
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Given the following reaction, when [E] is decreasing at 0.2 mol/L s, how fast is [G] increasing?
2D(g) + 3E(g) + 5F(g) --> 7G(g) + 6H(g)
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
The rate of a chemical reaction is the change in concentration over the change in time and is a metric of the "speed" at which a chemical reactions occurs and can be defined in terms of two observables:
- The Rate of Disappearance of Reactants
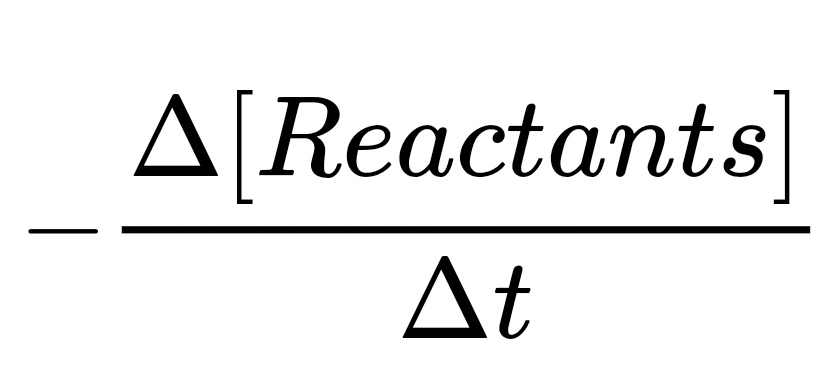
Note this is negative because it measures the rate of disappearance of the reactants.
- The Rate of Formation of Products
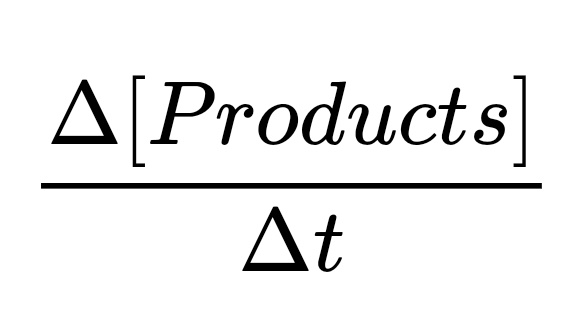
This is the rate at which the products are formed.
They both are linked via the balanced chemical reactions and can both be used to measure the reaction rate.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the reaction: 4NH3 (g) + 7O2 (g) → 4NO2 (g) + 6H2 (g), if H2 is produced at a rate of 3.5 x 10-3 M/s, O2 is consumed at a rate of... A. -2.5 x 10-2 M/s B. -4.1 x 10-3 M/s C. -2.1 x 10-2 M/s D. -3.0 x 10-3 M/s E. -5.8 x 10-4 M/sarrow_forward8:59 Question 11 of 13 For the following reaction mechanism, what is the catalyst? NO(g) + O3(g) A) O(g) O(g) + NO₂(g) - → B) O₂(g) O3(g) C) O3(g) 5GW Submit O2(g) + O(g) NO2(g) + O2(g) DINOGl Tap here or pull up for additional resources O2(g) + NO(g)arrow_forward1.a) For the reaction below, A[HBr]/At = 5.0 x 10-5 M/s. What is the rate of formation of Br2 ? 2 HBr(g) > Br,(g) + H2(g) а. 5.0 x 10-5 M/s b. 2.5 х 10-5 М/s с. 1.0 х 10-4 Ms d. 1.0 x 10-5 M/s 1b) Assume that you doubled the concentration of HBr in the previous problem and the rate increased by a factor of 4. What would be the rate law for this reaction? a. rate = k[HBr] b. rate = k[HBr]? c. rate = k[HBr]4 d. rate=[Br2][H2]/[HBr]?arrow_forward
- (a) Consider the combustion of butane, given below: 2 C4H10(g) + 13 O2(g) 8 CO2(g) + 10 H2O(g) If C4H10(g) is decreasing at the rate of 0.700 mol/s, what are the rates of change of O2(g), CO2(g), and H2O(g)?O2(g)/t = mol/sCO2(g)/t = mol/sH2O(g)/t = mol/s(b) The decomposition reaction given below: 2 N2O5(g) 4 NO2(g) + 1 O2(g) is carried out in a closed reaction vessel. If the partial pressure of N2O5(g) is decreasing at the rate of 634 torr/min, what is the rate of change of the total pressure in the vessel?Ptot /t = torr/minarrow_forwardConsider the reaction: C(s) + 2 H₂(g) → CH4 (8) A reaction mixture is made with some amount of C and H₂ and an initial CH4 partial pressure of 0.0 atm. After 5.0 s, the CH, partial pressure is measured to be 0.7 atm. Calculate the average rate of change of H₂ (in atm/s) in the first 5.0s of the reaction. Be sure to include the correct sign (+/-) with your answer. Report your answer to 2 significant figures without the unit. Example: 0.015 Type your answer...arrow_forwardAssuming both reactions are at the same temperature, Which one would produce product faster? II Both would produce product at the same rate Not enough information to tell Iarrow_forward
- QUESTION 13 A proposed mechanism for the decomposition of ozone consists of the three steps shown below. Identify the catalyst. Step 1: 03(g) + NO(g) → O2(g) +NO2(g) Step 2: NO2(g) → NO(g) + O(g) Step 3: 0(g) +03(g)→2 02(g) OA. There is no catalyst OB. NO O CO OD. NO2 OE. 03 of water? Thearrow_forwardQUESTION 46 Consider the reaction potential energy diagram. What describes the catalyzed forward reaction pathway? 35 10 Progross of the Reaction O Ea = 10 kJ-mol and AH = -15 kJ mol-1 O E = 10 kJ-mol1 and AH = 15 kJ mol-1 %3D O Ea = 25 kJ mol1 and AH = -15 kJ mol-1 %3D O Eg = 25 kJ mo and AH - 15 kJ mol1arrow_forwardA chemist runs a reaction at 25.0 C and determines that the reaction proceeds far too slowly. She decides that the reaction needs to speed up by a factor of 16. At what temperature should she run the reaction?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY