
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Colchicine is a medication most commonly used to treat inflammatory arthritis called gout. Colchicine interferes with the functioning of the spindle apparatus during mitosis by preventing the chromatids from lining up in the centre of the cell. In a cell, the spindle fibres are used to control the movement and segregation of chromosomes during division.
Which stage of mitosis is affected by Colchicine?
_______(choose between: stages 1 and 5, stages 2 and 6, stages 3 and 7 or stages 4 and 8) which are in ________ (choose between: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphrase or telophase)
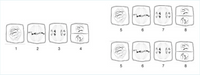
Transcribed Image Text:6
3
4
య
1
8
6.
2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Answer each question with a paragraph; 3-5 sentences each. Explain the difference between a proto-oncogene and a tumor-suppressor gene. Explain the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Explain the difference between positive regulation of the cell cycle and negative regulation of the cell cycle. Explain the difference between normal p53 and mutated p53. Find two differences and two similarities between binary fission and mitosis.arrow_forwardIn the absence of cdc25 cells would not be able to undergo mitosis. True or False?arrow_forwardMitosis: Naming the Stages of Mitosis The pictures of the mitotic stages below are NOT in the correct chronological sequence. Name each stage of mitosis, A to E. Each answer choice is used once and only once. E. Picture A [Choose ] Picture B (Choose ] Picture C [Choose ) Picture D Choose] Picture E Choose]arrow_forward
- Explain how mitosis is involved with development of cancer.arrow_forwardUsing my chart attached, can you please help me answer this question? According to your results, what porportion (or percentage) of time do onion root cells spend in Mitosis?arrow_forwardIn July 2015, a report was released indicating the gram-negative bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosawas found on hospital sinks 10 years after the initial outbreak in a neonatal intensive care unit. unit. aeruginosa usually causes localized ear and eye infections but can cause pneumonia or septicemia in vulnerable individuals like newborn babies. Explain how presence of this reported P. aeruginosa could lead to a recurrence of nosocomial disease. Would infection from this pathogenic species be considered a primary or opportunistic?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education