use fiscal policy to end the recession immediately. But Raj Kumar, a member of the opposition, has claimed that fiscal policy is too expensive, and anyways there is no reason to end the recession because it will end on its own. To counter his argument, your boss has asked you to calculate how much lower GDP would be by the end of the recession if the…arrow_forward
- Draw and properly label three graphs of money supply-money demand (in one graph), investment demand, and AD-AS (6%). Then, referring to the graphs in your explanation, use one of the three traditional monetary tools to explain how the monetary transmission mechanism works to close recessionary and also inflationary gaps. (9%)arrow_forwardContinued monetary tightening 05 October 2022 The Monetary Policy Committee today increased the Official Cash Rate (OCR) to 3.5% from 3.0%. The Committee agreed it remains appropriate to continue to tighten monetary conditions at pace to maintain price stability and contribute to maximum sustainable employment. Core consumer price inflation is too high and labour resources are scarce. Global consumer price pressures remain heightened. The global demand for goods and services is exceeding supply capacity, putting upward pressure on prices. Food and energy prices are being particularly exacerbated by the war in Ukraine. A recent decline in oil prices and an easing in some supply-chain constraints have seen headline inflation measures fall in some countries. However, core measures of inflation have risen and persist. Central banks are tightening monetary conditions, implying a weaker growth outlook for New Zealand's trading partners. In New Zealand, the level of domestic spending has…arrow_forwardCurrent U.S. monetary policy is best described as: Aimed at keeping inflation low and stable and growth high and stable Determining the denominations of a country's currency One of the most important functions of Congress Attempting to keep inflation constant at zero percentarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education