
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Presented in the left graph are trends in sales revenue and cash received from customers over a six-year period. In the right graph are trends in cost of goods sold and cash paid for inventory over a six-year period. All inventory is purchased with cash.
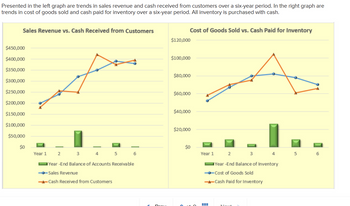
Transcribed Image Text:Presented in the left graph are trends in sales revenue and cash received from customers over a six-year period. In the right graph are
trends in cost of goods sold and cash paid for inventory over a six-year period. All inventory is purchased with cash.
$450,000
Sales Revenue vs. Cash Received from Customers
Cost of Goods Sold vs. Cash Paid for Inventory
$120,000
$400,000
$350,000
$300,000
$250,000
$200,000
$100,000
$80,000
$60,000
$40,000
$150,000
$100,000
$20,000
$50,000
$0
$0
Year 1
2
3
4
5 6
Year 1
2
3
4
5
6
Year-End Balance of Accounts Receivable
Year-End Balance of Inventory
-Sales Revenue
-Cash Received from Customers
-Cost of Goods Sold
-Cash Paid for Inventory
Transcribed Image Text:Click here to open the graphs in a new tab.
Required:
1. In Year 1, which is higher - Sales Revenue or Cash Received?
2. In which year is it most likely the company had a large sale on account without cash
being collected?
3. In which year does it appear the cash from that large sale on account is collected?
4. In a year that cash received from customers is greater than sales revenue, the year-
end balance of Accounts Receivable:
5. In Year 1, which is higher - Cost of Goods Sold or Cash Paid?
6. In which year is it most likely the company had a large purchase of inventory without
it being sold?
7. In which year does it appear the excess inventory was sold without an additional
cash purchases of inventory to replace it?
8. In a year that cash paid to purchase inventory is greater than cost of goods sold, the
year-end balance of Inventory:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Following is an incomplete current-year income statement. Determine Net Sales, Cost of goods sold and Net Income. Additional information follows: Return on total assets is 16% (average total assets is $62,500). Inventory turnover is 5 (average inventory is $7,800). Accounts receivable turnover is 8 (average accounts receivable is $7,700). Income Statement Net Sales Cost of goods sold Selling, general, and administrative expenses 8800 Income tax expenses 3800 Net Incomearrow_forwardThe financial statements of the Sunland Company report net sales of $384000 and accounts receivable of $50400 and $33600 at the beginning of the year and the end of the year, respectively. What is the average collection period for accounts receivable in days?arrow_forwardA condensed income statement for Weber Associates and a partially completed vertical analysis follow. Required: 1. Complete the vertical analysis by computing each missing line item as a percentage of net revenues. TIP: In the prior year, Cost of Goods Sold was 31 percent of Net Revenues, computed as ($1,397 ÷ $4,571). 2. Does Cost of Goods Sold, as a percentage of Net Revenues, represent better or worse performance in 2019 as compared to 2018? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Complete the vertical analysis by computing each missing line item as a percentage of net revenues. TIP: In the prior year, Cost of Goods Sold was 31 percent of Net Revenues, computed as ($1,397 ÷ $4,571). (Decreases should be indicated by a minus sign. Round your answers to the nearest whole percent.) Net Revenues Cost of Goods Sold Research and Development Expense Sales and Marketing Expense General and Administrative Expense Income from Operations Other…arrow_forward
- Please help mearrow_forwardWhat is the ratio that measures the number of days on average the company takes to turn its inventory into sales? Days sales outstanding Days inventory outstatnding Days payable outstatnding Days order outstandingarrow_forwardIn a common-sized income statement, 100% is the a. net cost of goods sold b. gross profit c. sales d. net incomearrow_forward
- Rahularrow_forwardNeed the answers in that formats thank youarrow_forwardWhat are the following amounts for the year ended 2/1/20: Net Sales _________ Cost of Goods Sold ____________ Gross Margin ____________ Gross Margin Percentage ____________ Operating Income ____________ Net Income ____________arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education