
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781285199047
Author: John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
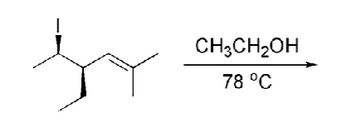
Transcribed Image Text:CH3CH2OH
78 °C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- (b) Study the following themochemical data very carefully: Ciz(g) - 2ci(g) I2(g) IC(g) - 1(g) + CI(g) I2(s) → 12(g) AH° = 242.3 kJ AH° = 151.0 kJ 21(g) AH° = 211.3 kJ AH° = 62.8 kJ I2(s) reacts with Cl2(g) to produce ICI(g). Write the chemical equation to produce ONLY one mole of ICI(g) (i) Calculate AH° for the reaction of I2(s) with Cl2(g) to form 1 mole of ICI(g). Use all the data given above. (ii) What law did you use to calculate AH° above? (iii) What are the names of the following processes? I2(s) → 12(g) I2(g) 21(g) ICI(g) I(g) + Cl(g)arrow_forwardNazCr207 H2, Ni 100 atm 150 °Carrow_forward[References] Given the following data СэНа (9) + 302(9) — 2 СО2(9) + 2Н,0() 2C2 H6 (g) + 702(9) → 4 CO2(g) + 6H2O(1) 2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2 O(1) ΔΗ -1411.0 kJ AH = -3119.8 kJ AH=-571.7 kJ calculate A H for the reaction C2H4 (9) + H2 (g) → C2H6 (9) ΔΗΞ kJ Submit Answer Try Another Version 3 item attempts remainingarrow_forward
- → N203(g) AH° (1) NO(g) + NO2(g) =-39.8 kJ rxn → N2O5(g) AH° rxn (2) NO(g) + NO2(g) + O2(g) =-112.5 kJ (3) 2NO2(g) → N2O4(g) AH :-57.2 kJ rxn (4) 2NO(g) + 02g) → 2NO2(g) AH° =-114.2 kJ rxn AH° subl (5) N2O5(s) N2O5(g) = 54.1 kJ Calculate the heat of reaction for N203(g) + N2O5(s) → 2N2O4(g) ΔΗ- kJarrow_forwardWhat mass of water will give up 240 calories when the temperature drops from 100 deg C to 68 deg C. 1 calorie = 4.184 J.arrow_forwardGiven the following data: Pa(s) + 6 Clz9) → 4PCI3(g) AH = -1225.6 kJ Pa(s) + 5 O2(g) → P4010(5) AH = -2967.3 kJ PCI3(g) + Clz(g) → PCI5(a) AH = -84.2 kJ PCI3(9) + O2lg) → ClaPO(9) AH = -285.7 kJ Calculate AH for the reaction P,O1015) + 6 PCI5(9) → 10 Cl3PO(g)arrow_forward
- You are given the following data: 2H(g) > H₂(g) - 2Br(g) - Br₂ (g) 2HBr(g) → H₂(g) + Br₂ (g) kJ mol → x10 ΔΗ° = -436.4 Calculate AH° for the reaction. H(g) + Br(g) HBr (g) Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. X ΔΗ° = -192.5 ΔΗ° = 72.4 kJ mol kJ mol kJ molarrow_forwardGiven the following data: C2H4(g) + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l) DH = -1411.0 kJ 2 C2H6(g) + 7 O2(g) → 4 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(l) DH = -3120.0 kJ 2 H2(g) + O2(g) → 2 H2O(l) DH = -571.6 kJ Calculate the enthalpy of the reaction: C2H4(g) + H2(g) → C2H6(g) DH = ___ kJarrow_forwardg) CH₂CI NaCN CH3CN Δarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning