
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Review Chapter 15, Table 15.4, Prisoner Dilemma. Suppose the game starts with both Jesse and Frank planning to “Stay Mum” in the lower right cell. Discuss how each player would evaluate the situation and decide whether to change decisions. If each player makes decisions to minimize the penalty, in which cell will this game end? Is there a Nash equilibrium?
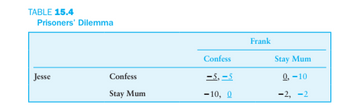
Transcribed Image Text:TABLE 15.4
Prisoners' Dilemma
Jesse
Confess
Stay Mum
Confess
-5, -5
-10, Q
Frank
Stay Mum
0,-10
-2, -2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I hope you can draw a picture and analyze it, thank you.arrow_forwardWe can see from the payoff matrix that there are no pure strategy Nash equilibrium in this game because at least one firm would always have an incentive to change its behavior. From Nash's theorem, we know there must be at least one Nash equilibrium so there must be a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium for this game. Find the mixed strategy Nash equilibrium by first deleting all dominated strategies in the game What's the expected payoff to Firm 2 in the equilibrium?arrow_forwardConsider the following Guessing Game. There are n = 10 players simultaneously choosing a number in {1, 2, 3}. The winners are those closest to 1/2 the average guess (they evenly split the prize between the winners if there is more than one). Find the set of rationalizable strategy profiles. Justify your answer. please no handwriting and this course about game theory (topic Rationalizability) answer with all steps, pleasearrow_forward
- Suppose you are interested in applying equilibrium theory to the following game, where 01 Nash equilibrium in which player 2 plays a sub-optimal action. {E, F}. Show that there is Bayesian Player 2 A • 1,1 GF Player 1 R • -1,0 NF 0,0 Nature A • 1,0 GE 1-p R -1, –1 NE 0,0arrow_forwardConsider the following game: PLAYER 2 Left Middle Right Up 0,0 2,5 5.4 PLAYER 1 Middle 1,2 7,3 4,3 Down 5,5 3, 1 2, 1 Which of the following statements is true? There are two Nash equilibria, and they are both Pareto efficient. There is a unique Nash equilibrium. There are two Nash equilibria, and they are both Pareto inefficient. There are two Nash equilibria, but only one is Pareto efficient. None of these.arrow_forwardConsider a Prisoners' Dilemma game involving two players, N = {1,2}, each of whom may choose either to co-operate (C) or to defect (D). The payoffs this game are illustrated in the below table. Player 1 receives the first listed payoff in each cell while player 2 receives the second listed payoff in each cell. 2 с 3,3 4,0 D 0,4 1, 1 a. Solve for the pure strategy Nash equilibrium of this static game. Are the players able to co-operate with one another? Explain why or why not. Suppose now that the above game is repeated infinitely many times and let 8 > 0 denote the common discount factor between periods. Suppose that the two players make the following agreement: "Play C in every period. If D is ever played, play D in every period thereafter." b. Explain how the one-deviation principle can be used to check whether the above agreement represents a subgame perfect Nash equilibrium of the infinitely repeated game. c. Use the method described in part b. of this question to calculate the…arrow_forward
- Tyler and Pam are arrested and charged with armed robbery. The police interview both suspects separately about their involvement in the crime. Each suspect has to make a decision. They can betray the other suspect by confessing that they both committed the crime, or they can cooperate with the other suspect by remaining silent. The table shows the sentences that Tyler and Pam will receive given their choices. Use the table to answer the question. What will be the dominant strategy outcome for Tyler and Pam? They both get 10 years. Pam gets 5 years, and Tyler gets 15 years. O They both get 12 years. O Tyler gets 5 years, and Pam gets 15 years. Tyler Stay silent Confess Stay silent Pam gets 10 years Tyler gets 10 years Pam gets 15 years Pam Tyler gets 5 years Confess Pam gets 5 years Tyler gets 15 years Pam gets 12 years Tyler gets 12 yearsarrow_forwardJohn and Jane usually vote against each other’s party in the SSC elections resulting to negating or offsetting their votes. If they vote for their party of choice, each of them gains four units of utility (and lose four units of utility from a vote against their party of choice). However, it costs each of them two units of utility for the hassle of actually voting during the SSC elections. A. Diagram a game in which John and Jane choose whether to vote or not to vote.arrow_forwardQUESTION 4 Suppose there are 2 players in a non- cooperative game theory situation. Player A can move Up or Down while Player B can choose Left or Right. The following matrix contains the payoffs that each player receives under 4 scenarios. The first number in each cell refers to the payoffs for Player A. Player A Up Down A. B. C. 10, 60 D. 20, 80 Player B Suppose Player A moves first and Player B moves second. There is one equilibrium, Up, Left Left There is one equilibrium: Down, Right. 50, 90 40, 50 There are two equilibria, (Down, Left) and (Up, Right) Right There is one equilibrium in this game, Up Rightarrow_forward
- Suppose two players play the prisoners' dilemma game a finite number of times, both players are rational, and the game is played with complete information, is a tit-for-tat strategy optimal in this case? Explain using your own words.arrow_forwardA special situation that is taken from game theory where two individuals, even though they would benefit from working together, have incentives to act differently is calledarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education