
Economics:
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781285859460
Author: BOYES, William
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
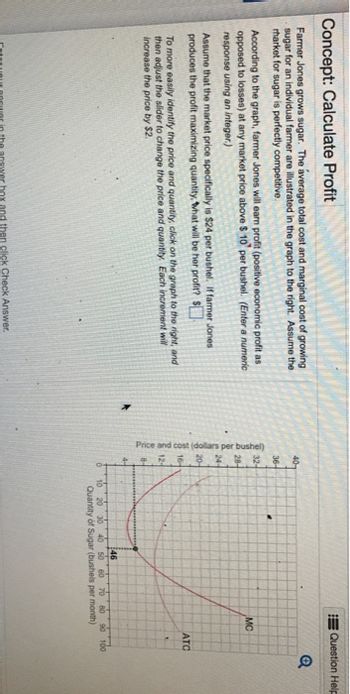
Transcribed Image Text:Concept: Calculate Profit
Farmer Jones grows sugar. The average total cost and marginal cost of growing
sugar for an individual farmer are illustrated in the graph to the right. Assume the
rharket for sugar is perfectly competitive.
According to the graph, farmer Jones will earn profit (positive economic profit as
opposed to losses) at any market price above $10 per bushel. (Enter a numeric
response using an integer.)
Assume that the market price specifically is $24 per bushel. If farmer Jones
produces the profit maximizing quantity, what will be her profit? $
To more easily identify the price and quantity, click on the graph to the right, and
then adjust the slider to change the price and quantity. Each increment will
increase the price by $2.
Enter your answer in the answer box and then click Check Answer.
40-
36-
32-
MC
28-
24-
20-
Price and cost (dollars per bushel)
12-
ATC
46
20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Quantity of Sugar (bushels per month)
Question Help
Q
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Suppose Larry runs a small business that manufactures shirts. Assume that the market for shirts is a price-taker market, and the market price is $10 per shirt. The following graph shows Larry's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for the first seven shirts that Larry produces, including zero shirts. 125 100 TOTAL COST AND REVENUE (Dollars) 25 ☐ Total Cost ☐ -50 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 QUANTITY (Shirts) Total Revenue A Profit (?) Calculate Larry's marginal revenue and marginal cost for the first seven shirts he produces and plot them on the following graph. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot marginal revenue and the orange points (square symbol) to plot marginal cost. 25 2 COSTS AND REVENUE (Dollars per shirt) 0 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 QUANTITY (Shirts) Marginal Revenue Marginal Cost Larry's profit is maximized when he produces is shirts. When he does this, the marginal cost of the previous shirt he…arrow_forwardFarmer Lee grows strawberries. The average total cost and marginal cost of growing strawberries in the long run for an individual farmer are illustrated in the graph to the right. Suppose the market price is $7.05 per box. If so, then farmers will strawberries until the market price is $ number rounded to two decimal places.) per box. (Enter a numeric the market for a real enter exit Price and cost (dollars per box) 10- 9- 8- 5- 3- 2- 1. 0 MC ATC 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Quantity of strawberries (boxes per week) oarrow_forward3. Profit maximization using total cost and total revenue curves Suppose Jayden operates a handicraft pop-up retail shop that sells rompers. Assume a perfectly competitive market structure for rompers with a market price equal to $20 per romper. The following graph shows Jayden's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for rompers for quantities zero through seven (including zero and seven) that Jayden produces. 200 175 150 125 100 TOTAL COST AND REVENUE (Dollars) 75 50 25 25 ח ☐ -25 0 1 2 ☐ ☐ ? Total Revenue Total Cost Profit 5 6 7 8 3 4 QUANTITY (Rompers)arrow_forward
- The following graph plots daily cost curves for a firm operating in the competitive market for jumpsuits. Hint: Once you have positioned the rectangle on the graph, select a point to observe its coordinates. PRICE (Dollars per jumpsult) 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 10 W 0 Y ATC AVC 2 MC 4 8 QUANTITY (Thousands of jumpsuits per day) 6 10 + 14 16 18 12 20 Profit or Loss In the short run, given a market price equal to $15 per jumpsuit, the firm should produce a daily quantity of of On the preceding graph, use the blue rectangle (circle symbols) to fill in the area that represents profit or loss of the firm given the market price of $15 and the quantity of production from your previous answer. Note: In the following question, enter a positive number regardless of whether the firm earns a profit or incurs a loss. The rectangular area represents a rt-run thousand per day for the firm. jumpsuits.arrow_forwardSuppose that the market for cashmere sweaters is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 100 90 Profit or Loss 80 70 60 40 ATC 30 20 MC AVC 10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 QUANTITY (Thousands of sweaters per day) In the short run, at a market price of $45 per sweater, this firm will choose to produce 45,000 sweaters per day. On the preceding graph, use the blue rectangle (circle symbols) to shade the area representing the firm's profit or loss if the market price is $45 and the firm chooses to produce the quantity you already selected. Note: In the following question, enter a positive number, even if it represents a loss. The area of this rectangle indicates that the firm's would be thousand per day in the short run. PRICE (Dollars per sweater)arrow_forwardPlease show working and calculations.arrow_forward
- The graph below shows the marginal cost (MC), average variable cost (AVC), and average total cost (ATC) curves for a firm in a competitive market. These curves imply a short-run supply curve that has two distinct parts. One part, not shown, lies along the vertical axis (quantity-0); this represents a condition of production shutdown. Where is the other part? Use the straight-line tool to drawit. To refer to the graphing tutorial for this question type, please click here Price and cost 18 15 14 13 12 10 19/21 SUBMIT ANSWER 13 OF 21 QUESTIONS C OMPLETED 28 MacBook Pro 금□ F7 F8 F9 F1o F2 F3 F5arrow_forwardSuppose that the market for microwave ovens is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. PRICE (Dollars per oven) 100 90 80 70 40 30 20 10 0 0 5 0 MC ATC AVC 10 15 20 25 30 35 QUANTITY (Thousands of ovens) 40 45 50 (?)arrow_forwardTOTAL COST AND REVENUE (Dollars) -25 Suppose Lorenzo runs a small business that manufactures teddy bears. Assume that the market for teddy bears is a price-taker market, and the market price is $10 per teddy bear. The following graph shows Lorenzo's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue, and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for the first seven teddy bears that Lorenzo produces, including zero teddy bears. 125 Total Cost 100 Total Revenue 75 -50 1 2 5 6 QUANTITY (Teddy bears) Profit Calculate Lorenzo's marginal revenue and marginal cost for the first seven teddy bears he produces, and plot them on the following graph. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot marginal revenue and the orange points (square symbol) to plot marginal cost. ? COSTS AND REVENUE (Dollars per teddy bear) 2 3 5 QUANTITY (Teddy bears) Marginal Revenue Marginal Cost Lorenzo's profit is maximized when he produces teddy bears. When he does this, the marginal…arrow_forward
- Suppose Hubert runs a small business that manufactures shirts. Assume that the market for shirts is a price-taker market, and the market price is $10 per shirt. The following graph shows Hubert's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue, and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for the first seven shirts that Hubert produces, including zero shirts. TOTAL COST AND REVENUE (Dollars) 125 100 75 50 25 -25 -50 0 0 1 2 ☐ ■ U 3 4 5 QUANTITY (Shirts) L 6 Total Cost 7 8 Total Revenue Profit ? Calculate Hubert's marginal revenue and marginal cost for the first seven shirts he produces, and plot them on the following graph. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot marginal revenue and the orange points (square symbol) to plot marginal cost.arrow_forwardSuppose that the market for dress shirts is a perfectly competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. (?) 50 45 Profit or Loss 40 35 30 АТС 25 20 15 10 AVC MC 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 QUANTITY OF OUTPUT (Shirts) PRICE AND COST (Dollars per shirt)arrow_forward4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose that the market for blenders is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point. 100 90 80 Profit or Loss 70 АТС 30 AVC 20 MC 10 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY (Thousands of blenders per day) blenders per day. In the short run, at a market price of $50 per blender, this firm will choose to produce PRICE (Dollars per blender)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning


Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Cengage Learning
