
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
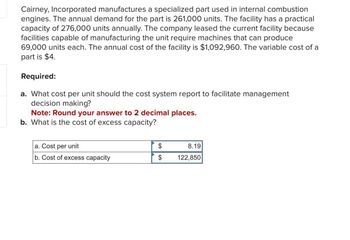
Transcribed Image Text:Cairney, Incorporated manufactures a specialized part used in internal combustion
engines. The annual demand for the part is 261,000 units. The facility has a practical
capacity of 276,000 units annually. The company leased the current facility because
facilities capable of manufacturing the unit require machines that can produce
69,000 units each. The annual cost of the facility is $1,092,960. The variable cost of a
part is $4.
Required:
a. What cost per unit should the cost system report to facilitate management
decision making?
Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
b. What is the cost of excess capacity?
a. Cost per unit
b. Cost of excess capacity
$
$
8.19
122,850
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A company makes 36,000 motors to be used in the production of its blender. The average cost per motor at this level of activity is: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead An outside supplier recently began producing a comparable motor that could be used in the blender. The price offered to the company for this motor is $23.95. There would be no other use for the production facilities and none of the fixed manufacturing overhead cost could be avoided. The annual financial advantage (disadvantage) for the company as a result of making the motors rather than buying them from the outside supplier would be: Multiple Choice O O O ($68,400) $214,200 $9.50 $ 8.50 $ 3.45 $ 4.40 90,000 $158,400arrow_forwardAhrends Corporation makes 46,000 units per year of a part it uses in the products it manufactures. The unit product cost of this part is computed as follows: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Unit product cost $ 14.30 23.90 3.00 28.30 $69.50 An outside supplier has offered to sell the company all of these parts it needs for $55.80 a unit. If the company accepts this offer, the facilities now being used to make the part could be used to make more units of a product that is in high demand. The additional contribution margin on this other product would be $368,000 per year If the part were purchased from the outside supplier, all of the direct labor cost of the part would be avoided. However, $24.90 of the fixed manufacturing overhead cost being applied to the part would continue even if the part were purchased from the outside supplier. This fixed manufacturing overhead cost would be applied to the company's remaining products What…arrow_forwardBenitez Company currently outsources a relay switch that is a component in one of its products. The switches cost $40 each. The company is considering making the switches internally at the following projected annual production costs: Unit-level material cost $ 8 Unit-level labor cost $ 7 Unit-level overhead $ 6 Batch-level set-up cost (4,000 units per batch) $ 30,000 Product-level supervisory salaries $ 40,000 Allocated facility-level costs $ 25,000 The company expects an annual need for 4,000 switches. If the company makes the product, it will have to utilize factory space currently being leased to another company for $2,000 a month. If the company decides to make the parts, total costs will be: Multiple Choice a.$18,000 more than if the switches are purchased. b.$43,000 more than if the switches are purchased. c.$22,000 less than if the switches are purchased. d.$25,000 less than if the switches are purchased.arrow_forward
- Division A has the capacity to produce 120,000 units. The normal selling price of each unit is P80. The variable cost incurred for each unit is P42. Total direct fixed cost for the relevant range is P1,150,000. Division B can use the products of Division A as an input in its manufacturing process but is currently acquiring the said products from an outside supplier. The price per unit is P75. Total annual demand is 30,000 units. Assuming sufficient capacity, what is the minimum acceptable transfer price to Division A? Assuming only 22,500 excess capacity, what is the minimum acceptable transfer price to Division A? Assuming only 22,500 excess capacity and that Division A can avoid variable selling cost per unit of P4 but will incur a one-time fixed cost of P30,000 for the order, what is the minimum acceptable transfer price to Division A? Assuming no excess capacity, what is the minimum acceptable transfer price to Division A? What is the maximum acceptable transfer…arrow_forwardColt Company owns a machine that can produce two specialized products. Production time for Product TLX is three units per hour and for Product MTV is five units per hour. The machine’s capacity is 2,600 hours per year. Both products are sold to a single customer who has agreed to buy all of the company’s output up to a maximum of 4,420 units of Product TLX and 5,995 units of Product MTV. Selling prices and variable costs per unit to produce the products follow. $ per unit Product TLX Product MTV Selling price per unit $ 11.50 $ 6.90 Variable costs per unit 3.45 4.14 Determine the company's most profitable sales mix and the contribution margin that results from that sales mix. (Round per unit contribution margins to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardJade Ltd. manufactures a product, which regularly sells for $67.75. This product has the following costs per unit at the expected production of 47,500 units: Cost Amount Direct labour $20.00 Direct materials 10.50 Manufacturing overhead (36% is variable) 24.00 The company has the capacity to produce 52,250 units. A wholesaler has offered to pay $77 for 12,000 units. If Jade Ltd. accepts this special order, operating income would increase (decrease) by how much?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education