
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
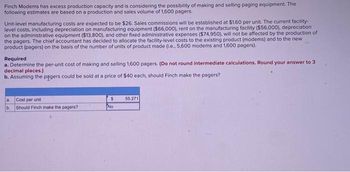
Transcribed Image Text:Finch Modems has excess production capacity and is considering the possibility of making and selling paging equipment. The
following estimates are based on a production and sales volume of 1,600 pagers.
Unit-level manufacturing costs are expected to be $26. Sales commissions will be established at $1.60 per unit. The current facility-
level costs, including depreciation on manufacturing equipment ($66,000), rent on the manufacturing facility ($56,000), depreciation
on the administrative equipment ($13,800), and other fixed administrative expenses ($74,950), will not be affected by the production of
the pagers. The chief accountant has decided to allocate the facility-level costs to the existing product (modems) and to the new
product (pagers) on the basis of the number of units of product made (i.e., 5,600 modems and 1,600 pagers).
Required
a. Determine the per-unit cost of making and selling 1,600 pagers. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 3
decimal places.)
b. Assuming the pagers could be sold at a price of $40 each, should Finch make the pagers?
Cost per unit
b. Should Finch make the pagers?
$
No
55.271
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The Knot manufactures men’s neckwear at its Spartanburg plant. The Knot is considering implementing a JIT production system. The following are the estimated costs and benefits of JIT production: a. Annual additional tooling costs $250,000 annually. b. Average inventory would decline by 80% from the current level of $1,000,000. c. Insurance, space, materials-handling, and setup costs, which currently total $400,000 annually, would decline by 20%. d. The emphasis on quality inherent in JIT production would reduce rework costs by 25%. The Knot currently incurs $160,000 in annual rework costs. e. Improved product quality under JIT production would enable The Knot to raise the price of its product by $2 per unit. The Knot sells 100,000 units each year. The Knot’s required rate of return on inventory investment is 15% per year. Q. Suppose The Knot implements JIT production at its Spartanburg plant. Give examples of performance measures The Knot could use to evaluate and control JIT…arrow_forwardMarkland Manufacturing manufactures desk lamps intends to increase capacity by obtaining new equipment. Two vendors have presented proposals. The purchase cost for proposal A is $30,000, and for proposal B, $80,000. Each proposal will produce lamps of the same quality. Proposal A is expected to produce lamps at $15.00/lamp, while proposal B is significantly more efficient and will produce them at $10.00/lamp. The revenue generated by the sale of each lamp is $20.00/unit. A. What is the point of indifference?B. The manufacturer expects to sell 12,000 lamps and has informed the vendors that it has chosen proposal B. The vendor of proposal A has offered to re-negotiate the purchase price of its proposal in order to win the contract. What purchase price will cause the manufacturerto reconsider its decision?arrow_forwardBirkenstock is considering adding a new Big Buckle sandal to its current product offerings. Birkenstock expects to price the shoes at $125 per pair. The variable costs to produce one pair are estimated to be: $20 per pair direct materials; $25 per pair direct labor; $5 per pair shipping costs and $5 per pair miscellaneous overhead. The fixed costs for this line of shoes are: $50,000 advertising/promotion; $125,000 manufacturing plant manager salary; $350,000 depreciation expense on manufacturing equipment; and $50,000 other miscellaneous fixed costs. • Birkenstock's best guess is that they will sell 12,000 pairs of Big Buckle sandals in 2021. What is Birkenstock's expected 2021 profit on this product? Type your answer in the first blank below.arrow_forward
- Trey's Trucks uses a standard part in the manufacture of several of its trucks. The cost of producing 60,000 parts is $160,000, which includes fixed costs of $90,000 and variable costs of $70,000. The company can buy the part from an outside supplier for $3.30 per unit and avoid 30% of the fixed costs. If the company makes the part, how much will its operating income be? O A. $135,000 greater than if the company bought the part O B. $101,000 greater than if the company bought the part O C. $101,000 less than if the company bought the part O D. $135,000 less than if the company bought the partarrow_forwardJordan Corporation, which makes and sells 80,600 radios annually, currently purchases the radio speakers it uses for $25 each. Each radio uses one speaker. The company has idle capacity and is considering the possibility of making the speakers that it needs. Jordan estimates that the cost of materials and labor needed to make speakers would be a total of $23 for each speaker. In addition, supervisory salaries, rent, and other manufacturing costs would be $181,000. Allocated facility-level costs would be $97,800. Required a. Determine the change in net income Jordan would experience if it decides to make the speakers. Net income will be lower byarrow_forwardJordan Inc. manufactures Product B, incurring variable product costs of $15.00 per unit and fixed product costs of $70,000. Total Selling and Administrative Expenses for the year are expected to be $15,700. Jordan desires a profit equal to a 10% rate of return on assets, $785,000 of assets are devoted to producing Product B, and 100,000 units are expected to be produced and sold. (a) Compute the markup percentage, using the product cost concept. (b) Compute the normal selling price of Product B. (a) (b)arrow_forward
- Harvey Automobiles uses a standard part in the manufacture of several of its trucks. The cost of producing 40,000 parts is $130,000, which includes fixed costs of $90,000 and variable costs of $40,000. The company can buy the part from an outside supplier for $3.30 per unit, and avoid 30% of the fixed costs. Assume that factory space freed up by purchasing the part from an outside source can be used to manufacture another product that can be sold for $179,000 profit. If Harvey Automobiles makes the part, what will its operating income be? $179,000 greater than if the company bought the part $49,000 greater than if the company bought the part $49,000 less than if the company bought the part $79,000 greater than if the company bought the partarrow_forwardJordan Electronics currently produces the shipping containers it uses to deliver the electronics products it sells. The monthly cost of producing 9,100 containers follows. Unit-level materials Unit-level labor Unit-level overhead Product-level costs Allocated facility-level costs $ 5,700 6,800 3,900 8,100 27,200 One-third of these costs can be avoided by purchasing the containers. Russo Container Company has offered to sell comparable containers to Jordan for $2.90 each. Required a. Calculate the total relevant cost. Should Jordan continue to make the containers? b. Jordan could lease the space it currently uses in the manufacturing process. If leasing would produce $12.300 per rhonth, calculate the total avoidable costs. Should Jordan continue to make the containers? a. Total relevant cost Should Jordan continue to make the containers? b. Total avoidable cost Should Jordan continue to make the containers?arrow_forwardDiamond Computer Company has been purchasing carrying cases for its portable computers at a purchase price of $84 per unit. The company, which is currently operating below full capacity, charges factory overhead to production at the rate of 50% of direct labor cost. The fully absorbed unit costs to produce comparable carrying cases are expected to be as follows: Direct materials $56 Direct labor 20 Factory overhead (50% of direct labor) 10 Total cost per unit $86 If Diamond Computer Company manufactures the carrying cases, fixed factory overhead costs will not increase and variable factory overhead costs associated with the cases are expected to be 10% of the direct labor costs. Required: A. Prepare a differential analysis, dated February 24 to determine whether the company should make (Alternative 1) or buy (Alternative 2) the carrying case. Refer to the lists of Labels and Amount Descriptions for the exact wording of the answer choices for text…arrow_forward
- Cairney, Incorporated manufactures a specialized part used in internal combustion engines. The annual demand for the part is 261,000 units. The facility has a practical capacity of 276,000 units annually. The company leased the current facility because facilities capable of manufacturing the unit require machines that can produce 69,000 units each. The annual cost of the facility is $1,092,960. The variable cost of a part is $4. Required: a. What cost per unit should the cost system report to facilitate management decision making? Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. b. What is the cost of excess capacity? a. Cost per unit b. Cost of excess capacity $ $ 8.19 122,850arrow_forwardSnipe Company has been purchasing a component, Part Q, for $19.20 per unit. Snipe is currently operating at 70% of capacity, and no significant increase in production is anticipated in the near future. The cost of manufacturing a unit of Part Q is estimated as follows: Direct materials $11.50 Direct labor 4.50 Variable factory overhead 1.12 Fixed factory overhead 3.15 Total $20.27 Prepare a differential analysis report dated March 12 of the current year. Round your answers to two decimal places. If an amount is zero, enter "0". Differential Analysis Make (Alternative 1) or Buy (Alternative 2) Part Q March 12 Make Buy Differential Part Q Part Q Effects (Alternative 1) (Alternative 2) (Alternative 2) Unit costs: Purchase price v 19.20 X 19.20 Direct materials v 11.50 X Direct labor v Variable factory overhead v Fixed factory overhead y Total unit costsarrow_forwardNeptune Company produces toys and other items for use in beach and resort areas. A small, inflatable toy has come onto the market that the company is anxious to produce and sell. The new toy will sell for $2.70 per unit. Enough capacity exists in the company's plant to produce 30,400 units of the toy each month. Variable expenses to manufacture and sell one unit would be $1.72, and fixed expenses associated with the toy would total $44,188 per month. The company's Marketing Department predicts that demand for the new toy will exceed the 30,400 units that the company is able to produce. Additional manufacturing space can be rented from another company at a fixed expense of $2,209 per month. Variable expenses in the rented facility would total $1.89 per unit, due to somewhat less efficient operations than in the main plant. Required: 1. What is the monthly break-even point for the new toy in unit sales and dollar sales. 2. How many units must be sold each month to attain a target profit…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education