
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
(a) Consider the chlorination of methane, given below:
1 CH4(g) + 4 Cl2(g) 1 CCl4(g) + 4 HCl(g)
If CH4(g) is decreasing at the rate of 0.600 mol/s, what are the rates of change of Cl2(g), CCl4(g), and HCl(g)?
Cl2(g)/t = mol/s
CCl4(g)/t = mol/s
HCl(g)/t = mol/s
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
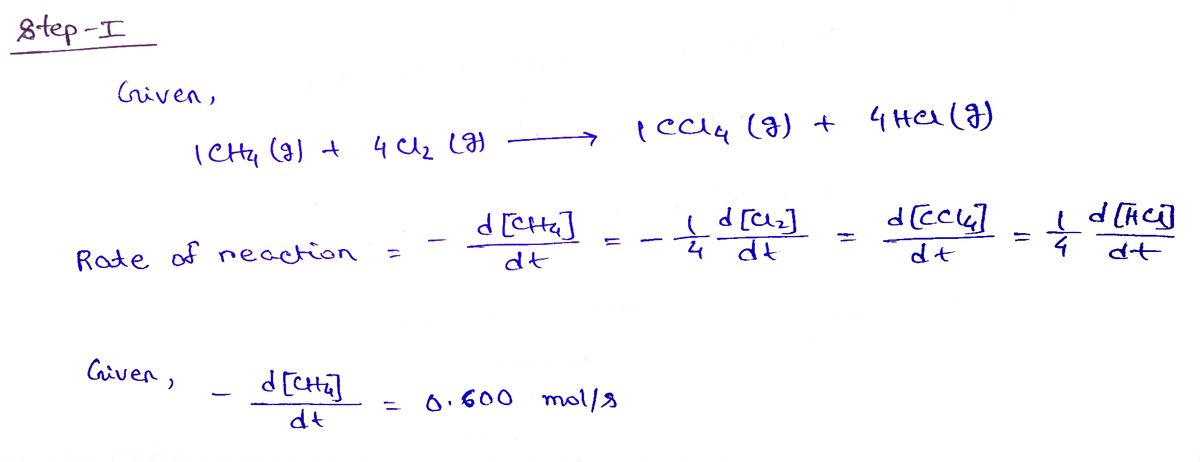
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Consider the reaction 4 NO2 (g) + 02 (g) 2 N205 (g) Suppose at a particular moment during the reaction, molecular oxygen is reacting at a rate of 0.024 M/sec. At what rate (M/sec) is NO, reacting? Hint: See below. Let A be O, and B as N205. Lowercase letters are coefficients from balanced equation. 1 A[A] a At 1 A[B] = - 1 A[C] c At 1 A[D] +- d At Rate b At O0.006 O0.024 O0.096 Onone of the abovearrow_forward(a) Consider the combustion of butane, given below: If C4H10(9) is decreasing at the rate of 0.880 mol/s, what are the rates of change of O₂(g), CO₂(g), and H₂O(g)? AO₂(g)/At = ACO₂(g)/At = AH₂O(g)/At = mol/s mol/s APtot/At = mol/s (b) The decomposition reaction given below: 2 NOCI(g) → 2 NO(g) + 1 Cl₂(g) is carried out in a closed reaction vessel. If the partial pressure of NOCI(g) is decreasing at the rate of 837 torr/min, what is the rate of change of the total pressure in the vessel? 2 C4H10(9) + 13 O₂(g) → 8 CO₂(g) + 10 H₂O(g) torr/minarrow_forwardPhosphine, PH3(g)PH3(g), decomposes according to the equation 4PH3(g)⟶P4(g)+6H2(g)4PH3(g)⟶P4(g)+6H2(g) The kinetics of the decomposition of phosphine at 950950 K was followed by measuring the total pressure in the system as a function of time. The data in the table were obtained in a run where the reaction chamber contained only pure phosphine at the start of the reaction. Time (min) Ptotal (Torr) 0.00 100 40.0 151 80.0 168 100 171 Choose the rate law that describes this reaction. rate=?(?PH3)−1rate=k(PPH3)−1 rate=?(?PH3)2rate=k(PPH3)2 rate=?rate=k rate=?(?PH3)−2rate=k(PPH3)−2 rate=?(?PH3)rate=k(PPH3) Calculate the value of the rate constant and determine the correct units.arrow_forward
- Consider the chlorination of methane, given below: 1 CH4(g) + 4 Cl2(g) 1 CCl4(g) + 4 HCl(g) If CH4(g) is decreasing at the rate of 0.230 mol/s, what are the rates of change of Cl2(g), CCl4(g), and HCl(g)?Cl2(g)/t = ______ mol/sCCl4(g)/t = ______ mol/sHCl(g)/t = ______ mol/s(b) The decomposition reaction given below: 2 NH3(g) 1 N2(g) + 3 H2(g) is carried out in a closed reaction vessel. If the partial pressure of NH3(g) is decreasing at the rate of 765 torr/min, what is the rate of change of the total pressure in the vessel?Ptot /t = ______ torr/minarrow_forwardTbed image Text: The gas phase decomposition of nitrogen dioxide at 383 °C NO₂(g) → NO(g) + ½/2O₂(g) is second order in NO2. In one experiment, when the initial concentration of NO2 was 0.136 M, the concentration of NO2 dropped to 3.62 x 10-2 M after 28.7 seconds had passed. Based on these data, the rate constant for the reaction is I Use the ices to access important M-¹ s-¹. destion. The ergy for the gas phase isoff zation JL 1arrow_forward#8arrow_forward
- (a) Consider the combustion of butane, given below: 2 C4H10(g) + 13 02(g) → 8 CO2(g) + 10 H20(g) If C4H10(g) is decreasing at the rate of 0.230 mol/s, what are the rates of change of 02(g), CO2(g), and H20(g)? A02(g)/At = mol/s ACO2(g)/At = mol/s AH20(g)/At = mol/s (b) The decomposition reaction given below: 2 NH3(g) → 1 N2(g) + 3 H2(g) is carried out in a closed reaction vessel. If the partial pressure of NH3(g) is decreasing at the rate of 898 torr/min, what is the rate of change of the total pressure in the vessel? APtot /At = torr/minarrow_forward9:54 AM Tue Nov 21 For the following reaction mechanism, what is the catalyst? NO(g)+O3(g) → NO2(g) + O2(g) A) O(g) O(g) +NO2(g) O2(g) + NO(g) B) O₂(g) C) O3(g) Question 20 of 20 D) NO(g) E) NO₂(g) O3(g) O2(g) + O(g) Tap here or pull up for additional resources 36% Submitarrow_forward11:27 2NH4+ (aq) + HCO3- (aq) The reaction is first order with respect to urea, and first order overall with a rate constant of 4.28 x 10^(-4)s^(-1) a. Write the rate law for this reaction. b. If the reaction begins with an initial urea concentration of 0.500 M, what will the concentration of urea in the solution be after 2500 s? C) Calculate the half life of this reaction. d. At what time (+) will the concentration of urea be 0.020 M? O □arrow_forward
- For the reaction: A(g)+1/2B(g)→2C(g). A) When C is increasing at a rate of 3.5×10−2 mol L−1 s−1 , how fast is B decreasing? Express your answer using two significant figures. B) How fast is A decreasing? Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forward(a) Consider the reaction of hydrogen sulfide with methane, given below: 1 CH4(g) + 2 H2S(g) 1 CS2(g) + 4 H2(g) If CH4(g) is decreasing at the rate of 0.580 mol/s, what are the rates of change of H2S(g), CS2(g), and H2(g)?H2S(g)/t = mol/sCS2(g)/t = mol/sH2(g)/t = mol/s(b) The decomposition reaction given below: 2 NOCl(g) 2 NO(g) + 1 Cl2(g) is carried out in a closed reaction vessel. If the partial pressure of NOCl(g) is decreasing at the rate of 733 torr/min, what is the rate of change of the total pressure in the vessel?Ptot /t = torr/minarrow_forwardButadiene, C4H6 (used to make synthetic rubber and latex paints) dimerizes to C3H12 with a rate law of rate = 0.014 L/mol• s [C4H6J. If the remaining concentration of CAH, is 0.047 M after 0.35 hours, what is the initial concentration of CAH6 in molar? Report a numerical value with 3 decimal places, without units.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY