
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781285869759
Author: Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
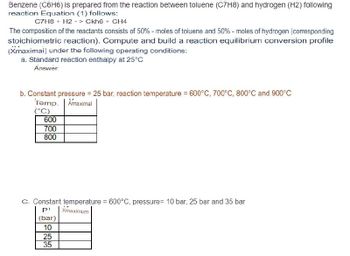
Transcribed Image Text:Benzene (C6H6) is prepared from the reaction between toluene (C7H8) and hydrogen (H2) following
reaction Equation (1) follows:
C7H8 + H2 -> Ckh6+ CH4
The composition of the reactants consists of 50% - moles of toluene and 50% - moles of hydrogen (corresponding
stoichiometric reaction). Compute and build a reaction equilibrium conversion profile
(Xmaximai) under the following operating conditions:
a. Standard reaction enthalpy at 25°C
Answer:
b. Constant pressure = 25 bar, reaction temperature = 600°C, 700°C, 800°C and 900°C
Temp. Amaximal
(°C)
600
700
800
C. Constant temperature = 600°C, pressure= 10 bar, 25 bar and 35 bar
P
Xmaximum
(bar)
10
25
35
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 4.) For the following equilibrium reaction state what happens when the following reagents are added NaOH(aq) + HСІ(ад) + НОН(аq) + NaCI(aq)+д a.) Mg(ОН)2 b.) КCІ с.) KBr d.) Heat (A) e.) CH;CH,COH (an acid) f.) decrease in temp.arrow_forwardPlease answer correct significant figarrow_forwardWhich reaction will have a pressure equilibrium constant (Kp) that is greater than the concentration equilibrium constant (K)? O CH3 COOH(aq) + H20(1)=H30*(aq)+ CH3 CO0 (aq) O 2H,0;(g)=2H,0() + O2(g) O 2503(9) = 250,(g) +O2(g) O l2(g) + H2(g)=2HI(g)arrow_forward
- Predict the equilibrium concentration of H₂O in the reaction described below (for which Kc = 1.79 at the reaction temperature) by constructing an ICE table, writing the equilibrium constant expression, and solving for the equilibrium concentration. Complete Parts 1-3 before submitting your answer. 2 H₂S(g) + SO₂(g) = 3 S(s) + 2 H₂O(g) Initial (M) Change (M) Equilibrium (M) -3.x 0.025 + 2x The reaction mixture initially contains 0.050 M H₂S and 0.050 M SO₂. Fill in the ICE table with the appropriate value for each involved species to determine the concentrations of all reactants and products. 0 1 2 H₂S(g) + 0.050 + x 0.025 + 3x 0.050 0.050 + 2x 0.025 - Xx +X 2 SO₂(g) 0.050 + 3x 0.025 - 2x +2x 0.050 - x 0.025-3x 3 3 S(s) +3x 0.050 - 2x --X + 0.050-3x NEXT > 2 H₂O(g) RESET -2x 0.025 + xarrow_forward7:04 Question 11 of 13 Construct the expression for Kc for the following reaction. CH3COOH(aq) + H₂O(l): H3O+ (aq) Kc = 1 Submit CH3COO-(aq) + Drag the tiles into the numerator or denominator to form the expression. Each reaction participant must be represented by one tile. Do not combine terms. Tap here or pull up for additional resources RESET [H3O+] 2[H3O+] [H3O+]² 2[H3O+]² [H₂O] [H₂O]² 2[H₂O] 2[H₂O]² [CH3COO-] 2[CH3COO-] [CH3COO-]² 2[CH3COO-]² [CH₂COOH] 2[CH3COOH] [CH₂COOH]² 2[CH3COOH]arrow_forwardThe equilibrium reaction of propyl alcohol (C3H,OH) and acetic acid (CH3COOH) resulting from the hydrolysis of propyl acetate (CH3COOC3H;) is given below. CH3COOC3H, + H20 CH3COOH + C3H5OH Which of the following is the equilibrium (K) constant? O a. K = [CH3COOHJ [C3H7OH] / [CH3COOC3H;] [H2O] O b. K = [CH§COOH] [C3H;OH] / [CH3COOC3H;] O c. K= [CH3CO0C3H7] [H20] / [CH3COOH] [C3H7OH] O d. K = [CH3COOC3H;] / [CH3COOH] [C3H;OH]arrow_forward
- 11-please see attachedarrow_forward4 (a) Calculate the value of Kc for the reaction: PC15 ( PC13 ( + Cl2 (g) AH = Positive Given that when 8.4 mol of PC15 (g) is mixed with 1.8 mol of PC13 (g) and allowed to come to equilibrium in a 10 dm³ container the amount of PC15 (g) at equilibrium is 7.2 mol. Kc = (b) Explain the effect of the following changes below on the value of Kc: (i) Increasing temperature (ii) Lowering the concentration of chlorine (Cl₂) (iii) Addition of a catalystarrow_forward5:15 7 of paner cdn.fbsbx.com 32 of 34 JOIVO the Tonowing propies below. white your stat 1. Determine the Keq for the following equilibrium: 2CH4(9) C₂H₂(g) + 3H₂(g) (CH4 = 2.5 x 10-³ M; C₂H₂ = 0.01375; H₂ = 0.04125) Done 2. Determine the pH of the following: a. [H] = 1.0 x 10-² b. pOH = 4.5 C. [H+] = 8.5 x 10-6 3. Determine the pH of the buffer solution below: 0.25 M NH3 and 0.30 M NH4+ with pka = 4.76 SAN PEDRO RELOCATION CENTER NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL - SCIENCE DEPART ûarrow_forward
- Make sure answer is correct significant fogarrow_forwardCan you explain the concept? And the steps to take to find the answerarrow_forwardEthyl acetate is synthesized in a nonreacting solvent (not water) according to the following reaction: CH3 CO2H+ C2H; OH = CH3 C02C,H; + H2O К — 2.2 Acetic acid Ethanol Ethyl acetate For the following mixtures, will the concentration of H2 O increase, decrease, or remain the same as equilibrium is established? а. [CH3CO-С2H:] — 0.22 М, [Н,0] — 0.10 М, [CH3 CO2H] — 0.010 М, [С, Нs Он] — 0.010 м decrease increase O remain the same b. [CH3 CO2 C2H3] 3D 0.22 М, [Н2о) —D 0.0020 М, [СH; CO2H] — 0.0020 М, [С2H5 ОН — 0.10 м decrease X increase O remain the same c. [CH3 CO2C2H3] 3D 0.88 М, [Н20] - 0.12 М, [СH3СО2Н 3D 0.044 М, [С Hs ОН — 6.0м decrease O remain the same increase d. [CH; CO2C2H;] 3D 4.4 М, [Н20] %3D 4.4 М, [СН3СОН — 0.88 м, [С, H; ОН] — 10.0м increase O remain the same decrease e. What must the concentration of water be for a mixture with [CH3CO2 C2H5] = 1.0 M, [CH3CO2H] = 0.10 M, and [C2H5 OH] = 6.0 M to be at equilibrium? Concentration = 0.09 X Marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning