
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Consider the following data for two products of Vigano Manufacturing.
| Activity | Budgeted Cost | Activity Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Machine setup | $ 19,000 | (20 machine setups) |
| Parts handling | 15,200 | (16,000 parts) |
| Quality inspections | 22,800 | (100 inspections) |
| Total budgeted |
$ 57,000 |
| Unit Information | Product A | Product B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units produced | 1,900 | units | 380 | units |
| Direct materials cost | $ 29 | per unit | $ 39 | per unit |
| Direct labor cost | $ 49 | per unit | $ 59 | per unit |
| Direct labor hours | 2 | per unit | 2.50 | per unit |
1. Using a plantwide overhead rate based on 4,750 direct labor hours, compute the total product cost per unit for each product.
2. Consider the following additional information about these two products. If activity-based costing is used to allocate overhead cost, (a) compute overhead activity rates, (b) allocate overhead cost to Product A and Product B and compute overhead cost per unit for each, and (c) compute product cost per unit for each.
| Actual Activity Usage | Product A | Product B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Setups | 8 | setups | 12 | setups |
| Parts | 10,000 | parts | 6,000 | parts |
| Inspections | 40 | inspections | 60 | inspections |
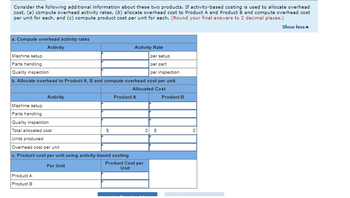
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following additional information about these two products. If activity-based costing is used to allocate overhead
cost, (a) compute overhead activity rates, (b) allocate overhead cost to Product A and Product B and compute overhead cost
per unit for each, and (c) compute product cost per unit for each. (Round your final answers to 2 decimal places.)
Show less
a. Compute overhead activity rates
Activity
Machine setup
Parts handling
Quality inspection
per setup
per part
per inspection
b. Allocate overhead to Product A, B and compute overhead cost per unit
Allocated Cost
Activity
Machine setup
Parts handling
Quality inspection
Total allocated cost
Units produced
Product A
Product B
$
Activity Rate
Overhead cost per unit
c. Product cost per unit using activity-based costing
Per Unit
Product A
Product Cost per
Unit
0 $
Product B
0
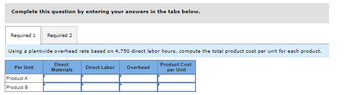
Transcribed Image Text:Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Required 1 Required 2
Using a plantwide overhead rate based on 4,750 direct labor hours, compute the total product cost per unit for each product.
Direct
Materials
Product Cost
per Unit
Per Unit
Product A
Product B
Direct Labor Overhead
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Assign overhead using traditional costing and ABC. E5.21 (LO 1, 2, 4) Shady Lady sells window coverings to both commercial and residential customers. The following information relates to its budgeted operations for the current year: Revenues Commercial $300,000 Residential $480,000 Direct material costs $ 30,000 Direct labour costs 100,000 Overhead costs 55,000 Operating income (loss) 185,000 $115,000 $ 70,000 300,000 162,000 532,000 $(52,000) The controller, Susan Chan, is concerned about the residential product line. She cannot understand why this line is not more profitable given that window coverings are less complex to install for resi- dential customers. In addition, the residential client base resides close to the company office, so travel costs are not as expensive on a per-client visit for residential customers. As a result, she has decided to take a closer look at the overhead costs assigned to the two product lines to determine whether a more accurate product costing model…arrow_forwardAnthon Corporation has provided the following information regarding last month's activities. Units produced (actual) Master production budget Direct materials Direct labor Overhead Standard costs per unit Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Actual costs Direct materials purchased and used Direct labor Overhead 10,500 $ 237,600 201,600 267,000 $ 3.96 per liter x 5 liters per unit of output $ 33.60 per hour x 0.5 hour per unit $ 28.50 per direct labor-hour $ 207,480 (53,200 liters) 176,472 (5,160 hours) 272,000 (58% is variable) Variable overhead is applied on the basis of direct labor-hours Required: Calculate all variable production cost price and efficiency variances and fixed production cost price and production volume variance- Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Indicate the effect of each veriance by selecting "F" for favorable, or "U" for unfavorable. If there is no effect, do not select either option.arrow_forwardcompute the budgeted factory overhead rate (i.e., the $ rate per activity base hour, etc.) for department xarrow_forward
- Panamint Systems Corporation is estimating activity costs associated with producing disk drives, tapes drives, and wire drives. The indirect labor can be traced to four separate activity pools. The budgeted activity cost and activity base data by product are provided below. Activity Cost Activity Base Procurement $331,200 Number of purchase orders Scheduling 206,700 Number of production orders Materials handling 450,000 Number of moves Product development 799,500 Number of engineering changes Production 1,521,400 Machine hours Number of Number of Number Number of Number Purchase Production of Engineering Machine of Orders Orders Moves Changes Hours Units Disk drives 4,030 290 1,340 13 2,100 1,600 Tape drives 2,500 175 600 8,400 3,900 Wire drives 11,200 730 3,600 22 10,400 2,800 The activity rate for the materials handling cost pool is O a. $81.23 per move Ob. $18.68 per move Oc. $72.79 per move Od. $172.97 per movearrow_forwardActivity Casting Assembly Inspecting Budgeted Activity Cost Activity Base Machine hours Direct labor hours Number of inspections Number of setups Number of loads $312,000 201,620 36,400 Setup 37,000 Materials handling 42,750 Corporate records were obtained to estimate the amount of activity to be used by the two products. The estimated activity-base usage quantities and units produced follow: Activity Base Entry Dining. Total Machine hours 5,510 4,890 10,400 Direct labor hours 4,740 7,120 11,860 Number of inspections 1,980 620 2,600 Number of setups 200 50 250 Number of loads 750 200 950 Units produced 11,000 5,500 16,500 a. Determine the activity rate for each activity. If required, round the rate to the nearest dollar. Activity Rate Activity Casting per machine hour foot lehne hourarrow_forwardCraftmore Machining reports the following budgeted overhead cost and related data for this year. Activity Budgeted Cost Activity Cost Driver Budgeted Activity Usage Assembly $ 399,750 Direct labor hours (DLH) 13,000 Product design 61,500 Engineering hours (EH) 1,230 Electricity 20,500 Machine hours (MH) 10,000 Setup 51,250 Setups 410 Total $ 533,000 Required:1. Compute a single plantwide overhead rate assuming the company allocates overhead cost based on 13,000 direct labor hours.2. Job 31 used 240 direct labor hours and Job 42 used 520 direct labor hours. Allocate overhead cost to each job using the single plantwide overhead rate from part 1.3. Compute an activity rate for each activity using activity-based costing.4. Allocate overhead costs to Job 31 and Job 42 using activity-based costing. Activity Cost Driver Activity Usage Job 31 Job 42 Direct labor hours (DLH) 240 520 Engineering hours (EH) 27 33 Machine hours (MH) 60 60 Setups 5 7arrow_forward
- Dawson Company manufactures small table lamps and desk lamps. The following shows the activities per product and the total overhead information: Units Setups Inspections Assembly (dlh) 2,700 4,000 8,000 8,000 Small table lamps Desk lamps Activity Setups 9,150 15,250 44,400 44,400 Total Activity-Base Usage Budgeted Activity Cost 12,000 $102,000 24,400 129,320 77,700 310,800 Inspections Assembly (dlh) The total factory overhead to be allocated to desk lamps is Oa. $456,995 Ob. $228,498 Oc. $587,565 Od. $326,425arrow_forwardRiverbed Manufacturing has five activity cost pools and two products (a budget tape vacuum and a deluxe tape vacuum). Information is presented below: Activity Cost Pools Ordering and Receiving Machine Setup Machining Assembly Inspection Budget $ Cost Driver Orders Setups Machine hours Deluxe $ Parts Inspections Overhead cost per unit Est. Overhead $144,000 311,400 1,023,000 1,624,000 314,000 per unit Est. Use of Cost Drivers Budget per unit 600 500 150,000 1.200,000 550 Deluxe 400 Compute the overhead cost per unit for each product. Production is 700.000 units of Budget and 200.000 units of Deluxe. (Round per machine hour and per part values to 3 decimal places, eg 52.711. Round overhead cost per unit to 2 decimal places, e.g. 12.25 and cost assigned to 0 decimal places, eg. 2,500.) 400 100,000 800,000 450arrow_forwardPanamint Systems Corporation is estimating activity costs associated with producing disk drives, tapes drives, and wire drives. The indirect labor can be traced to four separate activity pools. The budgeted activity cost and activity base data by product are provided below. Activity Cost Activity Base Procurement $323,200 Number of purchase orders Scheduling 202,000 Number of production orders Materials handling 437,000 Number of moves Product development 700,700 Number of engineering changes Production 1,408,000 Machine hours Number ofPurchaseOrders Number ofProductionOrders NumberofMoves Number ofEngineeringChanges MachineHours NumberofUnits Disk drives 4,170 440 1,480 14 2,400 2,100 Tape drives 1,600 225 570 4 9,100 3,700 Wire drives 12,700 890 4,400 30 10,700 2,400 The activity rate for the procurement activity cost pool is a.$63.42 per purchase order b.$17.50 per purchase…arrow_forward
- s Laval produces lighting fixtures. Budgeted information for its two production departments follows. The departments use machine hours (MH) and direct labor hours (DLH). Overhead cost Direct labor hours Machine hours Fabricating $ 1,260,000 Desk lamp 131,600 DLH 90,000 MH 28,000 DLH 72,500 MH Laval reports the following for one of its products, a desk lamp. Fabricating Department Number of Direct Labor Hours Units per Unit 6,000 4 DLH per unit Assembly $ 336,000 Machine Hours per Unit 3 MH per unit Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required: 1. Determine the plantwide overhead rate using 159,600 direct labor hours as the allocation base. 2. Determine the overhead cost per unit for the desk lamp using the plantwide overhead rate. 3. Compute departmental overhead rates based on machine hours in the Fabricating department and direct labor hours in the Assembly department. 4. Determine the overhead cost per unit for the desk lamp using the departmental overhead rates. Complete this question…arrow_forwardDawson Company manufactures small table lamps and desk lamps. The following shows the activities per product and the total overhead information: Line Item Description Units Setups Inspections Assembly (dlh) Small table lamps 4,000 3,500 9,450 45,600 Desk lamps 8,100 7,000 15,750 45,600 Activity Total Activity-Base Usage Budgeted Activity Cost Setups 10,500 $95,550 Inspections 25,200 168,840 Assembly (dlh) 79,800 255,360 The total factory overhead to be allocated to desk lamps is a. $315,145 b. $409,689 c. $567,261 d. $189,087arrow_forwardPlease do not give solution in image formatarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education