
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337399425
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
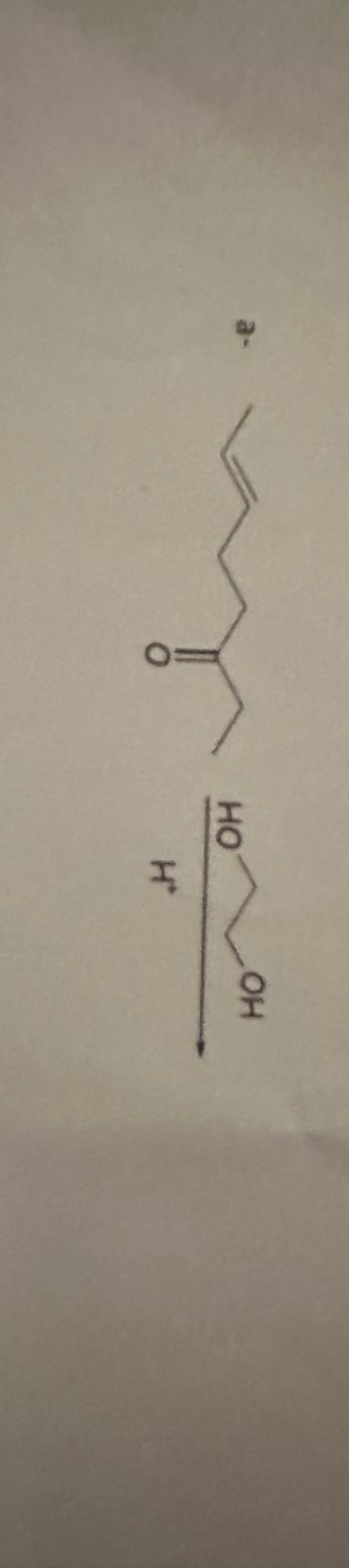
Transcribed Image Text:The image shows a chemical structure of a reaction. The reaction diagram includes:
1. **Reactant Structure**: On the top part, there is a linear representation of a carbon chain. It includes a ketone group (indicated by a carbon double-bonded to oxygen). The carbon chain appears to have seven carbon atoms with a double bond present within the chain.
2. **Reagent**: Below the arrow, there is a notation of "I₂" with an adjacent structure indicating iodine in the presence of hydroxide ions (OH⁻).
**Reaction Explanation**:
- The chemical structure represents a ketone reacting with iodine (I₂) in the presence of hydroxide ions (OH⁻).
- This typically indicates the iodoform reaction, where methyl ketones or alcohols that oxidize to methyl ketones are treated with iodine and a base to yield iodoform as a precipitate.
This information can be used to understand reactions involving halogenation and study the properties of carbonyl compounds.
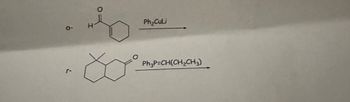
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts two chemical reactions involving organic compounds.
1. **Reaction 1:**
- **Reactant:** The reactant is a cyclohexenone structure with an aldehyde group attached (O═H).
- **Reagent:** Ph₂CuLi (Diphenylcopper lithium).
- **Process:** This reaction involves the addition of the Ph₂CuLi to the α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compound (cyclohexenone), potentially leading to a conjugate addition or 1,4-addition.
2. **Reaction 2:**
- **Reactant:** The structure is a bicyclic compound with an oxygen heteroatom in one of the rings.
- **Reagent:** Ph₃P=CH(CH₂CH₃) (Wittig reagent).
- **Process:** This is a Wittig reaction, where the phosphonium ylide reacts with the carbonyl group of the bicyclic compound to form an alkene by replacing the carbonyl oxygen with a C=C bond.
These reactions are commonly used in organic synthesis for modifying carbonyl compounds and creating new carbon-carbon double bonds.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- . For the reaction N2(g)+3H2(g)2NH3(g), list the types of bonds that must be broken and the type of bonds that must form for the chemical reaction to take place.arrow_forward12. Name each chemical and complete the reaction ↑ Add file + H₂Oarrow_forwardThe true statement concerning the accompanying diagram is: Ep reactant products Reaction Progressarrow_forward
- Subject- chemistryarrow_forwardWhat is the law of mass action? O The ratio of the product concentrations to the reactant concentrations is a constant that depends on the system. O The ratio of product concentrations to reactant concentrations raised to stoichiometric coefficients is a constant at equilibrium. O The ratio of product concentrations is always a constant based on the stoichiometry of the chemical reaction. O The reaction will proceed until all of the reactants are consumed to form the products of the reaction.arrow_forwardCould someone please help me with this? No Plagirisim Please! Use the table below to complete the following: Based on your observations, develop a model to describe how the following changes impact a chemical system at equilibrium Increasing the concentration of a reactant in a system Decreasing the concentration of a reactant in a system Increasing the concentration of a product in a system Decreasing the concentration of a product in a system Adding heat to a system Removing heat from a system Model Format Reactants Products Change applied Expected direction of shift Explanation Increasing the concentration of a reactant in a system Shift right toward product Because an increase in reactant then the system needs to adjust for equilibrium by shifting to the opposing side Decreasing the concentration of a reactant in a system Increasing the concentration of a product in a system Decreasing the concentration of a product in a system Adding…arrow_forward
- 1) Can you explain in full detail what you think is happening on the molecular level for this reaction? Specifically, the role of each reactant. 2)Using a molecular level explanation, please explain why this reaction occurs? Specifically, why the reactants form the products shown.arrow_forwardO Launch Meeting - Zoom O Launch Meeting - Zoom od212ou%3D2591470&isprv &drc3D1&qi=24592388cfql%=D08drnb- ttempt 1 A honeycomb-shape casing of the metals platinum (Pt), rhodium (Rh), and palladium (Pd) in catalytic converters of automobiles cause more reactions to take place that produce less harmful gases without being affected by the reaction. These metals are catalysts because: They cause the reactions without being affected. They are formed into a honeycomb shape. They are metals. They help produce less harmful gasses.arrow_forward10. Lead (II) carbonate reacts with nitric acid to form lead (II) nitrate, water and carbon dioxide. 11. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) decomposes to produce liquid water and oxygen gas. 12. Magnesium chlorate decomposes to form magnesium chloride and oxygen gas. 13. Sodium sulfide reacts with nickel (II) nitrate to form nickel sulfide and sodium nitrate. 14. Aluminum, when hot enough, burns in air to form aluminum oxide. 15. Copper (I) oxide, heated in the presence of methane gas (CH4), produces pure copper metal and the gases carbon dioxide and water. 16. Solutions of sodium carbonate and iron (III) chloride react to form solid iron (III) carbonate and sodium chloride in solution.arrow_forward
- F3 4 g # E F4 14 $ R F F5 is 5 F6 T G B The reaction N₂ (g) + 2 O2 (g) → 2 NO2 (g) and therefore heat is 1 A) endothermic, released B) endothermic, absorbed C) exothermic, released F7 JL D) exothermic, absorbed Y H F8 Question 2 of 5 & 7 N Q U DELL F9 * 8 P M I F10 ( 9 K F11 ) O L ΔΗ= 66.4 kJ by the reaction. F12 P PrtScr 1 W @to Insert Delete Backspace Poarrow_forwardHelp pleasearrow_forwardPlease answer all!!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Chemistry
ISBN:9781559539418
Author:Angelica Stacy
Publisher:MAC HIGHER


Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co