
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
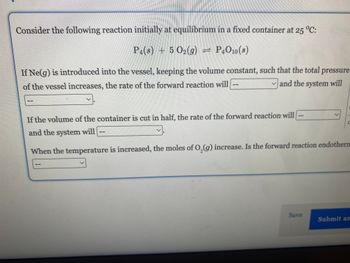
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following reaction initially at equilibrium in a fixed container at 25 °C:
P4(s) + 5 O₂(g) = P4O10(s)
If Ne(g) is introduced into the vessel, keeping the volume constant, such that the total pressure
of the vessel increases, the rate of the forward reaction will
and the system will
If the volume of the container is cut in half, the rate of the forward reaction will
and the system will
-
--
--
11
V
When the temperature is increased, the moles of O₂(g) increase. Is the forward reaction endotherm
Save
1.
Submit an
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
A system in its equilibrium state will remain in that state indefinitely as long as it is undisturbed. If the equilibrium is destroyed by subjecting the system to a change of pressure, temperature, or the number of moles of a substance, then a net reaction will tend to take place that moves the system to a new equilibrium state. Le Chatelier's principle says that this net reaction will occur in a direction that partially offsets the change.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following system at equilibrium at 698 K. 2 HI(g)→ H₂(g) + I₂ (9) Use the References to access importa When some HI(g) is removed from the equilibrium system at constant temperature, the reaction must O run in the forward direction to reestablish equilibrium. O run in the reverse direction to reestablish equilibrium. O remain the same. It is already at equilibrium. The concentration of H₂ will O increase. O decrease. O remain the same.arrow_forwardFor the reaction at equilibrium: 2 H2O (g) +2 Cl 2 (g) + energy4 HCI (g) + O2 (g), If the temperature in the reaction vessel is decreased: O [H2O] will decrease. [H2O] will increase. [H2O] will not change.arrow_forward1. The diagrams below represent the following reversible chemical reaction: H2(g) + 12 (g) =2 HI (g) At 448 °C, the equilibrium constant, K, for this reaction is 51 Initial Conditions: Temperature = 448 °C Volume of the container = 2.0 L 0 = 1 mole H2 (g) = 1 mole I2 (g) 00 00 .. 00 00 •. What is the initial molar concentration of hydrogen. [H:]? What is the initial molar concentration of iodide, [I2]? M This system will reach equilibrium when rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. Write the equilibrium constant expression, Kc, for this reaction: Calculate the equilibrium concentrations for H;(g), I (g) and HI (g) H2(g}_ + l2 (g) 2 HI (g) [H2] [L2] [HI Initial Change Equilibrium +2x -X-arrow_forward
- A chemical engineer is studying the following reaction: N2(9)+3H,(g) → 2NH,(g) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction is 0.00029. The engineer charges ("fills") three reaction vessels with nitrogen and hydrogen, and lets the reaction begin. She then measures the composition of the mixture inside each vessel from time to time. Her first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time she measures the compositions. reaction compound pressure expected change in pressure vessel N2 52.94 atm f increase OI decrease (no change) H2 23.44 atm O t increase OI decrease O (no change) A NH3 14.08 atm O t increase I decrease (no change) N2 47.16 atm O f increase I decrease (no change) В H2 20.07 atm O f increase O I decrease (no change) NH3 11.95 atm O f increase OI decrease (no change) N2 47.80 atm O f increase OI decrease (no change) H2 21.97 atm O f increase OI decrease (no…arrow_forwardFor the reaction of NO2 to form NO and O2, which reaction vessel (all at different temperatures) would yield the smallest equilibrium constant? 2 NO2(g) +2 NO(g) + O2(g) → is supposed to be an equilibrium arrowarrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 CO2(g) <-->2 CO(g) + O2(g) , K = 4.3 x 10-21 at a particular temperature. If initial [CO2] = 0.01 M and all other initial concentrations are zero, what is [CO2] at equilibrium? Please provide answer to two decimal places.arrow_forward
- A student ran the following reaction in the laboratory at 1080 K: 2SO3(g) 2S02(g) + O₂(g) When he introduced SO3(g) at a pressure of 0.886 atm Into a 1.00 L evacuated container, he found the equilibrium partial pressure of SO3(g) to be 0.340 atm. Calculate the equilibrium constant, Kp, he obtained for this reaction. Kp = Submit Answer 44 $ T R F V/ % 5 Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remaining T Cengage Learning Cengage Technical Support F5 G ^ 6 MacBook Air Y H & 7 RN U * 0 J ► 11 F8 M ( 9 ►► K F9 O 1 F11 + { Save and Exit = F12 11arrow_forward13arrow_forwardConsider the reaction: 2S (s) + 30₂ (9)2SO3(g) Write the equilibrium constant for this reaction in terms of the equilibrium constants, K₁ and K₂, for the reactions below: 3 80 For answers with both a subscript and a superscript, enter the subscript first. For example, enter K if the first equilibrium constant should be squared. K = E D S(s) + O2(g) → SO₂(g) K₁ SO₂(g) + 1/2O₂(g) SO3(9) K₂ 13 с Submit Answer $ 888 FA F4 R F Show Hint V Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remaining % 5 T Cengage Learning Cengage Technical Support F G 6 B MacBook Air FO Y H & 7 N F7 U J * 00 8 ➤11 FO I M ( 9 V K O < H дв ) O L F10 question. P command F11 A ; Previous { + alt #2 “ . ? option Save and Exit I 1 delete 1 ente rearrow_forward
- 14. The following reaction is allowed to come to equilibrium and then the volume is increased. Predict the effect of the indicated volume change once equilibrium is restored. H2O(g) + CO2(g) double arrow H2CO3(g) The reaction will shift right. The reaction will shift left. There will be no effect. Effect can not be determined from information provided.arrow_forwardAn evacuated reaction vessel is filled with 0.800 atm of N₂ and 1.681 atm of Br2. When equilibrium is established according to the reaction below, there are 1.425 atm of Br2 remaining in the vessel. What is the equilibrium partial pressure of NBr3? 2 NBr3 (g) = N₂ (g) + 3 Br2 (g)arrow_forwardA chem ngineer is studying the following reaction: + HCN(aq) + NH3(aq) → CN¯(aq)+NH (aq) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 1.1. C The engineer charges ("fills") four reaction vessels with hydrogen cyanide and ammonia, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the composition of the mixture inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions. reaction vessel A B C compound HCN NH3 CN NH4 HCN NH3 CN NH₁ HCN NH₂ CN NHA 4 concentration 0.28 M 0.12 M 1.05 M 0.94 M 0.67 M 0.51 M 0.66 M 0.55 M 0.31 M 0.15 M 1.02 M 0.91 M expected change in concentration ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↓ decrease ↓decrease ↓ decrease 888888 ↓decrease ↓ decrease ↓decrease ↓ decrease ↓ decrease ↓decrease…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY