Zoom Add Page Part II: Fill in the blank. Choose the best term to complete the sentence from the word bank provided. Some terms may be used more than once. I point each. 2. down into CO2 and H₂O. Insert 1. is the process which uses light energy from the sun to power a chemical process that builds high energy organic molecules as its products. is the process in which oxygen and organic molecules (glucose) are consumed and broken 3. The three stages of cellular respiration are Table Chart Text Shape Media Comment 9. 4. In glycolysis, a 6-carbon glucose molecule is broken down into to two 3-carbon 5. The "falling" of electrons down the they fall. Some of this energy is used by the cells to make ATP. 6. In anaerobic fermentation, glucose can be broken down without the presence of this important molecule: 8. Fill in the blanks for the overall equation for cellular respiration: +6 6 +6 7. Both and are the two main electron shuttles (electron carriers) working in cellular chain. respiration that carry electrons from glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the citric acid cycle to the electron transport 10. This enzyme is used in oxidative phosphorylation to create ATP: Word Bank: Glucose (C6H12O6) Pyruvate Oxidative Phosphorylation Cilia Flagella Photosynthesis Oxygen (0₂) Water (H₂O) ATP Synthase releases energy as these electrons lose PE when I +32-38 are the short, hair-like structures used to move cells or other substances along the surfaces of the cell. are the long-hair like structures that move the entire cell via a whipping motion. and Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) Electron Transport Chain NADH Cellular Respiration FADH₂ Glycolysis Citric Acid Cycle ATP molecules. Spontaneous Generation MacBook Pro Co
Zoom Add Page Part II: Fill in the blank. Choose the best term to complete the sentence from the word bank provided. Some terms may be used more than once. I point each. 2. down into CO2 and H₂O. Insert 1. is the process which uses light energy from the sun to power a chemical process that builds high energy organic molecules as its products. is the process in which oxygen and organic molecules (glucose) are consumed and broken 3. The three stages of cellular respiration are Table Chart Text Shape Media Comment 9. 4. In glycolysis, a 6-carbon glucose molecule is broken down into to two 3-carbon 5. The "falling" of electrons down the they fall. Some of this energy is used by the cells to make ATP. 6. In anaerobic fermentation, glucose can be broken down without the presence of this important molecule: 8. Fill in the blanks for the overall equation for cellular respiration: +6 6 +6 7. Both and are the two main electron shuttles (electron carriers) working in cellular chain. respiration that carry electrons from glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the citric acid cycle to the electron transport 10. This enzyme is used in oxidative phosphorylation to create ATP: Word Bank: Glucose (C6H12O6) Pyruvate Oxidative Phosphorylation Cilia Flagella Photosynthesis Oxygen (0₂) Water (H₂O) ATP Synthase releases energy as these electrons lose PE when I +32-38 are the short, hair-like structures used to move cells or other substances along the surfaces of the cell. are the long-hair like structures that move the entire cell via a whipping motion. and Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) Electron Transport Chain NADH Cellular Respiration FADH₂ Glycolysis Citric Acid Cycle ATP molecules. Spontaneous Generation MacBook Pro Co
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Chapter6: Energy, Enzymes, And Biological Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1TYK: The capacity to do work best defines: a metabolic pathway. entropy. kinetic or potential energy. a...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Zoom
Add Page
Part II: Fill in the blank. Choose the best term to complete the sentence from the word bank provided. Some terms may
be used more than once. I point each.
2.
down into CO2 and H₂O.
Insert
1.
is the process which uses light energy from the sun to power a chemical process that builds
high energy organic molecules as its products.
is the process in which oxygen and organic molecules (glucose) are consumed and broken
3. The three stages of cellular respiration are
Table Chart Text Shape Media Comment
9.
4. In glycolysis, a 6-carbon glucose molecule is broken down into to two 3-carbon
5. The "falling" of electrons down the
they fall. Some of this energy is used by the cells to make ATP.
