
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
What membrane transport family is this protein part of? What are the roles of the different domains of this protein?
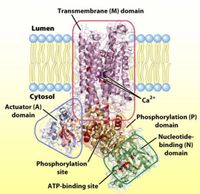
Transcribed Image Text:Transmembrane (M) domain
Lumen
Cytosol
Ca2+
Actuator (A)
domain
Phosphorylation (P)
domain
Nucleotide-
binding (N)
domain
Phosphorylation'
site
ATP-binding site'
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
The endoplasmic reticulum ( ER) is an important organelle which serves as an intracellular calcium ( Ca2 +) store that can be released into the cytoplasm quickly to cause a variety of cellular responses. To reach the cell surface, transmembrane proteins must pass through the secretory pathway, where they can communicate with other cells and respond to signalling signals.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Is the movement of sodium through SGlut-1 during co-transport simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport, or secondary active transport? And is the movement of glucose through SGlut-1 during co-transport simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, primary active transport, or secondary active transport?arrow_forwardWhy do most molecules require the assistance of proteins to cross the cellular membrane? What factors limit diffusion of molecules across the cellular membrane?arrow_forwardConsider the amino acids on the image below. Which of the following amino acids would be most likely to be found in the part of an integral membrane protein that is located within the membrane? (Select all answers that apply.) Asparagine (Asn) Lysine (Lys) Phenylalanine (Phe) Valine (Val) Glutamic acid (Glu) Methionine (Met)arrow_forward
- 1) Describe the role of the signal sequence and the signal recognition particle (SRP) in targeting and processing proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. 2) What is the function of the trans-Golgi network?arrow_forwardIntegral membrane proteins are anchored in lipid bilayers. Which of the following groups of amino acid residues would likely be found in the portion that crosses the lipid bilayer? Nonpolar Polar Acidic Chargedarrow_forwardWhat could happen to the proteins of cells treated with high amounts of free radicals that would effect the diffusion of those treated cells?arrow_forward
- How common are type I, type II, and type III membrane proteins?arrow_forwardWhat features in the chemical composition of phospholipids make them ideal components of the cytoplasmic membrane?arrow_forwardCell membranes are fluid, and thus proteins can diffuse laterally within the lipid bilayer. However, sometimes the cell needs to localize proteins to a particular membrane domain. Name three mechanisms that a cell can use to restrict a protein to a particular place in the cell membrane.arrow_forward
- What is an advantage of receptor mediated endocytosis as compared to pinocytosis? Then what is an advantage of pinocytosis compared to receptor mediated endocytosis?arrow_forwardwhere is Peripheral membrane protein made and how does it transfer to the membrane?arrow_forwardConsider two different proteins that are leaving from the Golgi in order to arrive in their common destination, a lysosome. In order for these two different proteins to be sent to the same place, what should they have in common? A) They must have the same primary structure B) They must have been imported into the cell by endocytosis. C) They must have the same tertiary structure D) They probably have the same glycosylation pattern. ..arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON