
Concept explainers
Carbon disulfide is a colorless, volatile, highly flammable liquid with a very unpleasant smell that is used as a solvent in some laboratory applications. The formula for carbon disulfide is CS2. Formal charges can be used to decide whether its connectivity is more likely to be C–S–S or S–C–S.
Part1: Add any nonzero formal charges to the atoms as applicable for the Lewis structure shown with connectivity C–S–S. All valence electrons have been included, and this structure follows the octet rule. If formal charges are equal to zero, they should not be included.
Part2: Add any nonzero formal charges to the atoms as applicable for the Lewis structure shown with connectivity C–S–S. All valence electrons have been included. If formal charges are equal to zero, they should not be included. (This structure is a resonance form of the structure in Part 1.)
part 3: Add any nonzero formal charges to the atoms as applicable for the Lewis structure shown with connectivity S–C–S. All valence electrons have been included, and this structure follows the octet rule. If formal charges are equal to zero, they should not be included.
picture 1 is part 1
picture 2 is part 2
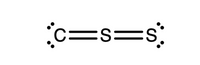
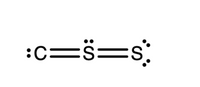
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

- A student proposes the following Lewis structure for the (PC14) ion. : Cl: - : : Cl P Cl: : | : Cl: Assign a formal charge to each atom in the student's Lewis structure. atom P formal charge left Cl ☐ top Cl ◎ right Cl bottom Cl Пarrow_forwardThe structure of nitric acid (HNO3), shown below, is incorrect. Which of the following statements, or combin statements, best describes the reason? The structure should have a +1 formal charge. oo many valence electrons in the molecule. e central Natom violates the octet rule. central N atom does not have a lone pair. HO :0=2arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution.arrow_forward
- Draw the Lewis structure for monochloramine, which is a covalent compound with the formula NH2Cl. Include all nonbonding electrons, such as lone pairs, and any nonzero formal charges. Draw the Lewis structure for hydrazine, which has the formula N2H4. Include all nonbonding electrons, such as lone pairs, and any nonzero formal charges.arrow_forwardTwo possible Lewis electron-dot diagrams for fulminic acid, HCNO, are shown below. Н—С%3DN—ӧ: Н—ё—N—ӧ: a. Explain why the diagram on the left is the better representation for the bonding in fulminic acid. Justify your choice based on formal charges. Fulminic acid can convert to isocyanic acid according to the equation below. HCNO(g)=HNCO(g) fulminic acid - isocyanic acid Fulminic Acid Isoeyanie Acid н-сек-ф н—й—с-б b. Using the Lewis electron-dot diagrams of fulminic acid and isocyanic acid shown in the boxes above and the table of average bond enthalpies below, determine the value of AH for the reaction of HCNO(g) to form HNCO(g). Enthalpy (kJ/mol) Enthalpy (kJ/mol) Enthalpy (kJ/mol) Bond Bond Bond N-O 201 C-N 615 Н-С 413 c=0 745 C=N 891 Н-N 391 c. A student claims that AS for the reaction is close to zero. Explain why the student's claim is accurate.arrow_forward5. There are three possible ways to linearly connect the atoms for an anion whose chemical formula is [CNO]. They are [CNO], [NOC], and [NCO]. Draw a Lewis structure (showing all bonds, lone pairs, and formal charges) for each of the three possible ions. Which is the most stable arrangement? (Hint: the most stable structure will be the one with the most octets, fewest and lowest formal charges, etc., as we discussed in class.)arrow_forward
- which of the following structures is/are correct lewis structures for a molecule with the chemical formula C2H6O and no formal chargesarrow_forwardSelect the Lewis structure for XeO2F2 which correctly minimizes formal charges. Show formal charges on each atom and that of the overall.arrow_forwardCalculate the formal charges of all of the atoms in each of the following molecules. Part A CO Enter the charge in the order in which the atoms are numbered. Seperate each charge with a comma. Make sure to include the appropriate "+" or "-" if the charge is not "O. :C=0: Πν ΑΣφarrow_forward
- proposed Lewis structure C=N :Z: N :Z: N || I :Z: N :Z: N Is the proposed Lewis structure reasonable? Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are: Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* 0 Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* .* * If two or more atoms of the same element don't satisfy the octet rule, just enter the chemical symbol as many times as necessary. For example, if two oxygen atoms don't satisfy the octet rule, enter "0,0". Śarrow_forward(b) The Murchison meteorite that landed in Australia in 1969 contained 92 different amino acids, including 21 found in Earth organism A skeleton structure (single bond only) of one of these extraterrestrial amino acids is shown below. Draw a Lewis structure, and identify any atoms having a nonzero formal charge. H3N. C ČH2 ČH3 (c) Draw the orbital diagrams and Lewis symbols to depict the formation of Na* and CI ions from the atoms. Give the formula of the compound formed. (d) The predicted bond length for HF is 109 pm (the sum of the covalent radii of H, 37 pm and F, 72 pm), however the actual bond length for HF is shorter (92 pm). It was observed that the difference between predicted and actual bond lengths becomes smaller going down the halogen group from HF to HI Describe these observationsarrow_forwardFor the phosphoric acid molecule (H3PO4), all four oxygen atoms are bonded to the central phosphorus atom and the three hydrogen atoms are bonded to different oxygen atoms. Several resonance structures can be drawn for H3PO4 but one structure is more important than the others. In the most important structure, the phosphorus atom has: a formal charge of +1 and a complete octet a formal charge of zero and a complete octet a formal charge of −1 and an expanded octet a formal charge of +5 and an expanded octet a formal charge of zero and an expanded octetarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





