
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
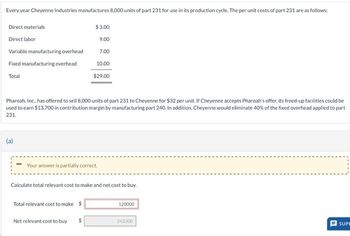
Transcribed Image Text:Every year Cheyenne Industries manufactures 8,000 units of part 231 for use in its production cycle. The per unit costs of part 231 are as follows:
Direct materials
Direct labor
Variable manufacturing overhead
Fixed manufacturing overhead
Total
Pharoah, Inc., has offered to sell 8,000 units of part 231 to Cheyenne for $32 per unit. If Cheyenne accepts Pharoah's offer, its freed-up facilities could be
used to earn $13,700 in contribution margin by manufacturing part 240. In addition, Cheyenne would eliminate 40% of the fixed overhead applied to part
231.
Your answer is partially correct.
$3.00
9.00
7.00
10.00
$29.00
Calculate total relevant cost to make and net cost to buy.
Total relevant cost to make $
Net relevant cost to buy
$
120000
242300
U
SUPR
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Session Company uses 5,000 units of Part Y each year as a component in the assembly of one of its products. The company is presently producing Part Y internally at a total cost of $72,000 as follows: Direct materials $18,000 Direct labor $20,000 Variable MOH $10,000 Fixed MOH $24,000 Total costs $72,000 An outside supplier has offered to provide Part Y at a price of $12 per unit. If Session Company stops producing the part internally, one-third of the fixed manufacturing overhead would be eliminated. Accepting the outside supplier's offer leads to an annual advantage/disadvantage of: Advantage of $4,000 Disadvantage of $4,000 Disadvantage of $12,000 Advantage of $12,000arrow_forwardCairney, Incorporated manufactures a specialized part used in internal combustion engines. The annual demand for the part is 261,000 units. The facility has a practical capacity of 276,000 units annually. The company leased the current facility because facilities capable of manufacturing the unit require machines that can produce 69,000 units each. The annual cost of the facility is $1,092,960. The variable cost of a part is $4. Required: a. What cost per unit should the cost system report to facilitate management decision making? Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. b. What is the cost of excess capacity? a. Cost per unit b. Cost of excess capacity $ $ 8.19 122,850arrow_forwardThe James Company manufactures widgets that sell for $120 each. The company's unit cost for each widget is as follows: A company in another state has offered to purchase 1,000 widgets from James Company at a cost of $90 each. If James were to accept this special order, no additional Fixed Manufacturing Overhead costs would be incurred. Should James accept this special order? Show relevant calculations.arrow_forward
- Voltaic Electronics uses a standard part in the manufacture of different types of radios. The total cost of producing 36,000 parts is $ 100,000, which includes fixed costs of $ 40,000 and variable costs of $ 60,000. The company can buy the part from an outside supplier for $2 per unit and avoid 20% of the fixed costs. Assume that the company can use the freed manufacturing space to make another product that can earn a profit of $ 15,000. If Voltaic outsources, what will be the effect on operating income?A. decrease of $11,000B. increase of $ 11,000C. increase of $ 15,000D . decrease of $ 8,000arrow_forwardMelbourne Corporation has traditionally made a subcomponent of its major product. Annual production of 30,000 subcomponents results in the following costs: Direct materials $ 250,000 Direct labor $ 200,000 Variable manufacturing overhead $ 190,000 Fixed manufacturing overhead $ 120,000 Melbourne has received an offer from an outside supplier who is willing to provide the 30,000 units of the subcomponent each year at a price of $28 per unit. There would be no effect of this decision on the total fixed manufacturing overhead of the company. Melbourne knows that the facilities now being used to manufacture the subcomponent could be rented to another company for revenue of $80,000 per year if the subcomponent were purchased from the outside supplier. The financial advantage (disadvantage) of making the subcomponent would be: Multiple Choice $0 $280,000 $120,000 $200,000arrow_forwardDelta produces a part that is used in the manufacture of one of its products. The costs associated with the production of 10,000 units of this part are as follows: Direct materials $ 90,000 Direct labor 130,000 Variable factory overhead Fixed factory overhead 140,000 Total costs $420,000 60,000 Of the fixed factory overhead costs, $60,000 is avoidable. 20) Conners has offered to sell 10,000 units of the same part to Delta for $36 per unit. Assuming there is no other use for the facilities, what is the effect on operating income if Delta buys from Conners? 21) Assuming no other use of their facilities, at what buying price per unit for Delta would Delta's operating income be the same whether they made the part or bought it from Conners?arrow_forward
- Edidas Company needs 20,000 units of Part GX to use in producing one of its products. If Edidas buys the Part GX from McMillan Company for $79 instead of making it, Edidas will not use the released facilities in another manufacturing activity. Twenty percent of the fixed overhead will continue irrespective of CEO Donald Mickey's decision. The cost per unit data are as follows: Cost to make the part Direct Materials Direct Labor (S) 30 15 Variable Overhead 20 Fixed Overhead 20 85 Required : 1. Explain which alternative is more attractive to Edidas, make or buy Part GX. 2. Assume there is new information that Edidas is negotiating to purchase cheaper raw materials from supplier (Twenty percent lower price). Is this information relevant or irrelevant? On the basis of financial considerations alone, should Edidas make or buy Part GX? Show your calculations 3. Based on requirement 2, what are relevant qualitative factors that Edidas should consider to decide whether to make or buy Part GX?…arrow_forwardEvery year Blue Industries manufactures 7,300 units of part 231 for use in its production cycle. The per unit costs of part 231 are as follows: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Total (a) $3.00 Total relevant cost to make $ 11.00 Net relevant cost to buy $ 8.00 Cullumber, Inc., has offered to sell 7,300 units f part 231 to Blue for $33 per unit. If Blue accepts Cullumber's offer, its freed-up facilities could be used to earn $10,700 in contribution margin by manufacturing part 240. In addition, Blue would eliminate 50% of the fixed overhead applied to part 231. 10.00 $32.00 Calculate total relevant cost to make and net cost to buy.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education