
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Consider the following game where two players have to decide if they want to buy a movie ticket or a baseball ticket. They have the highest payoffs when they both buy tickets to the same activity, but must decide simultaneously what to buy without knowing what the other person will do.
a. Does either player have a dominant strategy?
b. How many equilibria does this game have?
c. Is this an example of a prisoner’s dilemma? Explain.
d. What will be the outcome if your friend buys their ticket first and you can observe their choice?
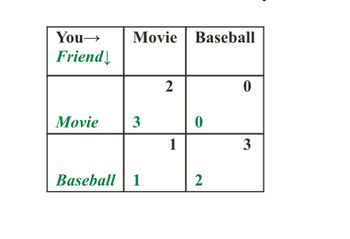
Transcribed Image Text:### Decision Matrix for Movie or Baseball Game
This decision matrix is designed to analyze choices between watching a movie or attending a baseball game, with you and a friend as decision-makers. The table is divided into rows and columns representing the different choices available to you and your friend, respectively.
#### Matrix Breakdown:
- **Columns**:
- **Movie**: Represents your choice to watch a movie.
- **Baseball**: Represents your choice to go to a baseball game.
- **Rows**:
- **Movie**: Represents your friend's choice to watch a movie.
- **Baseball**: Represents your friend's choice to attend a baseball game.
#### Payoff Values:
- **(Movie, Movie):** (3, 2)
- If both you and your friend choose to watch a movie, you receive a payoff of 3, and your friend receives a payoff of 2.
- **(Movie, Baseball):** (0, 1)
- If you choose to watch a movie but your friend chooses baseball, you receive a payoff of 0, and your friend receives a payoff of 1.
- **(Baseball, Movie):** (1, 0)
- If you choose baseball but your friend chooses to watch a movie, you receive a payoff of 1, and your friend receives a payoff of 0.
- **(Baseball, Baseball):** (2, 3)
- If both you and your friend choose to attend a baseball game, you receive a payoff of 2, and your friend receives a payoff of 3.
### Analysis:
This matrix helps visualize the potential outcomes and payoffs for each combination of choices between two friends deciding between leisure activities. It can be used to predict behavior or strategize in similar decision-making scenarios.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Step 1: Define Nash equilibrium.
VIEW Step 2: Explain does either player have a dominant strategy?
VIEW Step 3: Explain How many equilibria does this game have?
VIEW Step 4: Explain is this an example of a prisoner’s dilemma?
VIEW Step 5: Explain the outcome if your friend buys their ticket first and you can observe their choice.
VIEW Solution
VIEW Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following game : Stag Rabbit Stag 9, 9 0, 8 Rabbit 8, 0 7, 7 The first payoff is that of player 1 and the second that of player 2. a. ) Draw the extensive form of the simultaneous game. Find all the Nash equilibrium. p. Suppose player 1 moves first or we are in a sequential game now. Draw the extensive form in the sequential version. c. What is the subgame perfect Nash Equilibrium (SPNE) in the sequential version? d. ) Explain why it is an SPNE.arrow_forwardK In a game, there are two players: Player 1 and Player 2. They have two strategies to select from, A and B. Where the first payoff and the second payoff in every cell is for Player 1 and Player 2 respectively. Which of the following is an example of a game without a dominant strategy? (Check all that apply.) A. C. Player 1 Player 1 A B A B A 3,-3 1, 1 A 2,1 0,0 Player 2 Player 2 B 3, -3 5, -5 B 0,0 1,2 B. D. Player 1 Player 1 A B A B A 1,-1 -1, 1 Player 2 Player 2 A 3.5, -1.5 2.7, -1 B -1, 1 1,-1 B -5, 3 0,0 If the dominant strategy for Player 1 is selecting strategy A and the dominant strategy for Player 2 is strategy B, then A B is an example of a c From ame C Murat Çok Di id Kushn y My Handarrow_forwardThe following payoff table lists the profits of a buyer and a seller. The seller acts first by choosing a sale price ($9, $8, or $6). The buyer then decides the quantity of the good to purchase (two units, four units, six units, or eight units). a. Suppose the buyer and seller transact only once. Does the buyer have a dominant strategy? Depending on the price quoted, what is his best response? What price should the seller set? Explain carefully. Buyer Quantities 2 Units 4 Units 6 Units 8 Units P $9 10, 6 20, 5 30, 0 40, 8 Seller P $8 8, 8 16, 9 24, 6 32, 0 Prices P $6 4, 12 8, 17 12, 18 16, 16 b. Suppose the seller and buyer are in a multiyear relationship. Each month, the buyer quotes a price and the seller selects her quantity. How might this change each player’s behavior? c. Now suppose the buyer and seller are in a position to negotiate an agreement specifying price and quantity. Can they improve on the result in part (a)? Which quantity should they set? What price would be…arrow_forward
- Up ооооо Down Player 1 Up No EFFICIENT equilibrium exists Down Up Down Player 2 P1 gets $120 P2 gets $5 P1 gets $100 P2 gets $10 P1 gets $95 P2 gets $95 In the game above, what is/are the EFFICIENT sub-game perfect Nash equilibrium? (up,up) (up,down) (down, up) (down, down) P1 gets $15 P2 gets $25arrow_forwardSolve the following game: Push Not Push 4, 2 6, -1 Part a: Find the Nash equilibrium Not 2, 3 0, 0arrow_forwardThree politicians are voting on whether to allow themselves a salary increase of$3,500per a year. If they vote in favor of a raise, then they lose some public support, costing them each$1,500 per year. The salary increase passes if two or more politicians vote in favor of it. What is this game’s Nash equilibrium (or equilibria)? Explain. There is no need to draw a payoff matrix.arrow_forward
- The world has changed a bit. Microsoft and Google could still either cooperate or compete in the market for social media video software currently captured by Tik Tok, but their payoffs have changed. The table below shows their profits in billions of USD in each scenario. Use your mouse to point and click on the Nash equilibrium outcome(s). [There may be more than one so make sure you work out all the best response strategies]. Microsoft Cooperate 3,3 4,0 Cooperate O Don't cooperate O Google Don't cooperate O O 0,4 1,1arrow_forwardQ2 Consider a game between 2 payers (Ann and Bill) where each chooses between 3 actions (Up, Middle and Down). 1) Create a payoff matrix that reflects this. 2) Fill in payoff numbers that makes this game a Prisoner's Dilemma. 3) Explain why your game is a Prisoner's Dilemma.arrow_forward2arrow_forward
- In the game theory diagram. Is it firstly okay that I use decimals? And what is the Nash equilibrium and dominant strategies of each player. Where high = high price and low = low price. For the two companiesarrow_forwardConsider the following four games where players Row and Column each have two strategies: A and B. Which of the following games illustrates a prisoners’ dilemma?arrow_forwardLet's think about a traditional game theory principal agent game. In this game we have two players, Lauren and Jason Lauren will choose to invest $500 dollars with Jason If she doesn't invest the money, she keeps the $500 and Jason gets nothing If she does invest the money, then Jason has a choice-he can cooperate by investing Lauren's money and then splitting the profit of another $500. This would give Lauren $750 (her original $500 investment plus $250 of profit) and would give Jason $250. Jason's other choice is to appropriate, or to steal Lauren's money and not invest it. If he does this, Lauren ends up with nothing and Jason has the entire $500. The following diagram outlines this game. Principal Agent Game Jason (750.250) Invest appropriate 10. 500) doninve What will happen in this game? Lauren will not invest Lauren will invest and Jason will cooperate Lauren will invest and Jason will appropriate Next pagearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education