
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
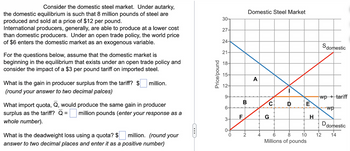
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the domestic steel market. Under autarky,
the domestic equilibrium is such that 8 million pounds of steel are
produced and sold at a price of $12 per pound.
International producers, generally, are able to produce at a lower cost
than domestic producers. Under an open trade policy, the world price
of $6 enters the domestic market as an exogenous variable.
For the questions below, assume that the domestic market is
beginning in the equilibrium that exists under an open trade policy and
consider the impact of a $3 per pound tariff on imported steel.
What is the gain in producer surplus from the tariff? $ million.
(round your answer to two decimal palces)
What import quota, Q, would produce the same gain in producer
surplus as the tariff? Q
million pounds (enter your response as a
whole number).
million. (round your
What is the deadweight loss using a quota? $
answer to two decimal places and enter it as a positive number)
Price/pound
30-
27-
24-
21-
18-
15-
12-
9-
6-
3-
0+
0
B
F
2
Domestic Steel Market
A
C
G
D
E
6
8
10
Millions of pounds
H
Sdomestic
wp + tariff
wp
12
D domestic
14
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Country X has 100 units of labour and country Y has 200 units of labour. Both countries produce computers and televisions. The unit labour requirements are given in the table below: Computers Televisions Country X 50 Country Y 100 Assume that free trade exists and that the relative price is such that both countries specialize completely in the industry in which they have a comparative advantage (neither country produces both goods). The supply of computers relative to televisions will be Select one: a. 0.02 (or 1/50) O b. 0.013 (or 1/75) c. 0.01 (or 1/100) d. impossible to determine without knowing the relative price of computers in terms of televisionsarrow_forwardAnswer the following with complete solution What is the production level of X and Y in nation A and nation B if they decide to trade? What is the level of consumption of nations A and B after trade? Show whether each nation will improve its welfare if it trades with another nation. Show full solutionarrow_forwardConsider two countries, Home and Foreign. In the figure below, the import demand ("IDHome") curve depicts Home's demand for Foreign's flash drives, and the import supply curve ("ISForeign") depicts Foreign's supply of flash drives to Home. Assume Home is a "large" country that levies a tariff against Foreign imports of flash drives, thereby shifting the relevant supply curve from ISForeign to ISForeign +t. For the following questions, please refer to the figure below. P $30 28 26 24 22 20 18 16 15-- 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 2 4 ISForeign +t 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 22 24 26 28 ISForeign IDHome 30 Q With free trade, Home's consumer surplus equals $112.50 and Foreign's producer surplus equals $112.50. With a tariff of $ 12 per flash drive, Home's consumer surplus equals $72, Foreign's producer surplus equals $ 36, Home's tariff revenue equals $72, and Home's deadweight loss equals $45. Of the Home's tariff revenue, $36 comes from Foreign's producers, and the rest comes from Home's consumers.…arrow_forward
- The answer should be typed.arrow_forwardSuppose Jordan is open to free trade in the world market for oranges. Because of Jordan's small size, the demand for and supply of oranges in Jordan do not affect the world price. The following graph shows the domestic oranges market in Jordan. The world price of oranges is Pw = $800 per ton. Throughout this problem, assume that changes in trade policies in other nations do not significantly affect the world market for oranges and that there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in oranges. Also assume that domestic supplies will satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place. On the following graph, use the green triangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing consumer surplus (CS) when the economy is at the free-trade equilibrium. Then, use the purple triangle (diamond symbols) to shade the area representing domestic producer surplus (PS). PRICE (Dollars per ton) 1280 1220 1160 1100 1040…arrow_forwardConsider a region with two export products (gloves and socks) and two local goods (tattoos and manicures). The production of each export good is subject to localization economies, so each city specializes in one export good. According to Mr. Wizard, “If my two assumptions (one for export products and one for local goods) are correct, all the cities in the region will be the same size.” Assume that Mr. Wizard’s logic is correct. List his assumptions and explain why together they imply the region’s cities will be the same size.arrow_forward
- Suppose Colombia is open to free trade in the world market for soybeans. Because of Colombia’s small size, the demand for and supply of soybeans in Colombia do not affect the world price. The following graph shows the domestic soybeans market in Colombia. The world price of soybeans is PW=$400 per ton.arrow_forwardRefer to the diagram to the right. The closed-economy 40 equilibrium price is $14. The world price is $8. What is the quantity of imports at the world price of $8 plus a $2 tariff? Imports 30 units. (Enter your response as a whole number) How much tariff revenue is generated by the $2 tariff? Tariff revenue $ (Enter your response as a whole number) 20- 18- 16- 14- 12- 10- 8- 6- 4- Price, P 20 A Shome 30 40 50 60 70 80 Quantity Pw+t Pw Drome 90 100arrow_forwardThe following graph shows the domestic supply of and demand for maize in Burundi. The world price (Pw) of maize is $270 per ton and is represented by the horizontal black line. Throughout the question, assume that the amount demanded by any one country does not affect the world price of maize and that there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in maize. Also, assume that domestic suppliers will satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place. 450 Domestic Demand Domestic Supply 430 410 390 370 350 330 310 290 P 270 250 40 80 120 180 200 240 280 320 360 400 QUANTITY (Tons of maize) If Burundi is open to international trade in maize without any restrictions, it will import tons of maize. Suppose the Burundian government wants to reduce imports to exactly 160 tons of maize to help domestic producers. A tariff of per ton will achieve this. A tariff set at this level would raise $ in revenue for the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education