6. In anaerobic fermentation, glucose can be broken down without the presence of this important molecule:
8. Fill in the blanks for the overall equation for cellular respiration:
+6
6
+6
7. Both
and
are the two main electron shuttles (electron carriers) working in cellular
chain.
respiration that carry electrons from glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the citric acid cycle to the electron transport
10. This enzyme is used in oxidative phosphorylation to create ATP:
Word Bank:
Glucose (C6H12O6)
Pyruvate
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Cilia
Flagella
Photosynthesis
Oxygen (0₂)
Water (H₂O)
ATP Synthase
releases energy as these electrons lose PE when
I
+32-38
are the short, hair-like structures used to move cells or other substances along the surfaces of the cell.
are the long-hair like structures that move the entire cell via a whipping motion.
and
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
Electron Transport Chain
NADH
Cellular Respiration
FADH₂
Glycolysis
Citric Acid Cycle
ATP
molecules.
Spontaneous Generation
MacBook Pro
Co
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Match the word to the sentence
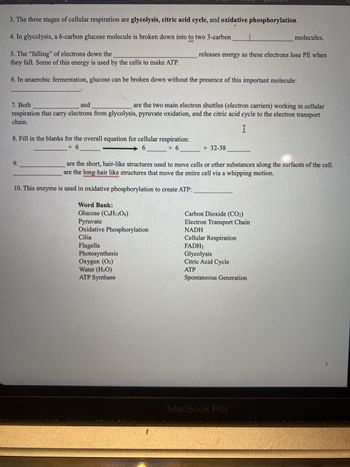
Transcribed Image Text:3. The three stages of cellular respiration are glycolysis, citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
4. In glycolysis, a 6-carbon glucose molecule is broken down into to two 3-carbon
5. The "falling" of electrons down the
they fall. Some of this energy is used by the cells to make ATP.
6. In anaerobic fermentation, glucose can be broken down without the presence of this important molecule:
8. Fill in the blanks for the overall equation for cellular respiration:
+ 6
6
+6
7. Both
and
are the two main electron shuttles (electron carriers) working in cellular
respiration that carry electrons from glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the citric acid cycle to the electron transport
chain.
I
9.
10. This enzyme is used in oxidative phosphorylation to create ATP:
releases energy as these electrons lose PE when
Word Bank:
Glucose (C6H12O6)
Pyruvate
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Cilia
Flagella
Photosynthesis
Oxygen (0₂)
Water (H₂O)
ATP Synthase
+ 32-38
are the short, hair-like structures used to move cells or other substances along the surfaces of the cell.
are the long-hair like structures that move the entire cell via a whipping motion.
molecules.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Electron Transport Chain
NADH
Cellular Respiration
FADH2
Glycolysis
Citric Acid Cycle
ATP
Spontaneous Generation
MacBook Pro
3
Solution
Follow-up Question
Match the word to the sentence
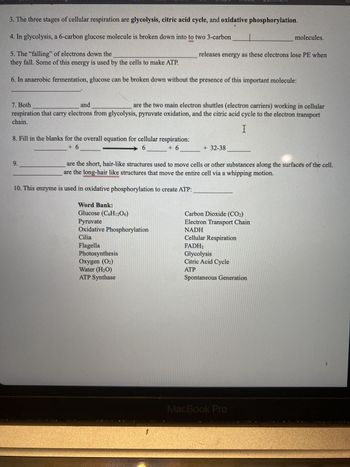
Transcribed Image Text:3. The three stages of cellular respiration are glycolysis, citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
4. In glycolysis, a 6-carbon glucose molecule is broken down into to two 3-carbon
5. The "falling" of electrons down the
they fall. Some of this energy is used by the cells to make ATP.
6. In anaerobic fermentation, glucose can be broken down without the presence of this important molecule:
8. Fill in the blanks for the overall equation for cellular respiration:
+ 6
6
+6
7. Both
and
are the two main electron shuttles (electron carriers) working in cellular
respiration that carry electrons from glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the citric acid cycle to the electron transport
chain.
I
9.
10. This enzyme is used in oxidative phosphorylation to create ATP:
releases energy as these electrons lose PE when
Word Bank:
Glucose (C6H12O6)
Pyruvate
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Cilia
Flagella
Photosynthesis
Oxygen (0₂)
Water (H₂O)
ATP Synthase
+ 32-38
are the short, hair-like structures used to move cells or other substances along the surfaces of the cell.
are the long-hair like structures that move the entire cell via a whipping motion.
molecules.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Electron Transport Chain
NADH
Cellular Respiration
FADH2
Glycolysis
Citric Acid Cycle
ATP
Spontaneous Generation
MacBook Pro
3
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning