
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
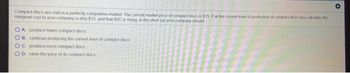
Transcribed Image Text:Compact discs are sold in a perfectly competitive market. The current market price of compact discs is $15. If at the current level of production of compact docs you calculate the
marginal cost to your company is also $15, and that AVC is rising, in the short run your company should
OA produce fewer compact discs
OB. continue producing the current level of compact discs
OC. produce more compact discs
OD. raise the price of its compact discs
*
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question attahed in imagearrow_forwardThe figures below show (on the left) two possible demand curves and (on the right) two possible supply curves in the perfectly competitive hamburger market. Price per hamburger 0 A B D₂ D₁ Hamburgers per month Price per hamburger 0 Select one: a. Movement along D₁ from Point A to Point B. b. Demand shifts from D₁ to D₂. F c. Movement along S₁ from Point F to Point G. d. Demand shifts from D₂ to D₁. G Hamburgers per month Assume that people consume either hamburgers or hot dogs. What will be the result of a decrease in the price of hot dogs? Hint: Are hamburgers and hotdogs complements or substitutes? S₂ S₁arrow_forwardA local pizzeria only servers two items: pizzas and sandwiches. An increase in the demand for sandwiches will result in which of the following for the firm? O an increase the opportunity cost of producing pizzas O an increase in the amount of resources the firm devotes to producing pizzas O a decrease in the price of bread a decrease in the price of sandwiches a decrease in the firm's overall revenuearrow_forward
- If a profit-maximizing, competitive firm is producing a quantity at which marginal cost is between average variable cost and average total cost, it will O keep producing in the short run but exit the market in the long run. O shut down in the short run but return to production in the long run. O shut down in the short run and exit the market in the long run. O keep producing both in the short run and in the long run.arrow_forwardWhich is an example of an almost perfectly competitive market? O the market in licensed physical therapy services O the antique furniture market O the market in pain medications the stock market the National Hockey Leaguearrow_forwarder 11 i Suppose the market for corn is a purely competitive, constant-cost industry that is in long-run equilibrium. Now assume that an increase in consumer demand occurs. After all resulting adjustments have been completed, the new equilibrium price will be Multiple Choice OO O the same as the initial equilibrium price, but the new industry output will be greater than the original output. greater than the initial price, and the new industry output will be greater than the original output. less than the initial price, but the new industry output will be greater than the original output. the same as the initial equilibrium price, and the industry output will remain unchanged. 23 11,229 X OCT all Z Aarrow_forward
- PRICE A பயடு X Figure 16-8 B T LL L QUANTITY M MC ATC Demand MR Refer to Figure 16-8. Which of the following best describes the profit-maximizing outcome for the firm depicted her a. This firm is in long run equilibrium and will continue to earn zero profit. b. This firm is earning zero profit in the short run, but will earn a positive profit in the long run. c. This firm is incurring a short-run loss, but will earn zero profit in the long run. d. This firm is earning a short-run profit, but will earn zero profit in the long run.arrow_forward20 12 10 0 MC ATC -MR 10 Quantity (units) Figure 11.4.1 Refer to Figure 11.4.1, which shows the cost curves and marginal revenue curve of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. In the long run, market O supply will decrease. demand will decrease. O supply and market demand will decrease. supply will increase. O demand will increase.arrow_forwardThe short-run elasticity of supply curve is steep because O A. diminishing marginal returns restrict output in the short run. OB. production facilities have a fixed capacity in the short run. OC. new firms enter the market with new production facilities. OD. of both A and B. SURU O E. All of the above.arrow_forward
- How does an increase in market demand for a product in a perfectly competitive market affectthe short-run and long-run equilibrium? Show on a diagram and discuss the adjustments firms make in terms of price and quantity to reach the new equilibrium. Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardUrgently needarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education