
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
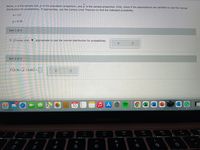
Transcribed Image Text:Below, n is the sample size, p is the population proportion, and p is the sample proportion. First, check if the assumptions are satisfied to use the normal
distribution for probabilities. If appropriate, use the Central Limit Theorem to find the indicated probability.
n= 111
p= 0.58
Part 1 of 2
It (Choose one) ▼ appropriate to use the normal distribution for probabilities.
Part 2 of 2
P(0.56<p<0.60) =
ост
10
MacBook Air
80
888
F7
FB
F9
F4
F3
&
%23
%24
6
7
8.
3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Select all that apply. We show that our sample statistics have (at minimum) a somewhat normal distribution because this allows us to use t and z critical values. this allows us to use t and z tables for probabilities. this tells us that our sampling is appropriate. normal distributions are cool and that's all we talk about in this class.arrow_forwardDetermine whether you can use the normal distribution to approximate the binomial distribution. If you can, use the normal distribution to approximate the indicated probabilities and sketch their graphs. If you cannot, explain why and use the binomial distribution to find the indicated probabilities. A survey of adults in a region found that 55% have encountered fraudulent charges on their credit cards. You randomly select 100 adults in the region. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. Determine whether a normal distribution can be used to approximate the binomial distribution. Choose the correct answer below. O A. Yes, because both np 25 and nq 2 5. O B. No, because np < 5. O c. No, because nq < 5. (a) Find the probability that the number who have encountered fraudulent charges on their credit cards is (a) exactly 57, (b) at least 57, and (c) fewer than 57. (Round to four decimal places as needed.) Sketch the graph of the normal distribution with the indicated probability shaded. O A.…arrow_forwardYou are playing a card came, and the probability that you will win a game is p If you play the game 601 times, what is the most likely number of wins? (Round answer to one decimal place.) μl = Let X represent the number of games (out of 601) that you win. Find the standard deviation for the probability distribution of X. (Round answer to two decimal places.) 0= The range rule of thumb specifies that the minimum usual value for a random variable is u-20 and the maximum usual value is μ+20. You already found μ and o for the random variable X. 0.88. Use the range rule of thumb to find the usual range of X values. Enter answer as an interval using square- brackets and only whole numbers. usual values = Question Help: Written Example Message instructor Submit Question Jump to Answerarrow_forward
- You are playing a card came, and the probability that you will win a game is p = 0.73. If you play the game 1412 times, what is the most likely number of wins? (Round answer to one decimal place.) Let X represent the number of games (out of 1412) that you win. Find the standard deviation for the probability distribution of X. (Round answer to two decimal places.) O = The range rule of thumb specifies that the minimum usual value for a random variable is u-2o and the maximum usual value is p+2o. You already found u and o for the random variable X. Use the range rule of thumb to find the usual range of X values. Enter answer as an interval using square- brackets and only whole numbers. usual values =arrow_forwardAccording to the central limit theorem (CLT), no matter which distribution the data is collected from, as long as some conditions are met, we can always expect the sample average to behave like a normal random variable, i.e., the sampling distribution can be approximated by a normal distribution. Which is NOT a CLT condition for sample mean? Group of answer choices The original distribution of the data is Normal. A random sample with sample size is larger than 30 with no extreme outlier A random sample with sample size is less than 30 with no outliers. The sample size has to be larger than 10.arrow_forwardBelow, n is the sample size, p is the population proportion, and p is the sample proportion. First, check if the assumptions are satisfied to use the normal distribution for probabilities. If appropriate, use the Central Limit Theorem to find the indicated probability. n = 100 p = 0.22 Part 1 of 2 It is Part 2 of 2 appropriate to use the normal distribution for probabilities. P(0.20arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardSolve for Darrow_forwardBelow, n is the sample size, p is the population proportion, and p is the sample proportion. First, check if the assumptions are satisfied to use the normal distribution for probabilities. If appropriate, use the Central Limit Theorem to find the indicated probability. n=147 p=0.18 Part 1 of 2 It is appropriate to use the normal distribution for probabilities. Part 2 of 2 P(0.15arrow_forwardFind the probabilities for each, using the standard normal distribution. Shade the area of the region under the normal curve.arrow_forwardThe probability distribution of a random variable X is given below.arrow_forwardDetermine whether you can use the normal distribution to approximate the binomial distribution. If you can, use the normal distribution to approximate the indicated probabilities and sketch their graphs. If you cannot, explain why and use the binomial distribution to find the indicated probabilities. A survey of adults in a region found that 52% have encountered fraudulent charges on their credit cards. You randomly select 100 adults in the region. Complete parts (a) through (d) below ) Find the probability that the number who have encountered fraudulent charges on their credit cards is (a) exactly 54, (b) at least 54, and (c) fewer than 54. enter your response here (Round to four decimal places as needed.) .arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman